A long straight wire carries a current, $I =2$ ampere A semi-circular conducting rod is placed beside it on two conducting parallel rails of negligible resistance Both the rails are parallel to the wire The wire, the rod and the rails lie in the same horizontal plane, as shown in the figure Two ends of the semi-circular rod are at distances $1 \,cm$ and $4 \,cm$ from the wire At time $t =0$, the rod starts moving on the rails with a speed $v =30\, m / s$ (see the figure)
A resistor $R =14 \,\Omega$ and a capacitor $C _{0}=50\, \mu F$ are connected in series between the rails At time $t =0, C _{0}$ is uncharged. Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct? \([\mu_0 = 4 \pi \times 10^{-7}\) SI units. Take \(ln_2=0.7]\)
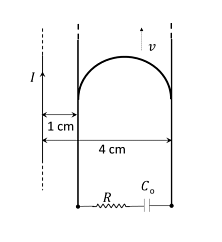
A resistor $R =14 \,\Omega$ and a capacitor $C _{0}=50\, \mu F$ are connected in series between the rails At time $t =0, C _{0}$ is uncharged. Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct? \([\mu_0 = 4 \pi \times 10^{-7}\) SI units. Take \(ln_2=0.7]\)

- Maximum current through $R$ is $1.2 \times 10^{-6}$ ampere
- Maximum current through $R$ is $3.8 \times 10^{-6}$ ampere
- Maximum charge on capacitor $C_{0}$ is $8.4 \times 10^{-12}$ coulomb
- Maximum charge on capacitor $C_{0}$ is $2.4 \times 10^{-12}$ coulomb
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
Given:
- Current in wire, \( I = 2 \, \text{A} \)
- Semi-circular rod moves with velocity \( v = 30 \, \text{m/s} \)
- Distances of rod ends from wire: \( r_1 = 1 \, \text{cm} = 0.01 \, \text{m}, \quad r_2 = 4 \, \text{cm} = 0.04 \, \text{m} \)
- Capacitor \( C_0 = 50 \, \mu\text{F} = 50 \times 10^{-6} \, \text{F} \), Resistor \( R = 14 \, \Omega \)
- \( \mu_0 = 4\pi \times 10^{-7} \, \text{H/m} \), \( \ln 2 = 0.7 \)
Step 1: Magnetic field at distance r from a long wire
\[ B(r) = \frac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi r} \]
Step 2: emf induced across the rod due to motion in magnetic field
Since the rod moves perpendicular to the field, the emf is: \[ \mathcal{E} = v \int_{r_1}^{r_2} B(r) \, dr = v \int_{r_1}^{r_2} \frac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi r} \, dr = v \cdot \frac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi} \cdot \ln\left( \frac{r_2}{r_1} \right) \] Substitute values: \[ \mathcal{E} = 30 \cdot \frac{4\pi \times 10^{-7} \cdot 2}{2\pi} \cdot \ln\left( \frac{0.04}{0.01} \right) = 30 \cdot 4 \times 10^{-7} \cdot \ln(4) \] \[ \ln 4 = \ln(2^2) = 2 \ln 2 = 2 \cdot 0.7 = 1.4 \] \[ \mathcal{E} = 30 \cdot 4 \times 10^{-7} \cdot 1.4 = 1.68 \times 10^{-5} \, \text{V} \]
Step 3: Maximum charge on capacitor
Maximum charge: \[ q_{\text{max}} = C_0 \cdot \mathcal{E} = 50 \times 10^{-6} \cdot 1.68 \times 10^{-5} = 8.4 \times 10^{-12} \, \text{C} \]
Correct Answer: Option (C): Maximum charge on capacitor is \( \boxed{8.4 \times 10^{-12}} \, \text{C} \)
Top Questions on Electromagnetic waves
- Three charges $+2q$, $+3q$ and $-4q$ are situated at $(0,-3a)$, $(2a,0)$ and $(-2a,0)$ respectively in the $x$-$y$ plane. The resultant dipole moment about origin is ___.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Electromagnetic waves
- In a perfectly inelastic collision, two spheres made of the same material with masses 15 kg and 25 kg, moving in opposite directions with speeds of 10 m/s and 30 m/s, respectively, strike each other and stick together. The rise in temperature (in °C), if all the heat produced during the collision is retained by these spheres, is (specific heat 31 cal/kg.°C and 1 cal = 4.2 J) :
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Electromagnetic waves
- The electric field of an electromagnetic wave travelling through a medium is given by \[ \vec{E}(x,t)=25\sin(2\times10^{15}t-10^{7}x)\,\hat{n}. \] Then the refractive index of the medium is ________. (All given measurements are in SI units)
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Electromagnetic waves
A laser beam has intensity of $4.0\times10^{14}\ \text{W/m}^2$. The amplitude of magnetic field associated with the beam is ______ T. (Take $\varepsilon_0=8.85\times10^{-12}\ \text{C}^2/\text{N m}^2$ and $c=3\times10^8\ \text{m/s}$)
