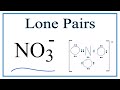
In $NO_3^-$ ion number of bond pair and lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom are :-
- 2,2
- 3,1
- 1,3
- 4,0
The Correct Option is D
Approach Solution - 1
In \(NO_3^-\) ion number of bond pair and lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom can be calculated as:

In the structure, there are 2σ, 1π, and one coordinate bond. The coordinate bond is theoretically equal to a double bond, but it behaves differently when an incoming ion approaches.
- A covalent bond type in which both electrons originate from the same atom is known as a coordinate bond, also known as a dative covalent bond.
- Since nitrogen cannot have five bonds, it joins with oxygen to create a coordinate bond.
- The number of bond pairs is assumed to be 1, despite the fact that coordinate bonds share two electrons.
- As a result, there are four bond pairs and no lone pairings.
Discover more from this topic: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Approach Solution -2
The Correct Answer is (D)
Real Life Applications
The real-life application includes:
- Use of nitrate ion in table salt.

- The fertilizers also includes nitrate ion on it.
- The use of these nitrate ions as explosives.
- In the case of food coloring also this has been used.

Question can also be asked as
- What is the valency electron of N atom ?
- What are the caveats of using excess nitrate as fertilizer?
- What is the role of nitrate ion with respect to plant roots?
- The role of nitrate ion in day to day life?
Approach Solution -3
A compound bond is the attraction force that keeps various constituents (atoms, particles, and so on) together in various synthetic species. An atom is bound to another by an atomic bond so that a particle can take shape. Then, a substance ties molecules together. With the aid of electron pairs between molecules, G N Lewis was the first to describe this phenomenon. He demonstrated Lewis' dot structure, which shows a compound holding between atom-sized particles.
Lone Pair
A lone pair, also known as a non-bonding pair, is a pair of valence electrons that are not shared with another atom. (They don't participate in sharing). Atoms' outermost electron shell contains lone pairs.
- Each atom shares an electron when two atoms join together to create a bond.
- The electrons involved in this relationship are referred to as the bond pairs of electrons.
- Example: All four hydrogen atoms in the methane molecule join with a central carbon atom to create a bond pair.
Bond Pair
Each atom shares an electron when two atoms join together to create a bond.
The electrons involved in this relationship are referred to as the bond pairs of electrons.
Example: All four hydrogen atoms in the methane molecule join with a central carbon atom to create a bond pair.
Learn with videos:
Top Questions on Chemical bonding and molecular structure
From the given following (A to D) cyclic structures, those which will not react with Tollen's reagent are :

- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure
- The wave numbers of three spectral lines of hydrogen atom are considered. Identify the set of spectral lines belonging to the {Balmer series. (\(R\) = Rydberg constant)}
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure
- Consider the reaction: \[ \text{Ph–CH=CH}_2 \xrightarrow[\text{peroxide}]{\text{HBr}} \text{Product} \] Which of the following statements are correct?
[A.] The reaction proceeds through a more stable radical intermediate.
[B.] The role of peroxide is to generate \(\mathrm{H^\bullet}\) radical.
[C.] During this reaction, benzene is formed as a byproduct.
[D.] \(1\)-Bromo-\(2\)-phenylethane is formed as a minor product.
[E.] The same reaction in absence of peroxide proceeds via a carbocation intermediate. Choose the correct answer.- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure
Compound 'P' undergoes the following sequence of reactions : (i) NH₃ (ii) $\Delta$ $\rightarrow$ Q (i) KOH, Br₂ (ii) CHCl₃, KOH (alc), $\Delta$ $\rightarrow$ NC-CH₃. 'P' is :


- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure
- Given below are two statements :
Statement I : The correct order in terms of bond dissociation enthalpy is \( Cl_2>Br_2>F_2>I_2 \).
Statement II : The correct trend in the covalent character of the metal halides is \( SnCl_2>SnCl_4 \), \( PbCl_2>PbCl_4 \) and \( UF_4>UF_6 \).
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below :- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Chemical bonding and molecular structure
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- Two cities X and Y are connected by a regular bus service with a bus leaving in either direction every T min. A girl is driving scooty with a speed of 60 km/h in the direction X to Y. She notices that a bus goes past her every 30 minutes in the direction of her motion, and every 10 minutes in the opposite direction. Choose the correct option for the period T of the bus service and the speed (assumed constant) of the buses.
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Relative Velocity
- A physical quantity P is related to four observations a, b, c, and d as follows: P = a3 b2 (c / √d) The percentage errors of measurement in a, b, c, and d are 1%, 3%, 2%, and 4% respectively. The percentage error in the quantity P is:
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Dimensional analysis and its applications
What is Microalbuminuria ?
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Human physiology
The output (Y) of the given logic implementation is similar to the output of an/a …………. gate.

- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Logic gates
- An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litre has 18.20 moles of oxygen. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, its gauge pressure drops to 11 atmospheric pressure at temperature \(27^\circ\)C. The mass of the oxygen withdrawn from the cylinder is nearly equal to: [Given, \(R = \frac{100}{12} \text{ J mol}^{-1} \text{K}^{-1}\), and molecular mass of \(O_2 = 32 \text{ g/mol}\), 1 atm pressure = \(1.01 \times 10^5 \text{ N/m}^2\)]
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Ideal-gas equation and absolute temperature
Concepts Used:
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Such a group of atoms is called a molecule. Obviously, there must be some force that holds these constituent atoms together in the molecules. The attractive force which holds various constituents (atoms, ions, etc.) together in different chemical species is called a chemical bond.
Types of Chemical Bonds:
There are 4 types of chemical bonds which are formed by atoms or molecules to yield compounds.
- Ionic Bonds - Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding which involves a transfer of electrons from one atom or molecule to another.
- Covalent Bonds - Compounds that contain carbon commonly exhibit this type of chemical bonding.
- Hydrogen Bonds - It is a type of polar covalent bonding between oxygen and hydrogen wherein the hydrogen develops a partial positive charge
- Polar Bonds - In Polar Covalent chemical bonding, electrons are shared unequally since the more electronegative atom pulls the electron pair closer to itself and away from the less electronegative atom.
Factors Affecting Bond Enthalpy in Chemical Bonding:
- Size of the Atom
- Multiplicity of Bonds
- Number of Lone Pair of Electrons Present
- Bond Angle