We wish to obtain an erect image of an object, using a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. What should be the range of distance of the object from the mirror? What is the nature of the image? Is the image larger or smaller than the object? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Solution and Explanation
Range of object distance = \(0\ cm\) to \(15\ cm\)
A concave mirror gives an erect image when an object is placed between its pole (P) and the principal focus (F).
Hence, to obtain an erect image of an object from a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm, the object must be placed anywhere between the pole and the focus. The image formed will be virtual, erect, and magnified in nature, as shown in the given figure.
Top Questions on Spherical Mirrors
- A concave mirror produces an image of an object such that the distance between the object and image is 20 cm. If the magnification of the image is \( -3 \), then the magnitude of the radius of curvature of the mirror is:
- JEE Main - 2025
- Physics
- Spherical Mirrors
- (ii) An object at a distance of 16 cm from a spherical mirror forms a virtual image at a distance of 12 cm behind the mirror. Determine the magnification of the image and type of the mirror.
- UP Board X - 2025
- Science
- Spherical Mirrors
- Image of an object formed by a concave mirror is real and of the size of the object. The object is placed -
- UP Board X - 2025
- Science
- Spherical Mirrors
- With the help of a suitable ray diagram, derive the formula \( \frac{1}{v} + \frac{1}{u} = \frac{1}{f} \) for a concave mirror.
- UP Board XII - 2025
- Physics
- Spherical Mirrors
- The length of the image formed by a concave mirror:
- UP Board XII - 2025
- Physics
- Spherical Mirrors
Questions Asked in CBSE X exam
- Find 'mean' and 'mode' of the following data : Frequency Distribution Table
Class 0 – 15 15 – 30 30 – 45 45 – 60 60 – 75 75 – 90 Frequency 11 8 15 7 10 9 - CBSE Class X - 2025
- Statistics
Leaves of the sensitive plant move very quickly in response to ‘touch’. How is this stimulus of touch communicated and explain how the movement takes place?
- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Plant Biology
- Two statements are given below. They are Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read both the statements carefully and choose the correct option. Assertion (A): Rupees is accepted as medium of exchange in India.
Reason (R): The World Bank legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment in India.- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Money and Credit
- Two statements are given below. They are Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read both the statements carefully and choose the correct option:
Assertion (A): Rupees is accepted as medium of exchange in India.
Reason (R): The World Bank legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment in India.- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Money and Credit
Read the following sources of loan carefully and choose the correct option related to formal sources of credit:
(i) Commercial Bank
(ii) Landlords
(iii) Government
(iv) Money Lende- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Money and Credit
Concepts Used:
Spherical Mirrors
A spherical mirror is a mirror which has been cut out of a spherical surface.
There are two kinds of spherical mirrors:
- Convex Mirror
- Concave Mirror
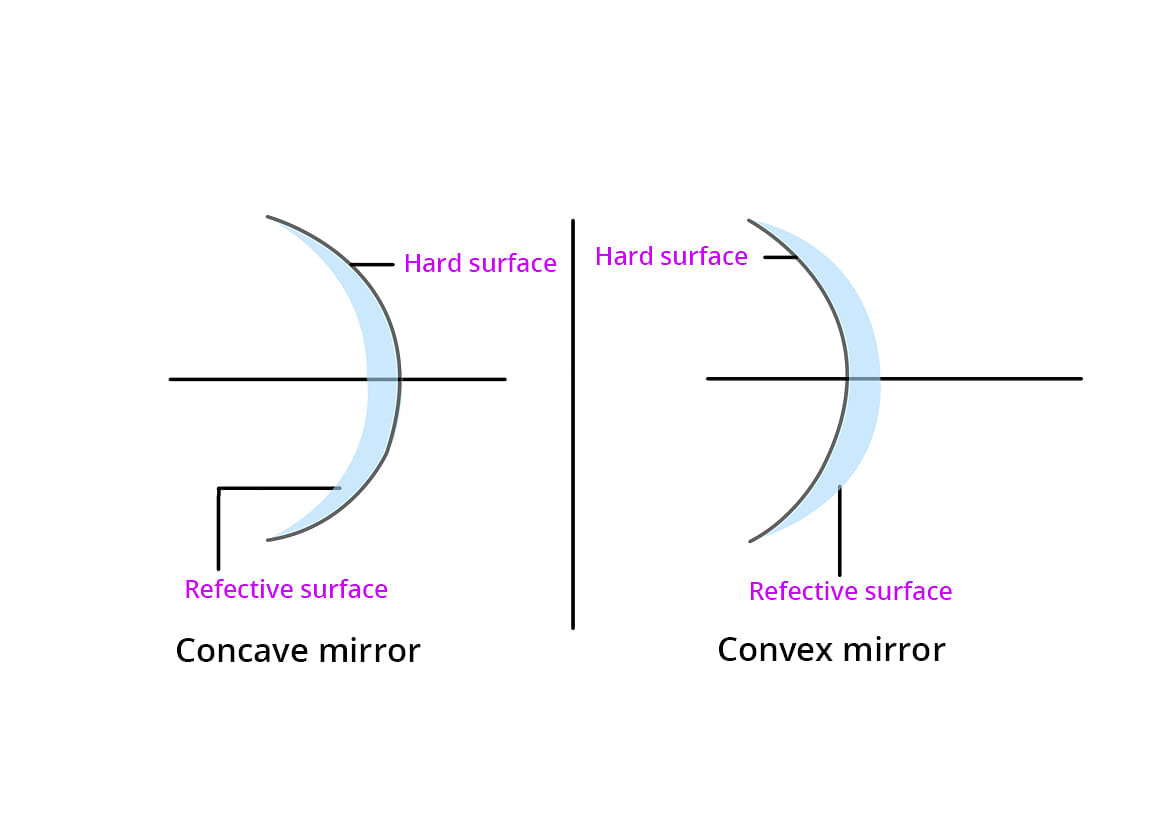
Concave Mirror
Concave mirrors are also called converging mirrors, because in these types of mirrors, light rays converge at a point after impact and reflect back from the reflective surface of the mirror.
Convex Mirror
The convex mirror has a reflective surface that is curved outward. Regardless of the distance between the subject and the mirrors, these mirrors are "always" virtual, upright and reduced.