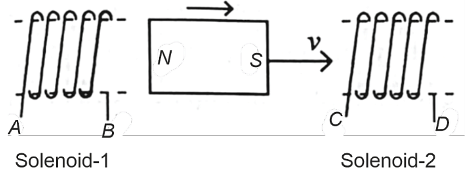
In the above diagram, a strong bar magnet is moving towards solenoid-2 from solenoid-1. The direction of induced current in solenoid-1 and that in solenoid-2, respectively, are through the directions :

In the above diagram, a strong bar magnet is moving towards solenoid-2 from solenoid-1. The direction of induced current in solenoid-1 and that in solenoid-2, respectively, are through the directions :
- AB and DC
- BA and CD
- AB and CD
- BA and DC
The Correct Option is A
Approach Solution - 1
When a strong bar magnet moves towards a solenoid, it induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the solenoid due to electromagnetic induction. The direction of the induced current can be determined using Lenz's Law, which states that the direction of the induced current is always such that it opposes the change in magnetic flux that produced it. Let's analyze the problem step by step:
- As the bar magnet approaches solenoid-1, the magnetic flux linked with solenoid-1 increases. To oppose this increase, the induced current in solenoid-1 will flow in such a direction that its own magnetic field opposes the field of the approaching magnet.
- Using the right-hand rule, if the north pole of the bar magnet is moving towards solenoid-1, the induced current in solenoid-1 will flow in direction AB. This creates an induced magnetic field with its north pole facing the approaching bar magnet.
- Now, consider solenoid-2. As the bar magnet moves away from solenoid-1 and approaches solenoid-2, it causes an increase in magnetic flux linking solenoid-2. Hence, the induced current in solenoid-2 will flow in such a direction that its magnetic field opposes the new incoming magnetic field.
- Using Lenz's Law again, if we apply the right-hand rule to solenoid-2, the induced current in solenoid-2 will flow in direction DC, creating an induced magnetic field with its south pole facing the bar magnet.
Therefore, the correct option is AB and DC, where the induced current in solenoid-1 flows in direction AB and in solenoid-2 flows in direction DC respectively.
Approach Solution -2

Step 1: Use Lenz’s Law
According to Lenz’s law, the induced current always flows in a direction such that it opposes the change in magnetic flux that causes it.
Step 2: Analyze Solenoid-1
As the bar magnet approaches solenoid-1, the magnetic flux increases. To oppose this increase, solenoid-1 generates a magnetic field opposite to the bar magnet’s field, inducing a current in the direction AB.
Step 3: Analyze Solenoid-2
For solenoid-2, the magnetic field due to the approaching bar magnet increases in the direction towards solenoid-1. To oppose this, solenoid-2 generates a magnetic field pointing away, inducing a current in the direction DC.
Top Questions on Solenoids and Toroids
- The magnitude of magnetic field inside a solenoid of length 0.3 m having 800 turns carrying a current of 6 A is
- CUET (UG) - 2025
- Physics
- Solenoids and Toroids
- The self-inductance of a solenoid depends on
- Bihar Board XII - 2025
- Physics
- Solenoids and Toroids
- The direction of magnetic field inside a current carrying solenoid is
- Bihar Board XII - 2025
- Physics
- Solenoids and Toroids
- (i) State any two factors on which the strength of magnetic field produced by a current-carrying solenoid depends.
- UP Board X - 2025
- Science
- Solenoids and Toroids
- (i) Draw magnetic lines of force due to a current carrying solenoid.
- UP Board X - 2025
- Science
- Solenoids and Toroids
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- Two cities X and Y are connected by a regular bus service with a bus leaving in either direction every T min. A girl is driving scooty with a speed of 60 km/h in the direction X to Y. She notices that a bus goes past her every 30 minutes in the direction of her motion, and every 10 minutes in the opposite direction. Choose the correct option for the period T of the bus service and the speed (assumed constant) of the buses.
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Relative Velocity
- A physical quantity P is related to four observations a, b, c, and d as follows: P = a3 b2 (c / √d) The percentage errors of measurement in a, b, c, and d are 1%, 3%, 2%, and 4% respectively. The percentage error in the quantity P is:
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Dimensional analysis and its applications
What is Microalbuminuria ?
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Human physiology
The output (Y) of the given logic implementation is similar to the output of an/a …………. gate.

- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Logic gates
- An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litre has 18.20 moles of oxygen. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, its gauge pressure drops to 11 atmospheric pressure at temperature \(27^\circ\)C. The mass of the oxygen withdrawn from the cylinder is nearly equal to: [Given, \(R = \frac{100}{12} \text{ J mol}^{-1} \text{K}^{-1}\), and molecular mass of \(O_2 = 32 \text{ g/mol}\), 1 atm pressure = \(1.01 \times 10^5 \text{ N/m}^2\)]
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Ideal-gas equation and absolute temperature