Question:
A diabetic patient presents with sudden-onset perineal pain. On examination, foul-smelling discharge, and necrotic tissue as seen in the image is noted. Which of the following is true about the given condition?
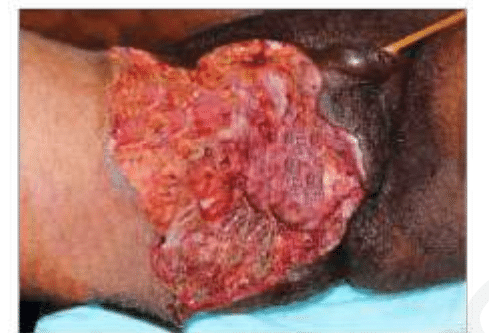
A diabetic patient presents with sudden-onset perineal pain. On examination, foul-smelling discharge, and necrotic tissue as seen in the image is noted. Which of the following is true about the given condition?


Updated On: Jun 18, 2025
- Anti-gas gangrene serum indicated for all cases
- Urinary diversion is the next step
- Bilateral orchidectomy must be done
- Mixed aerobic and anerobic infection
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is D
Solution and Explanation
The scenario describes a case of Fournier's gangrene, a necrotizing fasciitis affecting the perineal, perianal, and genital regions. Let's break down the key aspects of this condition:
- Cause: Fournier's gangrene is often caused by a mixed bacterial infection involving both aerobic and anaerobic organisms. The rapid progression and the polymicrobial nature of these infections require prompt recognition and treatment.
- Symptoms: The patient shows sudden-onset perineal pain, necrotic tissue, and foul-smelling discharge, all of which align with symptoms of Fournier's gangrene.
- Treatment: Immediate broad-spectrum antibiotics are administered, and surgical debridement of necrotic tissues is necessary. The most common pathogens are a mix of aerobic bacteria (like Escherichia coli) and anaerobic bacteria (such as Bacteroides and Clostridium species).
Evaluating the options:
- Anti-gas gangrene serum indicated for all cases: This is incorrect because anti-gas gangrene serum is not routinely indicated in Fournier's gangrene.
- Urinary diversion is the next step: While urinary diversion can be part of management if the urogenital tract is involved, it is not the primary focus initially.
- Bilateral orchidectomy must be done: This procedure is not a necessity for all cases and is only considered if there is testicular involvement and no viability.
- Mixed aerobic and anaerobic infection: Correct, as this option accurately describes the etiology of Fournier's gangrene.
Thus, the correct answer is: Mixed aerobic and anaerobic infection, as it correctly identifies the nature of the infection involved in Fournier's gangrene.
Was this answer helpful?
2
1
Top Questions on Diabetes
- Discuss the symptoms and laboratory investigations required to be done to diagnose diabetes.
- Define diabetes.
- Explain briefly about Diabetic Education.
- Fasting glucose level for a non-diabetic person should be ______.
- The following question consists of two statements – assertion (a) and reason (r). Answer selecting the appropriate option:
(a) : Insulin is released by pancreas.
(r) : It helps to utilize glucose.
View More Questions
Questions Asked in NEET PG exam
Which of the following cranial nerves is responsible for the motor innervation of the muscles of mastication?
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The normal pH of arterial blood is:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
Which enzyme is deficient in Gaucher’s disease?
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The anticoagulant effect of heparin is monitored using:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The causative agent of malaria is:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
View More Questions