What is the hybridization and geometry of the compound $ XeOF_4 $ ?
- $ sp^3\,d^2 $ and octahedral
- $ sp^3\,d $ and square pyramidal
- $ sp^3\,d $ and trigonal bipyramidal
- $ sp^3\,d^2 $ and square pyramidal
The Correct Option is D
Approach Solution - 1
$=\frac{1}{2}(V.E. +M.A. -c+a)$
For, $XeOF_{4}$
$V.E. =8; M.A.$ (monovalent atoms) $= 4$
$(X)=\frac{1}{2}(8+4)\Rightarrow 6$
i.e., $sp^{3} d^{2}$ hybridisation
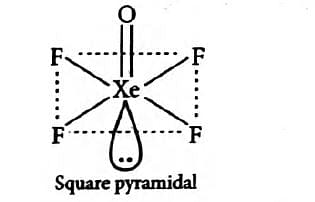
Approach Solution -2
The compound XeOF4, has 5 sigma bonds, 1 pi bond and 1 lone pair.
The sum of sigma and lone pair is 5 + 1= 6.
It means that there is one s orbital, 3 p orbitals and 2 d orbitals.
Therefore, the hybridization is sp3 d2.
Top Questions on Chemical bonding and molecular structure
From the given following (A to D) cyclic structures, those which will not react with Tollen's reagent are :

- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure
- The wave numbers of three spectral lines of hydrogen atom are considered. Identify the set of spectral lines belonging to the {Balmer series. (\(R\) = Rydberg constant)}
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure
- Consider the reaction: \[ \text{Ph–CH=CH}_2 \xrightarrow[\text{peroxide}]{\text{HBr}} \text{Product} \] Which of the following statements are correct?
[A.] The reaction proceeds through a more stable radical intermediate.
[B.] The role of peroxide is to generate \(\mathrm{H^\bullet}\) radical.
[C.] During this reaction, benzene is formed as a byproduct.
[D.] \(1\)-Bromo-\(2\)-phenylethane is formed as a minor product.
[E.] The same reaction in absence of peroxide proceeds via a carbocation intermediate. Choose the correct answer.- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure
Compound 'P' undergoes the following sequence of reactions : (i) NH₃ (ii) $\Delta$ $\rightarrow$ Q (i) KOH, Br₂ (ii) CHCl₃, KOH (alc), $\Delta$ $\rightarrow$ NC-CH₃. 'P' is :


- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure
- Given below are two statements :
Statement I : The correct order in terms of bond dissociation enthalpy is \( Cl_2>Br_2>F_2>I_2 \).
Statement II : The correct trend in the covalent character of the metal halides is \( SnCl_2>SnCl_4 \), \( PbCl_2>PbCl_4 \) and \( UF_4>UF_6 \).
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below :- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure
Questions Asked in JKCET exam
- Which of the following is not an example of an ideal solution?
- JKCET - 2024
- Colligative Properties
- What is the value of the Van't Hoff factor (i) for solutes that dissociate in water?
- JKCET - 2024
- Colligative Properties
- Which of the following do not show geometrical isomerism? (Assume all ligands are unidentate)
- JKCET - 2024
- coordination compounds
- Lewis concept does explain the behaviour of
- JKCET - 2024
- Acids and Bases
- In the reaction, $ H_2(g) + Br_2(g) = 2HBr(g) $, what will happen if there is a change in pressure?
- JKCET - 2024
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
Concepts Used:
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Such a group of atoms is called a molecule. Obviously, there must be some force that holds these constituent atoms together in the molecules. The attractive force which holds various constituents (atoms, ions, etc.) together in different chemical species is called a chemical bond.
Types of Chemical Bonds:
There are 4 types of chemical bonds which are formed by atoms or molecules to yield compounds.
- Ionic Bonds - Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding which involves a transfer of electrons from one atom or molecule to another.
- Covalent Bonds - Compounds that contain carbon commonly exhibit this type of chemical bonding.
- Hydrogen Bonds - It is a type of polar covalent bonding between oxygen and hydrogen wherein the hydrogen develops a partial positive charge
- Polar Bonds - In Polar Covalent chemical bonding, electrons are shared unequally since the more electronegative atom pulls the electron pair closer to itself and away from the less electronegative atom.
Factors Affecting Bond Enthalpy in Chemical Bonding:
- Size of the Atom
- Multiplicity of Bonds
- Number of Lone Pair of Electrons Present
- Bond Angle