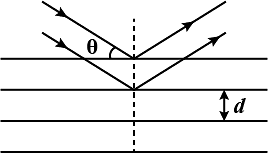
X-rays of wavelength λ get reflected from parallel planes of atoms in a crystal with spacing d between two planes as shown in the figure. If the two reflected beams interfare constructively,Then the condition for maxima will be(n is the order of interference fringe)

- d tanθ=nλ
- d sinθ=nλ
- 2d cosθ=nλ
- 2d sinθ=nλ
The Correct Option is D
Approach Solution - 1
Bragg’s Law and Path Difference Explanation:
In X-ray diffraction by a crystal, waves are reflected from different parallel crystal planes. The key idea is that the path difference between the rays reflected from successive planes should lead to constructive interference.
Geometry Insight:
Let the distance between two successive crystal planes be d. An incident ray hits the first plane at an angle θ and reflects, while another ray enters to the second plane, reflects, and emerges parallel to the first ray.
The extra distance traveled by the second ray is the sum of two segments:
- AM = distance going into the plane = $d\sin\theta$
- AN = distance coming out of the plane = $d\sin\theta$
Total path difference = $AM + AN = 2d\sin\theta$
Condition for Constructive Interference:
To observe a strong reflected beam, the path difference should be an integer multiple of the wavelength λ, that is:
$2d\sin\theta = n\lambda$
Where:
- d = spacing between planes
- θ = glancing angle
- n = order of diffraction (an integer)
- λ = wavelength of X-ray
Conclusion: The correct relation that gives the condition for constructive interference in X-ray diffraction is:
Option (D): $2d\sin\theta = n\lambda$
Approach Solution -2
Bragg's Law – Condition for Constructive Interference:
When X-rays are incident on a crystal, they are reflected from different parallel planes of atoms within the crystal. Due to the regular spacing of these planes, interference occurs between the reflected waves.
Constructive interference (which leads to maxima or bright spots) happens when the extra path traveled by the wave reflected from the lower plane is an integer multiple of the wavelength.
Path difference between rays reflected from adjacent planes is:
\( \text{Path difference} = 2d\sin\theta \)
To satisfy the condition for constructive interference, this path difference must be equal to an integer multiple of the wavelength:
\( 2d\sin\theta = n\lambda \)
Where:
- \( d \) = distance between atomic planes in the crystal
- \( \theta \) = angle of incidence/reflection
- \( \lambda \) = wavelength of the X-rays
- \( n \) = order of the reflected beam (1st order, 2nd order, etc.)
Therefore, the correct option is: (D): \( 2d \sin \theta = n \lambda \)
Top Questions on Wave optics
- Which of the following are true for a single slit diffraction? A. Width of central maxima increases with increase in wavelength keeping slit width constant.
B. Width of central maxima increases with decrease in wavelength keeping slit width constant.
C. Width of central maxima increases with decrease in slit width at constant wavelength.
D. Width of central maxima increases with increase in slit width at constant wavelength.
E. Brightness of central maxima increases for decrease in wavelength at constant slit width.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Wave optics
- The wavelength of light while it is passing through water is \(540\,\text{nm}\). The refractive index of water is \( \frac{4}{3} \). The wavelength of the same light when it is passing through a transparent medium having refractive index of \( \frac{3}{2} \) is _________ nm.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Wave optics
- When an unpolarized light falls at a particular angle on a glass plate (placed in air), it is observed that the reflected beam is linearly polarized. The angle of refracted beam with respect to the normal is ___. ($\tan^{-1}(1.52) = 57.7^\circ$, refractive indices of air and glass are 1.00 and 1.52, respectively.)
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Wave optics
- The kinetic energy of a simple harmonic oscillator is oscillating with angular frequency of 176 rad/s. The frequency of this simple harmonic oscillator is _________ Hz. [Take $\pi = \frac{22}{7}$]}
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Wave optics
- A particle having electric charge $3 \times 10^{-19}$ C and mass $6 \times 10^{-27}$ kg is accelerated by applying an electric potential of 1.21 V. Wavelength of the matter wave associated with the particle is $\alpha \times 10^{-12}$ m. The value of $\alpha$ is _________. (Take Planck's constant $= 6.6 \times 10^{-34}$ J.s)
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Wave optics
Questions Asked in WBJEE exam
- Figure shows the graph of angle of deviation \( \delta \) versus angle of incidence \( i \) for a light ray striking a prism. The prism angle is

- WBJEE - 2025
- Refraction Through A Prism
- Ruma reached the metro station and found that the escalator was not working. She walked up the stationary escalator with velocity \( v_1 \) in time \( t_1 \). On another day, if she remains stationary on the escalator moving with velocity \( v_2 \), the escalator takes her up in time \( t_2 \). The time taken by her to walk up with velocity \( v_1 \) on the moving escalator will be:
- WBJEE - 2025
- Relative Motion
- The compound(s) showing optical activity is/are
- WBJEE - 2025
- Stoichiometry and Stoichiometric Calculations
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct about the given compound?

- WBJEE - 2025
- Organic Chemistry
- X is an extensive property and x is an intensive property of a thermodynamic system. Which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
- WBJEE - 2025
- Thermodynamics
Concepts Used:
Wave Optics
- Wave optics are also known as Physical optics which deal with the study of various phenomena such as polarization, interference, diffraction, and other occurrences where ray approximation of geometric optics cannot be done. Thus, the section of optics that deals with the behavior of light and its wave characteristics is known to be wave optics.
- In wave optics, the approximation is carried out by utilizing ray optics for the estimation of the field on a surface. Further, it includes integrating a ray-estimated field over a mirror, lens, or aperture for the calculation of the transmitted or scattered field.
- Wave optics stands as a witness to a famous standoff between two great scientific communities who devoted their lives to understanding the nature of light. Overall, one supports the particle nature of light; the other supports the wave nature.
- Sir Isaac Newton stood as a pre-eminent figure that supported the voice of particle nature of light, he proposed a corpuscular theory which states that “light consists of extremely light and tiny particles, called corpuscles which travel with very high speeds from the source of light to create a sensation of vision by reflecting on the retina of the eye”.