The formula of a metal oxide is M0.96 O1. The fractions of metal that exists as M3+and M2+ ions in that oxide are respectively
The formula of a metal oxide is M0.96 O1. The fractions of metal that exists as M3+and M2+ ions in that oxide are respectively
0.083, 0.916
0.916, 0.083
0.88,0.12
0.12, 0.88
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
To solve the problem, we need to find the fractions of metal existing as $M^{3+}$ and $M^{2+}$ in the oxide with the formula $M_{0.96}O_1$.
1. Understand the oxidation states and formula:
Let the number of moles of $M^{3+}$ be $x$, and that of $M^{2+}$ be $(0.96 - x)$. The total negative charge from 1 mole of oxygen atoms (as $O^{2-}$) is -2. For the compound to be neutral, the total positive charge must also be +2.
2. Set up the equation for charge neutrality:
$3x + 2(0.96 - x) = 2$
Simplifying:
$3x + 1.92 - 2x = 2$
$x + 1.92 = 2$
$x = 2 - 1.92 = 0.08$
3. Find the fractions:
Fraction of $M^{3+} = \frac{0.08}{0.96} = 0.083$
Fraction of $M^{2+} = \frac{0.88}{0.96} = 0.916$
Final Answer:
The fractions of metal that exist as $M^{3+}$ and $M^{2+}$ are 0.083 and 0.916 respectively.
Top Questions on General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- What is used for the Thermite Reaction?
- BCECE - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- In the extraction of iron using blast furnace to remove the impurity (X), chemical (Y) is added to the ore. X and Y are respectively
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Which of the following compounds is used to cover the surface of a metallic object to prevent corrosion?
- KEAM - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- The incorrect statement about the Hall-Heroult process is:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Select the correct statement:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Questions Asked in TS EAMCET exam
- A body is projected vertically upward with an initial velocity of 40 m/s. Calculate the maximum height reached by the body. (Take \( g = 9.8 \, \text{m/s}^2 \))
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Kinematics
- The properties required for a material to be used as the core of an electromagnet are:
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Magnetism and matter
- Which of the following statements are correct?
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Colligative Properties
- At 27$^\circ$C, 100 mL of 0.05 M Cu$^{2+}$ solution is added to 1 L of 0.1 M KI. Find [KI] in resultant solution.
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Stoichiometry and Stoichiometric Calculations
- 4.0 g of a mixture containing Na₂CO₃ and NaHCO₃ is heated to 673K. Loss in mass of the mixture is found to be 0.62g. The percentage of sodium carbonate in the mixture is
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Stoichiometry and Stoichiometric Calculations
Concepts Used:
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
What are Ores and Minerals?
Minerals are the naturally occurring, homogeneous inorganic solid substances. They are having a definite chemical composition and crystalline structure, hardness and color. For example, copper pyrite, calamine, etc.
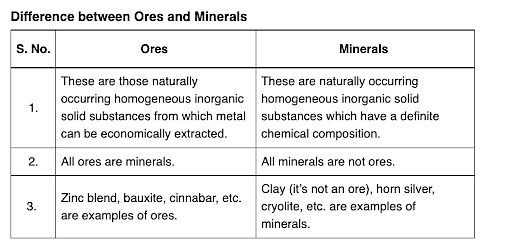
Impurities in an ore are called gauge. The removal of a gauge from the ore is called concentration ore.
Several steps are involved in the extraction of pure metal from ores. Major steps are as follows –
- Concentration of the ore
- Isolation of the metal from its concentrated ore
- Purification of the metal