Without using the Pythagoras theorem, show that the points (4, 4), (3, 5) and (-1, -1) are the vertices of a right angled triangle.
Solution and Explanation
The vertices of the given triangle are A (4, 4), B (3, 5), and C (-1, -1).
It is known that the slope (m) of a non-vertical line passing through the points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) is given by.
\(m = \frac {y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}, \ x_2≠x_1\)
∴ Slope of AB \((m_1) = \frac {5-4}{3-4} = -1\)
Slope of BC \((m_2) = \frac {-1-5}{-1-3}= \frac {-6}{-4} = \frac 32\)
Slope of CA \((m_3) =\frac { 4+1 }{ 4+1 }= \frac 55 = 1\)
It is observed that \(m_1m_3 = -1\)
This shows that line segments AB and CA are perpendicular to each other i.e., the given triangle is right-angled at A (4, 4).
Thus, the points (4, 4), (3, 5), and (-1, -1) are the vertices of a right-angled triangle.
Top Questions on Slope of a line
- A line passes through \( (-1, -3) \) and is perpendicular to \( x + 6y = 5 \). Its x-intercept is:
- KCET - 2025
- Mathematics
- Slope of a line
- If \( 3^x = 9^{x-1} \), then the value of \( x \) is:
- TS POLYCET - 2025
- Mathematics
- Slope of a line
- If points \( (5, 5) \), \( (10, k) \), and \( (-5, 1) \) are collinear, then the value of \( k \) is:
- JEECUP - 2024
- Mathematics
- Slope of a line
- Let the slope of the line \( 45x + 5y + 3 = 0 \) be \( 27r_1 + \frac{9r_2}{2} \) for some \( r_1, r_2 \in \mathbb{R} \).Then\[\lim_{x \to 3} \left( \int_3^x \frac{8t^2}{\frac{3r_1 x}{2} - r_2 x^2 - r_1 x^3 - 3x} \, dt \right)\]is equal to _____.
- JEE Main - 2024
- Mathematics
- Slope of a line
- A line passing through the point \( A(9, 0) \) makes an angle of \( 30^\circ \) with the positive direction of the x-axis. If this line is rotated about \( A \) through an angle of \( 15^\circ \) in the clockwise direction, then its equation in the new position is:
- JEE Main - 2024
- Mathematics
- Slope of a line
Questions Asked in CBSE Class XI exam
- Balance the following redox reactions by ion-electron method:
(a)MnO4- (aq) + I - (aq) → MnO2(s) + I2(s) (in basic medium)
(b) MnO4- (aq) + SO2(g) → Mn2+(aq) +HSO4- (aq) (in acidic solution)
(c) H2O2(aq)+Fe2+(aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + H2O (l) (in acidic solution)
(d) Cr2O72-+ SO2(g) → Cr3+ (aq) +SO42- (aq) (in acidic solution)- CBSE Class XI
- Oxidation Number
- Write the resonance structures for SO3 , NO2 and NO3-
- CBSE Class XI
- Kossel-Lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding
- At 700 K, equilibrium constant for the reaction:
\(H_2 (g) + I_2 (g) ⇋ 2HI (g)\)
is 54.8. If 0.5 mol L–1 of HI(g) is present at equilibrium at 700 K, what are the concentration of H2(g) and I2(g) assuming that we initially started with HI(g) and allowed it to reach equilibrium at 700 K?- CBSE Class XI
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
- Find the mean deviation about the mean for the data 4, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 17.
- CBSE Class XI
- Statistics
Find the mean deviation about the mean for the data 38, 70, 48, 40, 42, 55, 63, 46, 54, 44.
- CBSE Class XI
- Statistics
Concepts Used:
Straight lines
A straight line is a line having the shortest distance between two points.
A straight line can be represented as an equation in various forms, as show in the image below:
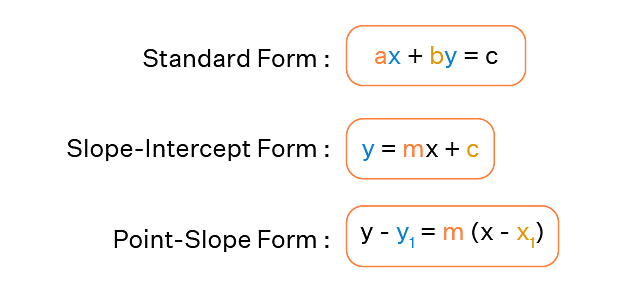
The following are the many forms of the equation of the line that are presented in straight line-
1. Slope – Point Form
Assume P0(x0, y0) is a fixed point on a non-vertical line L with m as its slope. If P (x, y) is an arbitrary point on L, then the point (x, y) lies on the line with slope m through the fixed point (x0, y0) if and only if its coordinates fulfil the equation below.
y – y0 = m (x – x0)
2. Two – Point Form
Let's look at the line. L crosses between two places. P1(x1, y1) and P2(x2, y2) are general points on L, while P (x, y) is a general point on L. As a result, the three points P1, P2, and P are collinear, and it becomes
The slope of P2P = The slope of P1P2 , i.e.
\(\frac{y-y_1}{x-x_1} = \frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}\)
Hence, the equation becomes:
y - y1 =\( \frac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1} (x-x1)\)
3. Slope-Intercept Form
Assume that a line L with slope m intersects the y-axis at a distance c from the origin, and that the distance c is referred to as the line L's y-intercept. As a result, the coordinates of the spot on the y-axis where the line intersects are (0, c). As a result, the slope of the line L is m, and it passes through a fixed point (0, c). The equation of the line L thus obtained from the slope – point form is given by
y – c =m( x - 0 )
As a result, the point (x, y) on the line with slope m and y-intercept c lies on the line, if and only if
y = m x +c