Question:
Which one of the following is not a part of a renal pyramid?
Which one of the following is not a part of a renal pyramid?
Updated On: May 3, 2024
- peritubular capillaries
- convoluted tubules
- collecting ducts
- loop of Henle
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
The medulla of kidney is divided into a number of conical areas, the medulla pyramids or renal pyramids. Peritubular capillaries, loop of Henle and collecting ducts lie in the medulla (renal pyramids) while convoluted tubules lie in the cortex of kidney.
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on excretory products and their elimination
- Which of the following is excretory material in birds?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- excretory products and their elimination
What is the primary function of Bowman’s capsule in nephron?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- excretory products and their elimination
- Match List I with List II
List I List II A Pons I Provides additional space for Neurons, regulates posture and balance. B Hypothalamus II Controls respiration and gastric secretions. C Medulla III Connects different regions of the brain. D Cerebellum IV Neurosecretory cells
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Biology
- excretory products and their elimination
- Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between the hormones ANF and Angiotensin 2 in terms of their physiological effects on the body?
- MHT CET - 2024
- Biology
- excretory products and their elimination
- Which of the following structures in the kidney is primarily responsible for the reabsorption of water and solutes from the filtrate?
- MHT CET - 2024
- Biology
- excretory products and their elimination
View More Questions
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- Two cities X and Y are connected by a regular bus service with a bus leaving in either direction every T min. A girl is driving scooty with a speed of 60 km/h in the direction X to Y. She notices that a bus goes past her every 30 minutes in the direction of her motion, and every 10 minutes in the opposite direction. Choose the correct option for the period T of the bus service and the speed (assumed constant) of the buses.
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Relative Velocity
- A physical quantity P is related to four observations a, b, c, and d as follows: P = a3 b2 (c / √d) The percentage errors of measurement in a, b, c, and d are 1%, 3%, 2%, and 4% respectively. The percentage error in the quantity P is:
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Dimensional analysis and its applications
What is Microalbuminuria ?
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Human physiology
The output (Y) of the given logic implementation is similar to the output of an/a …………. gate.

- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Logic gates
- An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litre has 18.20 moles of oxygen. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, its gauge pressure drops to 11 atmospheric pressure at temperature \(27^\circ\)C. The mass of the oxygen withdrawn from the cylinder is nearly equal to: [Given, \(R = \frac{100}{12} \text{ J mol}^{-1} \text{K}^{-1}\), and molecular mass of \(O_2 = 32 \text{ g/mol}\), 1 atm pressure = \(1.01 \times 10^5 \text{ N/m}^2\)]
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Ideal-gas equation and absolute temperature
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
Excretory products and their elimination
The physiological process of the elimination of metabolic waste from the body is called excretion. The excretory products comprise amino acids, carbon dioxide, urea, uric acid, water, and ammonia. Some of the Molluscs and Echinoderms excrete waste products from the body in the form of amino acids. Ammonia is the foremost excretory product in animals, it is derived from the proteins exists in the food we eat.
Excretory Products in Different Organisms:
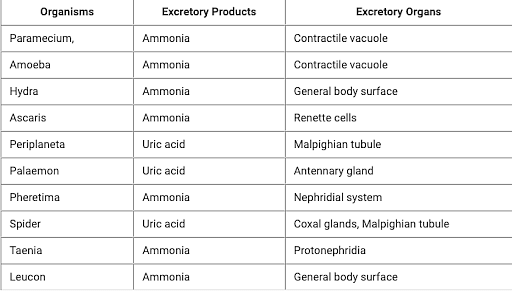
Read More: Excretion in Human Beings