What is meant by hybridisation of atomic orbitals? Describe the shapes of \(sp, sp ^2 , sp ^3\) hybrid orbitals.
Solution and Explanation
Hybridization is defined as an intermixing of a set of atomic orbitals of slightly different energies, thereby forming a new set of orbitals having equivalent energies and shapes.
For example, one \(2s-orbital\) hybridizes with two \(2p-orbitals\) of carbon to form three new \(sp ^2\) hybrid orbitals.
These hybrid orbitals have minimum repulsion between their electron pairs and thus, are more stable. Hybridization helps indicate the geometry of the molecule.
Shape of sp hybrid orbitals: sp hybrid orbitals have a linear shape. They are formed by the intermixing of s and porbitals as: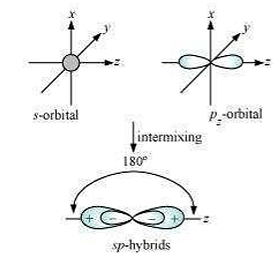
Shape of \(sp ^2\) hybrid orbitals:
\(sp ^2\) hybrid orbitals are formed as a result of the intermixing of one \(s-orbital\) and two \(2p-orbitals\). The hybrid orbitals are oriented in a trigonal planar arrangement as:
Shape of \(sp ^3\) hybrid orbitals:
Four \(sp ^3\) hybrid orbitals are formed by intermixing one \(s-orbital\) with three \(p-orbitals\). The four \(sp ^3\) hybrid orbitals are arranged in the form of a tetrahedron as:
Top Questions on Hybridisation
Arrange the following in increasing order of solubility product:
\[ {Ca(OH)}_2, {AgBr}, {PbS}, {HgS} \]- JEE Main - 2025
- Chemistry
- Hybridisation
Concentrated nitric acid is labelled as 75% by mass. The volume in mL of the solution which contains 30 g of nitric acid is:
Given: Density of nitric acid solution is 1.25 g/mL.- JEE Main - 2025
- Chemistry
- Hybridisation
Match List - I with List - II.
List - I (Saccharides) List - II (Glycosidic linkages found)
(A) Sucrose (I) \( \alpha 1 - 4 \)
(B) Maltose (II) \( \alpha 1 - 4 \) and \( \alpha 1 - 6 \)
(C) Lactose (III) \( \alpha 1 - \beta 2 \)
(D) Amylopectin (IV) \( \beta 1 - 4 \)Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- JEE Main - 2025
- Chemistry
- Hybridisation
Match List - I with List - II.
List - I (Complex) List - II (Hybridisation) (A) \([\text{CoF}_6]^{3-}\) (I) \( d^2 sp^3 \) (B) \([\text{NiCl}_4]^{2-}\) (II) \( sp^3 \) (C) \([\text{Co(NH}_3)_6]^{3+}\) (III) \( sp^3 d^2 \) (D) \([\text{Ni(CN}_4]^{2-}\) (IV) \( dsp^2 \)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- JEE Main - 2025
- Chemistry
- Hybridisation
- The change in hybridisation (if any) of the 'Al' atom in the following reaction is
AlCl3 + Cl- → AlCl4-
- KCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- Hybridisation
Questions Asked in CBSE Class XI exam
- Balance the following redox reactions by ion-electron method:
(a)MnO4- (aq) + I - (aq) → MnO2(s) + I2(s) (in basic medium)
(b) MnO4- (aq) + SO2(g) → Mn2+(aq) +HSO4- (aq) (in acidic solution)
(c) H2O2(aq)+Fe2+(aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + H2O (l) (in acidic solution)
(d) Cr2O72-+ SO2(g) → Cr3+ (aq) +SO42- (aq) (in acidic solution)- CBSE Class XI
- Oxidation Number
- Write the resonance structures for SO3 , NO2 and NO3-
- CBSE Class XI
- Kossel-Lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding
- At 700 K, equilibrium constant for the reaction:
\(H_2 (g) + I_2 (g) ⇋ 2HI (g)\)
is 54.8. If 0.5 mol L–1 of HI(g) is present at equilibrium at 700 K, what are the concentration of H2(g) and I2(g) assuming that we initially started with HI(g) and allowed it to reach equilibrium at 700 K?- CBSE Class XI
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
- Find the mean deviation about the mean for the data 4, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 17.
- CBSE Class XI
- Statistics
Find the mean deviation about the mean for the data 38, 70, 48, 40, 42, 55, 63, 46, 54, 44.
- CBSE Class XI
- Statistics
Concepts Used:
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Such a group of atoms is called a molecule. Obviously, there must be some force that holds these constituent atoms together in the molecules. The attractive force which holds various constituents (atoms, ions, etc.) together in different chemical species is called a chemical bond.
Types of Chemical Bonds:
There are 4 types of chemical bonds which are formed by atoms or molecules to yield compounds.
- Ionic Bonds - Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding which involves a transfer of electrons from one atom or molecule to another.
- Covalent Bonds - Compounds that contain carbon commonly exhibit this type of chemical bonding.
- Hydrogen Bonds - It is a type of polar covalent bonding between oxygen and hydrogen wherein the hydrogen develops a partial positive charge
- Polar Bonds - In Polar Covalent chemical bonding, electrons are shared unequally since the more electronegative atom pulls the electron pair closer to itself and away from the less electronegative atom.
Factors Affecting Bond Enthalpy in Chemical Bonding:
- Size of the Atom
- Multiplicity of Bonds
- Number of Lone Pair of Electrons Present
- Bond Angle