Integrate the function: \(\frac {1}{(x^2+1)(x^2+4)}\)
Solution and Explanation
∴\(\frac {1}{(x^2+1)(x^2+4)}\) = \(\frac {Ax+B}{(x^2+1)}+\frac {Cx+D}{(x^2+4)}\)
\(⇒1 = (Ax+B)(x^2+4)+(Cx+D)(x^2+1)\)
\(⇒1 = Ax^3+4Ax+Bx^2+4B+Cx^3+Cx+Dx^2+D\)
Equating the coefficients of \(x^3,x^2,x,\) and constant term,we obtain
\(A+C=0\)
\(B+D=0\)
\(4A+C=0\)
\(4B+D=1\)
On solving these equations, we obtain
\(A=0,\ B=\frac 13,\ C=0,\ D=-\frac 13\)
From equation(1), we obtain
\(\frac {1}{(x^2+1)(x^2+4)}\) = \(\frac {1}{3(x^2+1)}-\frac {1}{3(x^2+4)}\)
\(∫\)\(\frac {1}{(x^2+1)(x^2+4)}\) = \(\frac 13∫\frac {1}{x^2+1}dx-\frac {1}3∫\frac {1}{x^2+4}dx\)
=\(\frac 13\tan^{-1}x-\frac 13.\frac 12tan^{-1}\frac x2+C\)
=\(\frac 13tan^{-1}x-\frac 16tan^{-1}\frac x2+C\)
Top Questions on integral
- The value of the integral \( \int_0^1 x^2 \, dx \) is:
Let \( f : (0, \infty) \to \mathbb{R} \) be a twice differentiable function. If for some \( a \neq 0 \), } \[ \int_0^a f(x) \, dx = f(a), \quad f(1) = 1, \quad f(16) = \frac{1}{8}, \quad \text{then } 16 - f^{-1}\left( \frac{1}{16} \right) \text{ is equal to:}\]
- Let $ f(x) $ be a positive function and $I_1 = \int_{-\frac{1}{2}}^1 2x \, f\left(2x(1-2x)\right) dx$ and $I_2 = \int_{-1}^2 f\left(x(1-x)\right) dx.$ Then the value of $\frac{I_2}{I_1}$ is equal to ____
- Evaluate the integral: \[ \int \frac{x^2 + 2x}{\sqrt{x^2 + 1}} \, dx \]
- Evaluate the integral: \[ \int \sqrt{x^2 + 3x} \, dx \]
Questions Asked in CBSE CLASS XII exam
- Arora and Gurmeet were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2. Starting from 1st October, 2024 Arora withdrew ₹ 30,000 at the beginning of each quarter for his personal use. Interest on drawings was to be charged @ 12% per annum. Interest on Arora's drawings for the year ended 31st March, 2025 was:
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2026
- Partnership
The probability of hitting the target by a trained sniper is three times the probability of not hitting the target on a stormy day due to high wind speed. The sniper fired two shots on the target on a stormy day when wind speed was very high. Find the probability that
(i) target is hit.
(ii) at least one shot misses the target.
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2026
- Probability
- Identify and explain the various other forms of this disorder.
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2026
- Psychological Disorders
- If \[ P = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & -1 & 0 \\ 2 & 3 & 4 \\ 0 & 1 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \quad \text{and} \quad Q = \begin{bmatrix} 2 & 2 & -4 \\ -4 & 2 & -4 \\ 1 & -1 & 5 \end{bmatrix} \] find \( QP \) and hence solve the following system of equations using matrix method:
\[ x - y = 3,\quad 2x + 3y + 4z = 13,\quad y + 2z = 7 \] - Following reaction takes place in one step :
\( 2A + B \rightarrow 2C \)
How will the rate of above reaction change if the volume of the reaction vessel is decreased to one third of its original volume? Will there be any change in the order of reaction with the reduced volume?
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2026
- Chemical Kinetics
Concepts Used:
Integration by Partial Fractions
The number of formulas used to decompose the given improper rational functions is given below. By using the given expressions, we can quickly write the integrand as a sum of proper rational functions.
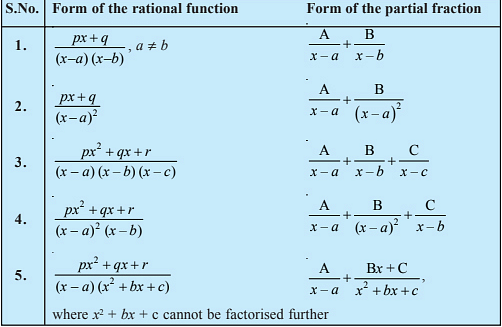
For examples,
