The total number of molecular orbitals formed from 2s and 2p atomic orbitals of a diatomic molecule is _________.
The total number of molecular orbitals formed from 2s and 2p atomic orbitals of a diatomic molecule is _________.
Solution and Explanation
The molecular orbitals formed from 2s and 2p atomic orbitals are as follows:
\(• Two\ molecular\ orbitals\ of\ 2s\ and\ σ ∗2s\)
\(• Six\ molecular\ orbitals\ of\ 2p: σ2pz, σ ∗2pz, π2px, π2py, π ∗2px, π ∗2py.\)
Thus, the total number of molecular orbitals formed is 8.
Top Questions on Molecular Orbital Theory
- Pair of species among the following having same bond order as well as paramagnetic character will be:
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Molecular Orbital Theory
- Among the species O$_2^+$, N$_2^-$, N$_2^{2-}$ and O$_2^-$ which have same bond order as well as paramagnetic in nature.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Molecular Orbital Theory
Regarding the molecular orbital (MO) energy levels for homonuclear diatomic molecules, the INCORRECT statement(s) is (are):
- JEE Advanced - 2025
- Chemistry
- Molecular Orbital Theory
- Arrange the following in increasing order of bond order: (A) He\(_2^+\)
(B) O\(_2^-\)
(C) HF
(D) NO\(^-\)- CUET (PG) - 2025
- Chemistry
- Molecular Orbital Theory
- Which of the following is the ratio of 5\(^\text{th}\) Bohr orbit \( (r_5) \) of He\(^+\) & Li\(^{2+}\)?
- JEE Main - 2025
- Chemistry
- Molecular Orbital Theory
Questions Asked in JEE Main exam
Consider an A.P. $a_1,a_2,\ldots,a_n$; $a_1>0$. If $a_2-a_1=-\dfrac{3}{4}$, $a_n=\dfrac{1}{4}a_1$, and \[ \sum_{i=1}^{n} a_i=\frac{525}{2}, \] then $\sum_{i=1}^{17} a_i$ is equal to
- JEE Main - 2026
- Arithmetic Progression
- A thin convex lens of focal length \( 5 \) cm and a thin concave lens of focal length \( 4 \) cm are combined together (without any gap), and this combination has magnification \( m_1 \) when an object is placed \( 10 \) cm before the convex lens.
Keeping the positions of the convex lens and the object undisturbed, a gap of \( 1 \) cm is introduced between the lenses by moving the concave lens away. This leads to a change in magnification of the total lens system to \( m_2 \).
The value of \( \dfrac{m_1}{m_2} \) is
- Two blocks with masses 100 g and 200 g are attached to the ends of springs A and B as shown in figure. The energy stored in A is E. The energy stored in B, when spring constants \(k_A, k_B\) of A and B, respectively satisfy the relation \(4k_A = 3k_B\), is :

- JEE Main - 2026
- Alternating current
- Correct statements regarding Arrhenius equation among the following are:
Factor \(e^{-E_a/RT}\) corresponds to fraction of molecules having kinetic energy less than \(E_a\).
At a given temperature, lower the \(E_a\), faster is the reaction.
Increase in temperature by about \(10^\circ\text{C}\) doubles the rate of reaction.
Plot of \(\log k\) vs \(\dfrac{1}{T}\) gives a straight line with slope \(= -\dfrac{E_a}{R}\).
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemical Kinetics
- If the image of the point \( P(1, 2, a) \) in the line \[ \frac{x - 6}{3} = \frac{y - 7}{2} = \frac{7 - z}{2} \] is \( Q(5, b, c) \), then \( a^2 + b^2 + c^2 \) is equal to
- JEE Main - 2026
- Distance of a Point From a Line
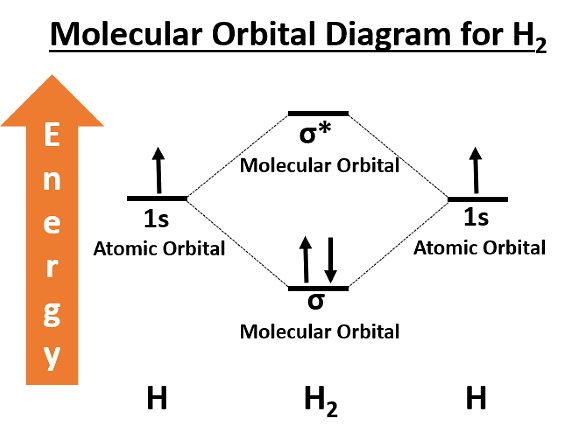
Concepts Used:
Molecular Orbital Theory
The Molecular Orbital Theory is a more sophisticated model of chemical bonding where new molecular orbitals are generated using a mathematical process called Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals (LCAO).
Molecular Orbital theory is a chemical bonding theory that states that individual atoms combine together to form molecular orbitals. Due to this arrangement in MOT Theory, electrons associated with different nuclei can be found in different atomic orbitals. In molecular orbital theory, the electrons present in a molecule are not assigned to individual chemical bonds between the atoms. Rather, they are treated as moving under the influence of the atomic nuclei in the entire molecule.