Question:
To find out degree of freedom, the correct expression is:
To find out degree of freedom, the correct expression is:
Updated On: Apr 21, 2025
\(f=\frac {2}{γ-1}\)
\(f=\frac {γ+1}{2}\)
\(f=\frac {2}{γ+1}\)
\(f=\frac {1}{γ+1}\)
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
∵ \(γ=1+\frac 2f\)
⇒ \(\frac 2f=γ-1\)
⇒ \(f=\frac {2}{γ-1}\)
So, the correct option is (A): \(f=\frac {2}{γ-1}\)
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on kinetic theory
- The equation for the RMS velocity is given as \[ v_{\text{rms}} = \sqrt{\frac{3RT}{M_0}} \] where \( R \) is the gas constant, \( T \) is the temperature, and \( M_0 \) is the molecular mass. If the temperature is increased, find the new RMS velocity \( v_{\text{rms}} \) when the temperature is doubled.}
- MHT CET - 2025
- Physics
- kinetic theory
- In a mixture of gases, the average number of degrees of freedom per molecule is 6. If the rms speed of the molecule is \(c\), what is the velocity of sound in the gas?
- BITSAT - 2025
- Physics
- kinetic theory
- The temperature at which the rms speed of hydrogen molecules is same as the rms speed of oxygen molecules at a temperature of $6495^\circ$C is
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Physics
- kinetic theory
- The specific heat capacity of one mole of water is (R is the universal gas constant):
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Physics
- kinetic theory
- Mean free path is inversely proportional to (n = number density, d = diameter of particle)
- KEAM - 2025
- Physics
- kinetic theory
View More Questions
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- Two cities X and Y are connected by a regular bus service with a bus leaving in either direction every T min. A girl is driving scooty with a speed of 60 km/h in the direction X to Y. She notices that a bus goes past her every 30 minutes in the direction of her motion, and every 10 minutes in the opposite direction. Choose the correct option for the period T of the bus service and the speed (assumed constant) of the buses.
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Relative Velocity
- A physical quantity P is related to four observations a, b, c, and d as follows: P = a3 b2 (c / √d) The percentage errors of measurement in a, b, c, and d are 1%, 3%, 2%, and 4% respectively. The percentage error in the quantity P is:
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Dimensional analysis and its applications
What is Microalbuminuria ?
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Human physiology
The output (Y) of the given logic implementation is similar to the output of an/a …………. gate.

- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Logic gates
- An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litre has 18.20 moles of oxygen. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, its gauge pressure drops to 11 atmospheric pressure at temperature \(27^\circ\)C. The mass of the oxygen withdrawn from the cylinder is nearly equal to: [Given, \(R = \frac{100}{12} \text{ J mol}^{-1} \text{K}^{-1}\), and molecular mass of \(O_2 = 32 \text{ g/mol}\), 1 atm pressure = \(1.01 \times 10^5 \text{ N/m}^2\)]
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Ideal-gas equation and absolute temperature
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
Kinetics Equations
It is branch of physics that defines motion with respect to space and time is known as kinematics.
Inverse Kinematics: Inverse Kinematics do the reverse of kinematics.
There are four basic kinematics equations:
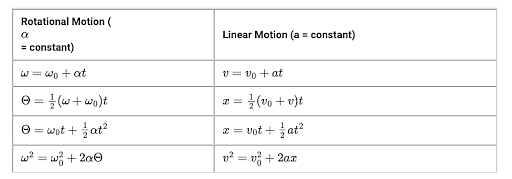
Rotational Kinematics Equations
Another branch of kinematics equations which deals with the rotational motion of anybody.