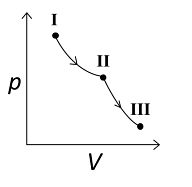
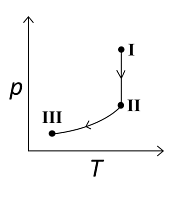
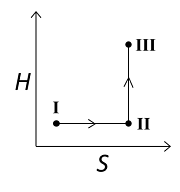
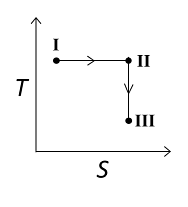
An ideal gas undergoes a reversible isothermal expansion from the state I to state II followed by a reversible adiabatic expansion from state II to state III. The correct plot(s) representing the changes from the state I to state III is(are)
(p: pressure, V: volume, T: temperature, H: enthalpy, S: entropy)
(p: pressure, V: volume, T: temperature, H: enthalpy, S: entropy)
The Correct Option is A, B, D
Solution and Explanation
For the reversible isothermal expansion from state I to II:
- Pressure decreases
- Volume increases
- Temperature remains constant
- Enthalpy (H) remains constant
- Entropy (S) increases
So, all options are correct for this expansion.
For the reversible adiabatic expansion from state II to III:
- Pressure decreases
- Volume increases
- Temperature decreases
- Enthalpy (H) decreases
- Entropy (S) remains constant
Option (C) does not follow the condition of decreasing enthalpy, so it is incorrect. Options (A), (B), and (D) all follow the conditions, so they are correct.
Therefore, correct graphical representations for the given conditions are (A), (B), and (D).
Top Questions on Enthalpy change
- The group 14 elements A and B have the first ionisation enthalpy values of 708 and 715 kJ mol$^{-1}$ respectively. The above values are lowest among their group members. The nature of their ions A$^{2+}$ and B$^{4+}$ respectively is:
- JEE Main - 2025
- Chemistry
- Enthalpy change
- The incorrect relationship in the following pairs in relation to ionisation enthalpies is:
- JEE Main - 2025
- Chemistry
- Enthalpy change
- Given below are two statements:
Statement (I): The radius of isoelectronic species increases in the order: \[ \text{Mg}^{2+} < \text{Na}^{+} < \text{F}^{-} < \text{O}^{2-} \] Statement (II): The magnitude of electron gain enthalpy of halogens decreases in the order: \[ \text{Cl} > \text{F} > \text{Br} > \text{I} \] In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:- JEE Main - 2025
- Chemistry
- Enthalpy change
- Consider the following cases of standard enthalpy of reaction (\( \Delta H_f^\circ \) in kJ mol\(^{-1}\)): \[ \text{C}_2\text{H}_6(g) + 7 \text{O}_2(g) \rightarrow 2 \text{CO}_2(g) + 3 \text{H}_2\text{O}(l) \quad \Delta H_1^\circ = -1550 \] \[ \text{C(graphite)} + \text{O}_2(g) \rightarrow \text{CO}_2(g) \quad \Delta H_2^\circ = -393.5 \] \[ \text{H}_2(g) + \frac{1}{2} \text{O}_2(g) \rightarrow \text{H}_2\text{O}(g) \quad \Delta H_3^\circ = -286 \] The magnitude of \( \Delta H_f^\circ \) of \( \text{C}_2\text{H}_6(g) \) is \(\_\_\_\_\_\) kJ mol\(^{-1}\) (Nearest integer).
- JEE Main - 2025
- Chemistry
- Enthalpy change
- The bond dissociation energies of gaseous H2, Cl2, and HCl are 104, 58, and 103 kcal, respectively. The enthalpy of formation of HCl gas would be:
- BCECE - 2025
- Chemistry
- Enthalpy change
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- Let $ x_0 $ be the real number such that $ e^{x_0} + x_0 = 0 $. For a given real number $ \alpha $, define $$ g(x) = \frac{3xe^x + 3x - \alpha e^x - \alpha x}{3(e^x + 1)} $$ for all real numbers $ x $. Then which one of the following statements is TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
- A linear octasaccharide (molar mass = 1024 g mol$^{-1}$) on complete hydrolysis produces three monosaccharides: ribose, 2-deoxyribose and glucose. The amount of 2-deoxyribose formed is 58.26 % (w/w) of the total amount of the monosaccharides produced in the hydrolyzed products. The number of ribose unit(s) present in one molecule of octasaccharide is _____.
Use: Molar mass (in g mol$^{-1}$): ribose = 150, 2-deoxyribose = 134, glucose = 180; Atomic mass (in amu): H = 1, O = 16- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Biomolecules
Let $ P(x_1, y_1) $ and $ Q(x_2, y_2) $ be two distinct points on the ellipse $$ \frac{x^2}{9} + \frac{y^2}{4} = 1 $$ such that $ y_1 > 0 $, and $ y_2 > 0 $. Let $ C $ denote the circle $ x^2 + y^2 = 9 $, and $ M $ be the point $ (3, 0) $. Suppose the line $ x = x_1 $ intersects $ C $ at $ R $, and the line $ x = x_2 $ intersects $ C $ at $ S $, such that the $ y $-coordinates of $ R $ and $ S $ are positive. Let $ \angle ROM = \frac{\pi}{6} $ and $ \angle SOM = \frac{\pi}{3} $, where $ O $ denotes the origin $ (0, 0) $. Let $ |XY| $ denote the length of the line segment $ XY $. Then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Conic sections
- Adsorption of phenol from its aqueous solution on to fly ash obeys Freundlich isotherm. At a given temperature, from 10 mg g$^{-1}$ and 16 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous phenol solutions, the concentrations of adsorbed phenol are measured to be 4 mg g$^{-1}$ and 10 mg g$^{-1}$, respectively. At this temperature, the concentration (in mg g$^{-1}$) of adsorbed phenol from 20 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous solution of phenol will be ____. Use: $\log_{10} 2 = 0.3$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Adsorption
- At 300 K, an ideal dilute solution of a macromolecule exerts osmotic pressure that is expressed in terms of the height (h) of the solution (density = 1.00 g cm$^{-3}$) where h is equal to 2.00 cm. If the concentration of the dilute solution of the macromolecule is 2.00 g dm$^{-3}$, the molar mass of the macromolecule is calculated to be $X \times 10^{4}$ g mol$^{-1}$. The value of $X$ is ____. Use: Universal gas constant (R) = 8.3 J K$^{-1}$ mol$^{-1}$ and acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m s$^{-2}\}$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Colligative Properties
Concepts Used:
Enthalpy change
Enthalpy Change refers to the difference between the heat content of the initial and final state of the reaction. Change in enthalpy can prove to be of great importance to find whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic.
Formula for change in enthalpy is:-
dH = dU + d(PV)
The above equation can be written in the terms of initial and final states of the system which is defined below:
UF – UI = qP –p(VF – VI)
Or qP = (UF + pVF) – (UI + pVI)
Enthalpy (H) can be written as H= U + PV. Putting the value in the above equation, we obtained:
qP = HF – HI = ∆H
Hence, change in enthalpy ∆H = qP, referred to as the heat consumed at a constant pressure by the system. At constant pressure, we can also write,
∆H = ∆U + p∆V
Standard Enthalpy of Reaction
To specify the standard enthalpy of any reaction, it is calculated when all the components participating in the reaction i.e., the reactants and the products are in their standard form. Therefore the standard enthalpy of reaction is the enthalpy change that occurs in a system when a matter is transformed by a chemical reaction under standard conditions.