Pyramid of numbers in a pond ecosystem is
Show Hint
The pyramid of numbers in a pond ecosystem is always upright. It represents the number of individual organisms at each level.
- irregular
- inverted
- upright
- spindle shaped.
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
The pyramid of numbers in a pond ecosystem is always upright. It represents the number of individual organisms at each level.
- In a pond, the producers (mainly phytoplanktons) are always the maximum in number.
- This number then shows a decrease towards the apex, primary consumers are lesser in number than the grasses.
- The secondary consumers are lesser in number than the primary consumers.
- Finally, the top consumers are the least in number. Thus, the pyramid becomes upright.
Alternate Approach
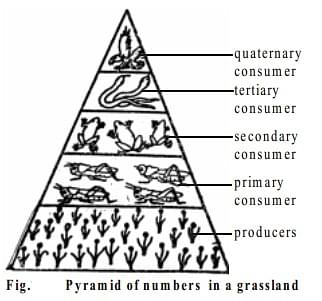
The number pyramid is also present in the grassland ecosystem. In this pyramid type, the number of consumers is also less than the number of producers.
Complete answer:
A pond ecosystem refers to a freshwater ecosystem where populations of species rely on each other for their nutrition and survival in the prevalent water climate.
- A pond is a calm water body that is too shallow for large temperature variations and too small for tidal activity.
- It typically has a dirty bottom having aquatic vegetation along the sides.
- A pond ecosystem contains abiotic components like light, temperature, carbon dioxide, dissolved oxygen, etc. and biotic components consisting of producers, consumers and decomposers.
- The producers including phytoplanktons, hydrilla, etc. are the green plants.
- The consumers are those heterotrophic organisms that consume producers.
- Some of the consumers in the ecosystem of the pond include insects, frogs, fishes, crabs, etc.
- Most decomposers of the pond ecosystem are saprophytes but some parasites are also found.
The number pyramid is a graphic representation that indicates the number of species at each trophic stage. It is an upright pyramid as in the ecosystem, producers are generally more abundant than the other trophic stages. The upright pyramid is located in the grassland ecosystem. This ecosystem is identified by autotrophs supporting smaller herbivores. In contrast, herbivores assist a reduced number of carnivores. This pyramid is also upright.
- The pond ecosystem reflects an upright pyramid of numbers.
- Phytoplankton, including algae and bacteria, are the producers here and thus the largest in number.
- The smaller herbivorous fish are fewer than the producers.
- Likewise, small carnivorous fish are less than herbivorous ones.
- Finally, the largest carnivorous fish or the apex consumers are the least counted.
Thus, the correct answer is option C, Upright.
Note: The highest energy in the pond ecosystem is at the producer level, followed by the primary consumer level, followed by the secondary consumer level.
Top Questions on Ecological Succession
- Arrange the following ecological succession in the lithosphere (rocks) from initial to final succession stages
(A) Moss stage
(B) Foliose-lichens stage
(C) Herbaceous stage
(D) Crustose-lichens stage
(E) Shrub stage
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- CUET (UG) - 2025
- Environmental Science
- Ecological Succession
- The species that invades a bare area is referred to as \(\underline{\hspace{2cm}}\).
- CUET (UG) - 2025
- Environmental Science
- Ecological Succession
- Which of the following is a pioneer species in the primary succession of a bare rock?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- Ecological Succession
- Which one of the following statements is wrong regarding ecological pyramids?
- CUET (UG) - 2024
- Biology
- Ecological Succession
- The sequence of communities of primary succession in water is:
(A) Phytoplanktons → Scrubs → Free floating hydrophytes → Rooted hydrophytes → Grasses → Trees.
(B) Phytoplanktons → Free floating hydrophytes → Rooted hydrophytes → Trees → Scrubs.
(C) Free floating hydrophytes → Scrubs → Phytoplanktons → Rooted hydrophytes → Grasses → Trees.
(D) Phytoplanktons → Rooted hydrophytes → Free floating hydrophytes → Reed swamps → Marsh meadows → Scrubs → Trees.- KCET - 2024
- Biology
- Ecological Succession
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- Two cities X and Y are connected by a regular bus service with a bus leaving in either direction every T min. A girl is driving scooty with a speed of 60 km/h in the direction X to Y. She notices that a bus goes past her every 30 minutes in the direction of her motion, and every 10 minutes in the opposite direction. Choose the correct option for the period T of the bus service and the speed (assumed constant) of the buses.
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Relative Velocity
- A physical quantity P is related to four observations a, b, c, and d as follows: P = a3 b2 (c / √d) The percentage errors of measurement in a, b, c, and d are 1%, 3%, 2%, and 4% respectively. The percentage error in the quantity P is:
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Dimensional analysis and its applications
What is Microalbuminuria ?
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Human physiology
The output (Y) of the given logic implementation is similar to the output of an/a …………. gate.

- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Logic gates
- An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litre has 18.20 moles of oxygen. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, its gauge pressure drops to 11 atmospheric pressure at temperature \(27^\circ\)C. The mass of the oxygen withdrawn from the cylinder is nearly equal to: [Given, \(R = \frac{100}{12} \text{ J mol}^{-1} \text{K}^{-1}\), and molecular mass of \(O_2 = 32 \text{ g/mol}\), 1 atm pressure = \(1.01 \times 10^5 \text{ N/m}^2\)]
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Ideal-gas equation and absolute temperature
Concepts Used:
Ecological Succession
Ecological succession is the steady and moderate change in a species of a given area with respect to the changing environment. Our nature consists of both biotic and abiotic factors. When these biotic and abiotic factors interact with each other to develop natural communities they give rise to such successions.
Ecological Succession:
When land is left on its own for years, it starts being occupied by microorganisms followed by wild shrubs and other large plants, which gives rise to a new ecosystem. The series of stages is quite predictable and inescapable. In order to understand the primary and secondary succession, we need to be very much clear about what ecological succession is as they are its types. This succession mainly focuses to bring about equilibrium in the ecosystem. When the target is achieved, it is called a climax community.
The number of species to survive is then decided based on achieving the equilibrium. In a community, these changes happen in a sequence, and such a community is known as a seral community which further is an intermediate stage of ecological succession advancing towards the climax community. All the succession begins with an instigating species. The instigate species or the first species build an initial biological community that is simpler in form. The initiation of this ecological succession separates it into the following three types –
- Primary succession
- Secondary succession
- Cyclic Succession