Question:
"Omnis-cellula-e-cellula" was given by
"Omnis-cellula-e-cellula" was given by
Updated On: Aug 15, 2022
- Virchow
- Hooke
- Leeuwenhoek
- Brown
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
Rudolf Virchow was the first to suggest that new cells are formed from the division of the pre-existing cells - onnris-cellulci-e-cellula (every cell is derived from a cell). Robert Hooke was the first to coin the term "cell" or small structures in a piece of cork under a microscope. His observations were published in a book named micrographia, Leeuwenhoek was the first person to observe and describe microscopic organisms and living cell. He observed nucleus in RBC of salmon fish and used simple lens and observed nuclei and unicellular organisms including bacteria. In 1676, he described the bacteria and gave the term animalcules. His observations laid the foundations for the science of bacteriology and microbiology. Robert Brown (1831) described and named nucleus.
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on Cell: the unit of life
- Which organelle in a eukaryotic cell is primarily responsible for synthesizing proteins destined for secretion?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- Cell: the unit of life
- Which organelle is primarily responsible for producing ATP in a cell?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- Cell: the unit of life
- Which of the following organisms or organelles contain 70S ribosomes?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- Cell: the unit of life
- What is the movement of cytoplasm within a cell called?
- MHT CET - 2024
- Biology
- Cell: the unit of life
- Given below are two statements: Statement I: Cell wall is freely permeable.
Statement II: Plasma membrane is selectively permeable.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below with reference to the structure of root hair:- MHT CET - 2024
- Biology
- Cell: the unit of life
View More Questions
Questions Asked in AIIMS exam
- The element Neodymium (Nd) belongs to the 4f series. What is its atomic number?
- AIIMS - 2024
- Modern Periodic Law And The Present Form Of The Periodic Table
- The correct increasing order of energy of orbitals in a hydrogen atom is:
- AIIMS - 2024
- Atomic Structure
- Which of the following is a globular protein?
- AIIMS - 2024
- Biomolecules
- Given that the surface charge density on a sphere is 200 μC/m2, what is the electric field at the surface of the sphere?
- AIIMS - 2024
- Electrostatics
- Which of the following is a crystalline solid?
- AIIMS - 2024
- The solid state
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
Cell: The Unit of Life
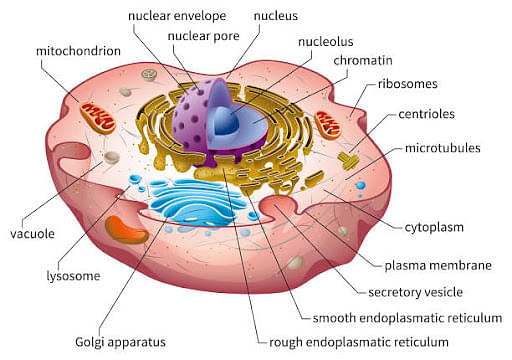
- A cell is derived as the functional and structural unit of life. Every cell is surrounded by a cell membrane that dissects the external and internal environments of the cell. The interior environment of a cell is called the cytoplasm.
- It carries cellular machinery and structural elements. The nucleus is present in the center of the cell, which includes all the hereditary information of an organism. Some of the molecules present in the cell are protein, carbohydrates, starch, and sugar.
Read More: Fundamental Unit of Life: Cell
Parts of Cell:
The different parts of a cell and their functions are as follows:
- Cell Membrane
- Cell Wall
- Nucleus
- Cytoplasm