The function of potassium ethyl xanthate in froth floatation process is to make the ore
- attracted towards water
- water repellant
- lighter
- heavier
The Correct Option is B
Approach Solution - 1
Potassium ethylxanthate is used as a collector in the froth flotation process. It is used to make the ore particles hydrophobic. By making the ore particles hydrophobic, they are more likely to attach to the bubbles in the flotation tank, allowing the desired ore to float to the surface, where it can be separated from other materials. In this context, the term "lighter" is used to describe the ore's ability to float. The ore becomes more buoyant in the flotation medium due to its hydrophobic properties.
Thus, the function of potassium ethylxanthate is to make the ore lighter.
Approach Solution -2
In the froth flotation process, potassium ethylxanthate is used as a collector. It selectively binds to the desired minerals (often sulfides), making them hydrophobic. This hydrophobicity allows the ore particles to attach to air bubbles and float to the surface, where they can be separated. The key function of potassium ethylxanthate is to make the ore lighter and hydrophobic so that it can be separated effectively from other components.
Thus, the function of potassium ethylxanthate is to make the ore \(\textbf{lighter}\).
Top Questions on General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- What is used for the Thermite Reaction?
- BCECE - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- In the extraction of iron using blast furnace to remove the impurity (X), chemical (Y) is added to the ore. X and Y are respectively
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Which of the following compounds is used to cover the surface of a metallic object to prevent corrosion?
- KEAM - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- The incorrect statement about the Hall-Heroult process is:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Select the correct statement:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Questions Asked in KCET exam
Match the following:
In the following, \( [x] \) denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to \( x \).
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- If \[ y = \frac{\cos x}{1 + \sin x} \] then:
- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- A function \( f(x) \) is given by:
\[ f(x) = \begin{cases} \frac{1}{e^x - 1}, & \text{if } x \neq 0 \\ \frac{1}{e^x + 1}, & \text{if } x = 0 \end{cases} \] Then, which of the following is true?- KCET - 2025
- Limits
- The function f(x) is given by:
For x < 0:
f(x) = ex + axFor x ≥ 0:
f(x) = b(x - 1)2
The function is differentiable at x = 0. Then,- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- The function \( f(x) = \tan x - x \)
- KCET - 2025
- Derivatives
Concepts Used:
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
What are Ores and Minerals?
Minerals are the naturally occurring, homogeneous inorganic solid substances. They are having a definite chemical composition and crystalline structure, hardness and color. For example, copper pyrite, calamine, etc.
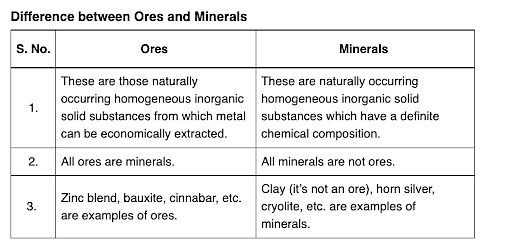
Impurities in an ore are called gauge. The removal of a gauge from the ore is called concentration ore.
Several steps are involved in the extraction of pure metal from ores. Major steps are as follows –
- Concentration of the ore
- Isolation of the metal from its concentrated ore
- Purification of the metal