Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its function.
Approach Solution - 1
Functions of the three parts of a neuron:
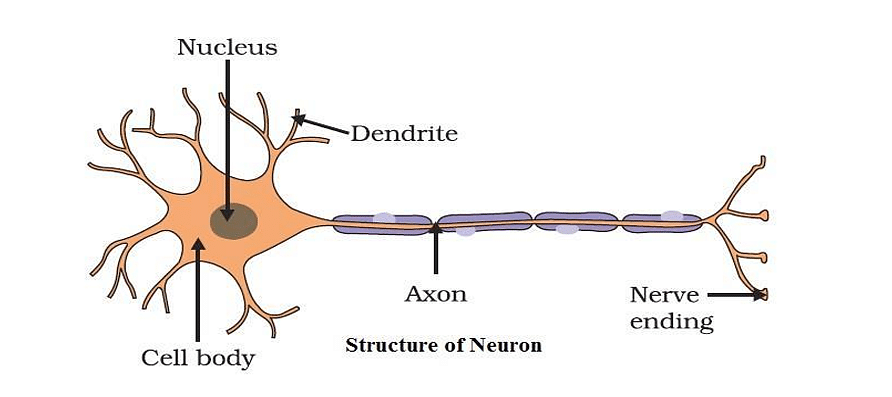
→ Axon: It conducts messages away from the cell body.
→ Dendrite: It receives information from axon of another cell and conducts the messages towards the cell body.
→ Cell body: It contains nucleus, mitochondria, and other organelles. It is mainly concerned with the maintenance and growth.
Approach Solution -2

A neuron, or nerve cell, is the basic building block of the nervous system. It consists of three main parts: the cell body (soma), dendrites, and an axon.
1. Cell Body (Soma): This is the central part of the neuron containing the nucleus. It maintains the cell's health and carries genetic information.
2. Dendrites: These are branch-like structures that receive messages from other neurons and conduct the information towards the cell body. They act like antennas, picking up signals from other neurons.
3. Axon: This is a long, slender projection that conducts electrical impulses away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands. The axon ends in terminal branches, which release neurotransmitters to transmit the signal to the next neuron.
Function of a Neuron:
- Neurons transmit information throughout the nervous system via electrical and chemical signals.
- The dendrites receive incoming signals from other neurons.
- These signals are processed in the cell body.
- If the signal is strong enough, it generates an electrical impulse that travels down the axon.
- The impulse reaches the axon terminals, where neurotransmitters are released to carry the signal to the next neuron or target cell.
This process enables the brain and nervous system to communicate and coordinate various functions throughout the body.
Top Questions on Animals – Nervous System
- Blood is
- Bihar Board X - 2025
- Science
- Animals – Nervous System
- The embryos of which one or more of the following animals show meroblastic cleavage?
- GATE XL - 2024
- Zoology
- Animals – Nervous System
- Which one of the following describes the “innate behavior” of an animal?
- GATE XL - 2023
- Zoology
- Animals – Nervous System
- Which one of the following animals has “Book Lungs” as a respiratory organ?
- GATE XL - 2023
- Zoology
- Animals – Nervous System
- What is the difference between the manner in which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and the movement in our legs?
- CBSE Class X
- Science
- Animals – Nervous System
Questions Asked in CBSE X exam
Leaves of the sensitive plant move very quickly in response to ‘touch’. How is this stimulus of touch communicated and explain how the movement takes place?
- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Plant Biology
- Rama is a farmer. She needs loan for agriculture work. Which of the following sources of loan will be beneficial for Rama? Choose the most appropriate option:
I. Bank
II. Agricultural Trader
III. Self-Help Group
IV. Government- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Money and Credit
Read the following sources of loan carefully and choose the correct option related to formal sources of credit:
(i) Commercial Bank
(ii) Landlords
(iii) Government
(iv) Money Lende- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Money and Credit
- Two statements are given below. They are Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read both the statements carefully and choose the correct option. Assertion (A): Rupees is accepted as medium of exchange in India.
Reason (R): The World Bank legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment in India.- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Money and Credit
- Rama is a farmer. She needs loan for agriculture work. Which of the following sources of loan will be beneficial for Rama? Choose the most appropriate option. I. Bank
II. Agricultural Trader
III. Self-Help Group
IV. Government- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Money and Credit
Concepts Used:
Human Nervous System
The human nervous system is responsible for controlling and coordinating all the activities of the human body.
The three major functions of the human nervous system are:
- Gathering or assembling sensory information from the body and external environment.
- Processing and interpreting the sensory information acquired.
- Conveying or transferring appropriate response to the sensory information acquired.
The nervous system is mainly divided into two, namely:
The Central Nervous System (CNS) comprises the brain and spinal cord.
- The brain is majorly involved in the perception and processing of sensory input. It also regulates or manages voluntary motor responses and homeostatic mechanisms.
- The spinal cord act as a pathway for the transmission of information between the brain and the peripheral nervous system. It also takes action on reflex actions.
The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) comprises sensory/motor neurons and ganglion.
Nervous System
The nervous system, often known as the neural system, is a sophisticated network of neurons dedicated to the transmission of messages. As we progress up the food chain, the neurological system becomes more sophisticated.

Functions of Nervous System:
The nervous system's most basic job is to govern the organism's movement and to influence the environment (e.g., through pheromones). This is accomplished by transmitting signals from one cell to another, or from one body component to another. Signals that travel to muscle cells cause muscles to contract, and signals that travel to endocrine cells cause hormones to be released into the circulation or other internal fluids to cause the nervous system's output.