Differentiate between :
(a) Racemose and cymose inflorescence
(b) Apocarpous and syncarpous ovary
(a) Racemose and cymose inflorescence
(b) Apocarpous and syncarpous ovary
Solution and Explanation
(a) Racemose inflorescence and Cymose inflorescence:
| Racemose inflorescence | Cymose inflorescence |
|---|---|
| Younger flowers are present at the tip while older flowers are arranged at the base of this inflorescence. Such an arrangement is called acropetal succession. | Younger flowers are present at the base of the inflorescence, while older flowers are present at the top. Such an arrangement is called basipetal succession. |
| The main axis in racemose inflorescence continues to grow and produce flowers laterally. | The main axis in cymose inflorescence has limited growth, which later terminates into a flower. |
(b) Apocarpous and syncarpous ovary:
| Apocarpous | syncarpous ovary |
|---|---|
| The flowers with apocarpus ovary have more than one carpel. These carpels are free. | The flowers with syncarpous ovary have more than one carpel. However, these carpels are fused. |
| It is found in lotus and rose flowers. | It is found in the flowers of tomato and mustard. |
Top Questions on The Inflorescence
- In a cymose type of inflorescence, the growth of the main axis terminates in a:
- UPSEE - 2016
- Biology
- The Inflorescence
- The inflorescence found in banana is
- UP CPMT - 2015
- Biology
- The Inflorescence
- The partial floral formula of a flower is $K_{\left(5\right)} C_{5}A_{\left(\infty\right)} \frac{G_{5}}{ }$ Which f the following set of information is conveyed here?
- WBJEE - 2014
- Biology
- The Inflorescence
- The inflorescence in which sessile flowers are borne acropetally on an elongated rachis, it is called
- AMUEEE - 2014
- Biology
- The Inflorescence
- Which one of the following is correct explanation for the floral formula $\quad\quad\% \Theta K_{\left(5\right)} C_{1+2+\left(2\right)}A_{\left(9\right)+1 }G_{1}$
- KEAM - 2013
- Biology
- The Inflorescence
Questions Asked in CBSE Class XI exam
- Balance the following redox reactions by ion-electron method:
(a)MnO4- (aq) + I - (aq) → MnO2(s) + I2(s) (in basic medium)
(b) MnO4- (aq) + SO2(g) → Mn2+(aq) +HSO4- (aq) (in acidic solution)
(c) H2O2(aq)+Fe2+(aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + H2O (l) (in acidic solution)
(d) Cr2O72-+ SO2(g) → Cr3+ (aq) +SO42- (aq) (in acidic solution)- CBSE Class XI
- Oxidation Number
- Write the resonance structures for SO3 , NO2 and NO3-
- CBSE Class XI
- Kossel-Lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding
- At 700 K, equilibrium constant for the reaction:
\(H_2 (g) + I_2 (g) ⇋ 2HI (g)\)
is 54.8. If 0.5 mol L–1 of HI(g) is present at equilibrium at 700 K, what are the concentration of H2(g) and I2(g) assuming that we initially started with HI(g) and allowed it to reach equilibrium at 700 K?- CBSE Class XI
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
- Find the mean deviation about the mean for the data 4, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 17.
- CBSE Class XI
- Statistics
Find the mean deviation about the mean for the data 38, 70, 48, 40, 42, 55, 63, 46, 54, 44.
- CBSE Class XI
- Statistics
Concepts Used:
Inflorescence
The term inflorescence comes under the method morphology of flowering plants. The Morphology of flowering plants is the study of different parts of the plants, which includes the leaves, flowers, fruits, and stems. In a plant, the flowers either grow individually or in a set of groups, and the groups of flowers are referred to as inflorescence.
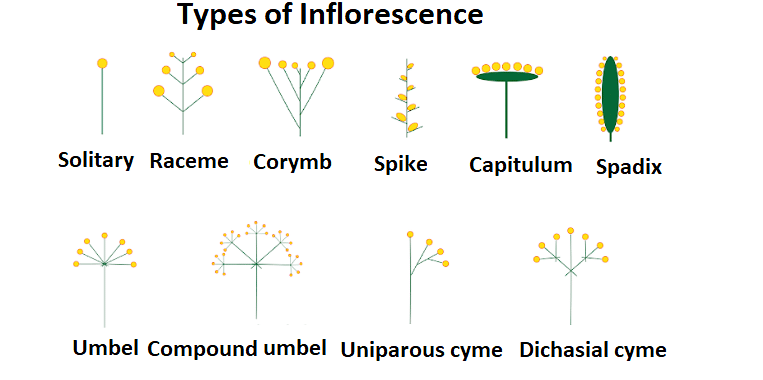
Inflorescence can also be referred to as the reproductive part of a plant that contains a group of flowers. It is responsible for the positioning of flowers on the floral axis and it is divided into two categories: racemose inflorescence and cymose inflorescence. In the racemose inflorescence, the main axis keeps on growing and the flower develops itself in an acropetal pattern while in the cymose inflorescence the termination of the main axis takes place and the flower grows in a basipetal pattern.