Which one is not the characteristics of the Hexose Monophosphate Pathway?
- It produces CO2
- It requires ATP for phosphorylation
- It is controlled by inhibition of glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase by NADPH
- It produces ribose 5-phosphate.
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
The Hexose Monophosphate (HMP) Pathway, also known as the Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP), is separate from glycolysis and primarily occurs in the cytoplasm of cells. It serves multiple biochemical functions, including the generation of NADPH and the synthesis of ribose-5-phosphate. Let's analyze each of the given options in the context of the HMP Pathway:
- It produces CO2: During the oxidative phase of the HMP Pathway, decarboxylation occurs, resulting in the release of carbon dioxide (CO2). Therefore, this is indeed a characteristic of the HMP pathway.
- It requires ATP for phosphorylation: The HMP pathway does not require ATP for its operation. Instead, it generates NADPH and ribose-5-phosphate without utilizing ATP. Thus, this statement is not a characteristic of the HMP pathway, making it the correct answer to the question.
- It is controlled by inhibition of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase by NADPH: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase is a key regulatory enzyme in the HMP pathway. Its activity is inhibited by high levels of NADPH, providing feedback control. Therefore, this is a characteristic of the pathway.
- It produces ribose 5-phosphate: Ribose-5-phosphate is synthesized during the non-oxidative phase of the HMP pathway, which is essential for nucleotide synthesis. Hence, this is a characteristic of the HMP pathway.
In conclusion, the statement "It requires ATP for phosphorylation" is not a characteristic of the Hexose Monophosphate Pathway, as the pathway operates without ATP consumption.
Top Questions on Biogenetic pathways
- The below structure represent the drug:
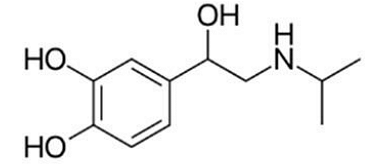
- GPAT - 2024
- Pharmacognosy
- Biogenetic pathways
- The below structure represent the drug:

- GPAT - 2024
- Pharmacognosy
- Biogenetic pathways
- Arrange the following intermediates in the synthesis of isoprenoids in the right sequence
A. Squalence
B. Farnesyl PP
C. Geranyl PP
D. Acetyl CoA
E. Mevalonate
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- GPAT - 2023
- Pharmacognosy
- Biogenetic pathways
- Which one of the following is an autosomal dominant syndrome in its inheritance?
- GPAT - 2023
- Pharmacognosy
- Biogenetic pathways
- Which of the following genes responsible for graft rejection in humans?
- GPAT - 2023
- Pharmacognosy
- Biogenetic pathways
Questions Asked in GPAT exam
- Match the following:
(1) Schedule FF
(2) Schedule F3
(3) Schedule V
(4) Schedule Y
Descriptions:
(P) Standards of patent and proprietary medicines
(Q) Requirements and guidelines for clinical trials
(R) Standards for sterilized umbilical tapes
(S) Standards for Ophthalmic preparations- GPAT - 2025
- Drug therapy
- If the label or the container bears the name of an individual or company purporting to be the manufacturer of the drug, which individual or company is fictitious or does not exist, it is:
- GPAT - 2025
- Drug therapy
- Manufacturing Specification for tooling has been standardized by?
- GPAT - 2025
- Pharmacy Profession & Introduction to Pharmaceuticals
- As per USP, the maximum concentration of benzalkonium chloride used as a preservative in parenteral formulations is
- GPAT - 2025
- Pharmaceutical Analysis
Match the following:
(P) Schedule H
(Q) Schedule G
(R) Schedule P
(S) Schedule F2
Descriptions:
(I) Life period of drugs
(II) Drugs used under RMP
(III) List of Prescription Drugs
(IV) Standards for surgical dressing
- GPAT - 2025
- Drug therapy