Extraction of zinc from zinc blende is achieved by
- electrolytic reduction
- roasting followed by reduction with carbon
- roasting followed by reduction with anothermetal
- roasting followed by self reduction
The Correct Option is B
Approach Solution - 1
The correct answer is Option is B) roasting followed by reduction with carbon
Zinc blende contains ZnS which is first roasted partially and then subjected to reduction with carbon
\(ZnS+O_2 \rightarrow ZnO+SO_2 Roasting\)
\(ZnO+C \xrightarrow{\Delta} Zn+CO \uparrow Carbon reduction\)
Read more from the chapter: General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Approach Solution -2
The correct answer is Option is B) roasting followed by reduction with carbon
Real Life Applications
The real-life applications of extracting zinc from zinc blende are as follows:
- Zinc is widely used in die casting.
- The process of galvanization also uses zinc. The steel is coated with zinc which prevents them from rusting.
- Zinc is also used in batteries and abrasives.

Question can also be asked as
- How is zinc extracted from zinc blende?
- What are the different methods of extracting zinc from zinc blende?
- Write the steps involved during the extraction of zinc from zinc blende.
Approach Solution -3
The correct answer is Option is B) roasting followed by reduction with carbon
Raw metals are obtained with the help of extraction from their concentrated ore. Ore is the mixture in which the metal is present in its original state. The metals have to be refined with the help of reducing agents. The three important steps in this process are:
- Concentration of ore
- Isolation of metal from the ore
- Purifying the metal
Conversion of the concentrated ores
The concentrated ores need to be converted into their oxides for further processing. The concentrated ore is in its carbonated form. The process that can convert the ores into their oxides is as follows:
- Calcination
- Roasting
Reduction of oxides to metal
The metal oxides are reduced to their free metals using reducing agents. The process of reductio occurs at a low temperature. The processes of reduction are:
- Smelting
- Reduction by water gas
- Reduction by hydrogen
- Alumino Thermite Process
- Auto reduction
For extraction of Zn from ZnS
- The ore is crushed and then concentration is done using the froth-floatation method.
- Then the roasting of the ore is done in the presence of air. It is done at 1200K.
- Then ZnO is reduced to Zn metal with the help of powdered coke and after heating in a fire clay retorts.
- Electrolytic refining is used for the purification of Zn metal
Read more:
| Related concepts | ||
|---|---|---|
| Carbonate | Hydrate oxides | Bauxite ore |
| Roasting | Reduction | Iron |
Top Questions on General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- What is used for the Thermite Reaction?
- BCECE - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- In the extraction of iron using blast furnace to remove the impurity (X), chemical (Y) is added to the ore. X and Y are respectively
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Which of the following compounds is used to cover the surface of a metallic object to prevent corrosion?
- KEAM - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- The incorrect statement about the Hall-Heroult process is:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Select the correct statement:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- Let $ x_0 $ be the real number such that $ e^{x_0} + x_0 = 0 $. For a given real number $ \alpha $, define $$ g(x) = \frac{3xe^x + 3x - \alpha e^x - \alpha x}{3(e^x + 1)} $$ for all real numbers $ x $. Then which one of the following statements is TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
- A linear octasaccharide (molar mass = 1024 g mol$^{-1}$) on complete hydrolysis produces three monosaccharides: ribose, 2-deoxyribose and glucose. The amount of 2-deoxyribose formed is 58.26 % (w/w) of the total amount of the monosaccharides produced in the hydrolyzed products. The number of ribose unit(s) present in one molecule of octasaccharide is _____.
Use: Molar mass (in g mol$^{-1}$): ribose = 150, 2-deoxyribose = 134, glucose = 180; Atomic mass (in amu): H = 1, O = 16- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Biomolecules
Let $ P(x_1, y_1) $ and $ Q(x_2, y_2) $ be two distinct points on the ellipse $$ \frac{x^2}{9} + \frac{y^2}{4} = 1 $$ such that $ y_1 > 0 $, and $ y_2 > 0 $. Let $ C $ denote the circle $ x^2 + y^2 = 9 $, and $ M $ be the point $ (3, 0) $. Suppose the line $ x = x_1 $ intersects $ C $ at $ R $, and the line $ x = x_2 $ intersects $ C $ at $ S $, such that the $ y $-coordinates of $ R $ and $ S $ are positive. Let $ \angle ROM = \frac{\pi}{6} $ and $ \angle SOM = \frac{\pi}{3} $, where $ O $ denotes the origin $ (0, 0) $. Let $ |XY| $ denote the length of the line segment $ XY $. Then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Conic sections
- Adsorption of phenol from its aqueous solution on to fly ash obeys Freundlich isotherm. At a given temperature, from 10 mg g$^{-1}$ and 16 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous phenol solutions, the concentrations of adsorbed phenol are measured to be 4 mg g$^{-1}$ and 10 mg g$^{-1}$, respectively. At this temperature, the concentration (in mg g$^{-1}$) of adsorbed phenol from 20 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous solution of phenol will be ____. Use: $\log_{10} 2 = 0.3$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Adsorption
- At 300 K, an ideal dilute solution of a macromolecule exerts osmotic pressure that is expressed in terms of the height (h) of the solution (density = 1.00 g cm$^{-3}$) where h is equal to 2.00 cm. If the concentration of the dilute solution of the macromolecule is 2.00 g dm$^{-3}$, the molar mass of the macromolecule is calculated to be $X \times 10^{4}$ g mol$^{-1}$. The value of $X$ is ____. Use: Universal gas constant (R) = 8.3 J K$^{-1}$ mol$^{-1}$ and acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m s$^{-2}\}$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Colligative Properties
Concepts Used:
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
What are Ores and Minerals?
Minerals are the naturally occurring, homogeneous inorganic solid substances. They are having a definite chemical composition and crystalline structure, hardness and color. For example, copper pyrite, calamine, etc.
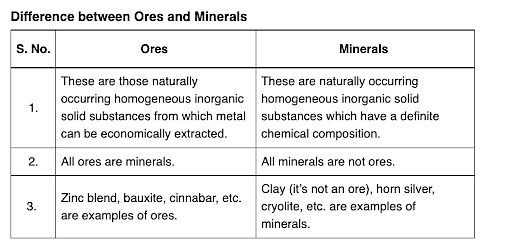
Impurities in an ore are called gauge. The removal of a gauge from the ore is called concentration ore.
Several steps are involved in the extraction of pure metal from ores. Major steps are as follows –
- Concentration of the ore
- Isolation of the metal from its concentrated ore
- Purification of the metal