The ratio of lone pair of electrons to bond pair of electrons in ozone molecule is:
The ratio of lone pair of electrons to bond pair of electrons in ozone molecule is:
2:1
3:2
2:3
1:2
The Correct Option is A
Approach Solution - 1
Step 1: Understand the Structure of Ozone Molecule (O3):
Ozone (O3) is a molecule composed of three oxygen atoms. It has a bent structure, and the bonding in ozone involves both bonding pairs of electrons and lone pairs of electrons. The lone pairs are present on the central oxygen atom, and the bonding pairs are shared between the atoms.
Step 2: Determine the Electron Configuration in Ozone:
Ozone has a total of 18 valence electrons. These electrons are arranged as follows:
- There are two bonds between the oxygen atoms, and one of the oxygen atoms has a lone pair of electrons.
- The central oxygen atom has two lone pairs and forms two bonds with the outer oxygen atoms.
Step 3: Count the Lone Pairs and Bond Pairs:
- Lone pairs: The central oxygen atom in ozone has two lone pairs.
- Bond pairs: There are three bond pairs between the oxygen atoms in the ozone molecule.
Step 4: Find the Ratio:
The ratio of lone pairs to bond pairs in the ozone molecule is:
Lone pairs : Bond pairs = 2 : 1
Final Answer:
The ratio of lone pairs to bond pairs of electrons in ozone molecule is 2:1.
Approach Solution -2
The correct option is: (A): 2:1.
The ozone molecule (O3) has a bent molecular geometry, and its electronic structure involves both lone pairs of electrons and bond pairs of electrons. The ratio of lone pair electrons to bond pair electrons in the ozone molecule is indeed 2:1. Let's explore the electronic structure of ozone and justify this ratio:
Molecular Geometry: Ozone (O3) has a bent molecular geometry. This means that the three oxygen atoms are not arranged in a straight line; instead, the central oxygen atom is bonded to the other two oxygen atoms, resulting in an angle less than 180 degrees.
Electron Distribution: In the Lewis structure of ozone, each oxygen atom forms a double bond with the central oxygen atom. This leaves a lone pair of electrons on the central oxygen atom.
Lone Pairs of Electrons: The central oxygen atom in the ozone molecule has two lone pairs of electrons. These lone pairs are not involved in any chemical bonding and are located in the regions of space around the oxygen atom where they repel the bonding electron pairs, causing the bent molecular geometry.
Bond Pairs of Electrons: Each oxygen atom in the ozone molecule is involved in two sigma (σ) bonds—one with the central oxygen atom and one with another terminal oxygen atom. These sigma bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals, resulting in a shared pair of electrons.
Top Questions on General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- What is used for the Thermite Reaction?
- BCECE - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- In the extraction of iron using blast furnace to remove the impurity (X), chemical (Y) is added to the ore. X and Y are respectively
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Which of the following compounds is used to cover the surface of a metallic object to prevent corrosion?
- KEAM - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- The incorrect statement about the Hall-Heroult process is:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Select the correct statement:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Questions Asked in TS EAMCET exam
- A body is projected vertically upward with an initial velocity of 40 m/s. Calculate the maximum height reached by the body. (Take \( g = 9.8 \, \text{m/s}^2 \))
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Kinematics
- The properties required for a material to be used as the core of an electromagnet are:
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Magnetism and matter
- Which of the following statements are correct?
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Colligative Properties
- At 27$^\circ$C, 100 mL of 0.05 M Cu$^{2+}$ solution is added to 1 L of 0.1 M KI. Find [KI] in resultant solution.
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Stoichiometry and Stoichiometric Calculations
- 4.0 g of a mixture containing Na₂CO₃ and NaHCO₃ is heated to 673K. Loss in mass of the mixture is found to be 0.62g. The percentage of sodium carbonate in the mixture is
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Stoichiometry and Stoichiometric Calculations
Concepts Used:
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
What are Ores and Minerals?
Minerals are the naturally occurring, homogeneous inorganic solid substances. They are having a definite chemical composition and crystalline structure, hardness and color. For example, copper pyrite, calamine, etc.
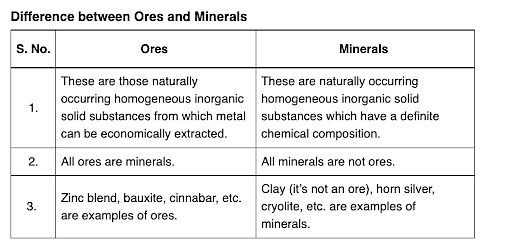
Impurities in an ore are called gauge. The removal of a gauge from the ore is called concentration ore.
Several steps are involved in the extraction of pure metal from ores. Major steps are as follows –
- Concentration of the ore
- Isolation of the metal from its concentrated ore
- Purification of the metal