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Electromagnetic waves
- The ratio of speeds of electromagnetic waves in vacuum and a medium, having dielectric constant k = 3 and permeability of $\mu = 2\mu_0$, is ($\mu_0$ = permeability of vacuum)
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Electromagnetic waves
Questions Asked in JEE Advanced exam
- Let $ x_0 $ be the real number such that $ e^{x_0} + x_0 = 0 $. For a given real number $ \alpha $, define $$ g(x) = \frac{3xe^x + 3x - \alpha e^x - \alpha x}{3(e^x + 1)} $$ for all real numbers $ x $. Then which one of the following statements is TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
- A linear octasaccharide (molar mass = 1024 g mol$^{-1}$) on complete hydrolysis produces three monosaccharides: ribose, 2-deoxyribose and glucose. The amount of 2-deoxyribose formed is 58.26 % (w/w) of the total amount of the monosaccharides produced in the hydrolyzed products. The number of ribose unit(s) present in one molecule of octasaccharide is _____.
Use: Molar mass (in g mol$^{-1}$): ribose = 150, 2-deoxyribose = 134, glucose = 180; Atomic mass (in amu): H = 1, O = 16- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Biomolecules
Let $ P(x_1, y_1) $ and $ Q(x_2, y_2) $ be two distinct points on the ellipse $$ \frac{x^2}{9} + \frac{y^2}{4} = 1 $$ such that $ y_1 > 0 $, and $ y_2 > 0 $. Let $ C $ denote the circle $ x^2 + y^2 = 9 $, and $ M $ be the point $ (3, 0) $. Suppose the line $ x = x_1 $ intersects $ C $ at $ R $, and the line $ x = x_2 $ intersects $ C $ at $ S $, such that the $ y $-coordinates of $ R $ and $ S $ are positive. Let $ \angle ROM = \frac{\pi}{6} $ and $ \angle SOM = \frac{\pi}{3} $, where $ O $ denotes the origin $ (0, 0) $. Let $ |XY| $ denote the length of the line segment $ XY $. Then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE?
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Conic sections
- Adsorption of phenol from its aqueous solution on to fly ash obeys Freundlich isotherm. At a given temperature, from 10 mg g$^{-1}$ and 16 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous phenol solutions, the concentrations of adsorbed phenol are measured to be 4 mg g$^{-1}$ and 10 mg g$^{-1}$, respectively. At this temperature, the concentration (in mg g$^{-1}$) of adsorbed phenol from 20 mg g$^{-1}$ aqueous solution of phenol will be ____. Use: $\log_{10} 2 = 0.3$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Adsorption
- At 300 K, an ideal dilute solution of a macromolecule exerts osmotic pressure that is expressed in terms of the height (h) of the solution (density = 1.00 g cm$^{-3}$) where h is equal to 2.00 cm. If the concentration of the dilute solution of the macromolecule is 2.00 g dm$^{-3}$, the molar mass of the macromolecule is calculated to be $X \times 10^{4}$ g mol$^{-1}$. The value of $X$ is ____. Use: Universal gas constant (R) = 8.3 J K$^{-1}$ mol$^{-1}$ and acceleration due to gravity (g) = 10 m s$^{-2}\}$
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Colligative Properties
Concepts Used:
Electromagnetic waves
The waves that are produced when an electric field comes into contact with a magnetic field are known as Electromagnetic Waves or EM waves. The constitution of an oscillating magnetic field and electric fields gives rise to electromagnetic waves.
Types of Electromagnetic Waves:
Electromagnetic waves can be grouped according to the direction of disturbance in them and according to the range of their frequency. Recall that a wave transfers energy from one point to another point in space. That means there are two things going on: the disturbance that defines a wave, and the propagation of wave. In this context the waves are grouped into the following two categories:
- Longitudinal waves: A wave is called a longitudinal wave when the disturbances in the wave are parallel to the direction of propagation of the wave. For example, sound waves are longitudinal waves because the change of pressure occurs parallel to the direction of wave propagation.
- Transverse waves: A wave is called a transverse wave when the disturbances in the wave are perpendicular (at right angles) to the direction of propagation of the wave.