Life cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is:
- Haplontic
- Diplontic
- Haplodiplontic
- None of the above
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
- The “baker’s yeast,” or Saccharomyces cerevisiae, exhibits both haploid as well as diploid lifecycles according to the environment; hence, it is called to have a haplodiplontic lifestyle.
- However, the diploid phase is more common and occurs during normal conditions.
- HAPLOID PHASE: In this phase, yeast cells reproduce asexually through budding. small bud grows out of the parent cell (haploid), differentiates, leaves the parent cell, and then grows into an individual cell.
- This phase is followed only during stressful conditions.
- DIPLOID PHASE: In this phase, two haploid cells of opposite mating types fuse to form one diploid cell.
- After that, it may go through the process of budding or undergo meiosis to produce 4 haploid spores.
So, the correct option is (C): Haplodiplontic.
Top Questions on biological classification
- Which of the following microorganisms is used in the production of curd from milk?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- biological classification
- In a DNA molecule, which of the following base-pairings is correct?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- biological classification
- Which is not a prime element?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- biological classification
- Study the following and choose the incorrect combinations:
I. Phylum: Porifera, Special cells: Lasso cells, Example: Spongilla
II. Phylum: Cnidaria, Special cells: Stinging cells, Example: Hydra
III. Phylum: Ctenophora, Special cells: Choanocytes, Example: Pleurobrachia
IV. Phylum: Platyhelminthes, Special cells: Flame cells, Example: Fasciola- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Zoology
- biological classification
- Study the following and choose the correct combinations:

- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Zoology
- biological classification
Questions Asked in OJEE exam
Consider the following statements: Statement I: \( 5 + 8 = 12 \) or 11 is a prime. Statement II: Sun is a planet or 9 is a prime.
Which of the following is true?
- OJEE - 2025
- Number System
The value of \[ \int \sin(\log x) \, dx + \int \cos(\log x) \, dx \] is equal to
- OJEE - 2025
- Calculus
The value of \[ \lim_{x \to \infty} \left( e^x + e^{-x} - e^x \right) \] is equal to
- OJEE - 2025
- Calculus
- Consider the function
\[ f(x) = \begin{cases} \frac{\log(1+3x) - \log(1-2x)}{x}, & x \neq 0 \\ k, & x = 0 \end{cases} \] If \( f \) is continuous at \( x = 0 \), then the value of \( k \) must be
- OJEE - 2025
- Calculus
- Pick out the most effective word(s) from the given words to fill in the blank to make the sentence meaningfully complete.
The miser gazed ...... at the pile of gold coins in front of him.
- OJEE - 2025
- Grammar
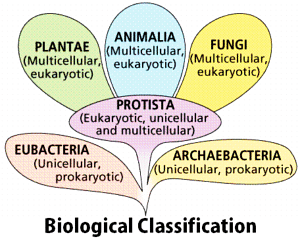
Concepts Used:
Biological Classification
The process of grouping living organisms into categories is called biological classification. The most modern 5-kingdom classification was put ahead by an eminent scientist R.H.Whittaker. The five-kingdom classification is based on the criteria like cell structure, mode of nutrition, body form, and reproduction. One of the most important characteristics of this system is that it follows the evolutionary sequence of living organisms. The organisms are classified into distinct taxa or levels like Kingdom, Phylum, Division, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species. The 5 kingdoms are as follows: