Archaebacteria differ from eubacteria in
Show Hint
Archaebacteria have different cell membrane structures than other bacteria. The lipids in archaebacteria cell membranes are ether-linked compared to ester-linked in other bacteria. Archaebacteria are similar to bacteria in morphology, structure, shape, mode of reproduction, and nutrition.
- cell membrane structure
- mode of nutrition
- cell shape
- mode of reproduction.
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
Archaebacteria differ from eubacteria in cell membrane structure.
The archaebacteria are considered to be the 'ancient' bacteria that comprise extremophiles like methanogens, halophiles, and thermophiles. They represent some of the most ancient life forms that continue to exist today. Generally, archaebacteria have the same shape, size, nutrition, and appearance as bacteria. They multiply by the means of binary fission.
However, archaebacteria cell walls lack peptidoglycan. They also have different membrane lipid bonds in comparison to bacteria and eukarya. Archea membrane lipids have ether bonds whereas bacteria have ester-linked lipids.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A.
Top Questions on biological classification
- Which of the following microorganisms is used in the production of curd from milk?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- biological classification
- In a DNA molecule, which of the following base-pairings is correct?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- biological classification
- Which is not a prime element?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- biological classification
- Study the following and choose the incorrect combinations:
I. Phylum: Porifera, Special cells: Lasso cells, Example: Spongilla
II. Phylum: Cnidaria, Special cells: Stinging cells, Example: Hydra
III. Phylum: Ctenophora, Special cells: Choanocytes, Example: Pleurobrachia
IV. Phylum: Platyhelminthes, Special cells: Flame cells, Example: Fasciola- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Zoology
- biological classification
- Study the following and choose the correct combinations:

- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Zoology
- biological classification
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- Two cities X and Y are connected by a regular bus service with a bus leaving in either direction every T min. A girl is driving scooty with a speed of 60 km/h in the direction X to Y. She notices that a bus goes past her every 30 minutes in the direction of her motion, and every 10 minutes in the opposite direction. Choose the correct option for the period T of the bus service and the speed (assumed constant) of the buses.
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Relative Velocity
- A physical quantity P is related to four observations a, b, c, and d as follows: P = a3 b2 (c / √d) The percentage errors of measurement in a, b, c, and d are 1%, 3%, 2%, and 4% respectively. The percentage error in the quantity P is:
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Dimensional analysis and its applications
What is Microalbuminuria ?
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Human physiology
The output (Y) of the given logic implementation is similar to the output of an/a …………. gate.

- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Logic gates
- An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litre has 18.20 moles of oxygen. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, its gauge pressure drops to 11 atmospheric pressure at temperature \(27^\circ\)C. The mass of the oxygen withdrawn from the cylinder is nearly equal to: [Given, \(R = \frac{100}{12} \text{ J mol}^{-1} \text{K}^{-1}\), and molecular mass of \(O_2 = 32 \text{ g/mol}\), 1 atm pressure = \(1.01 \times 10^5 \text{ N/m}^2\)]
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Ideal-gas equation and absolute temperature
Concepts Used:
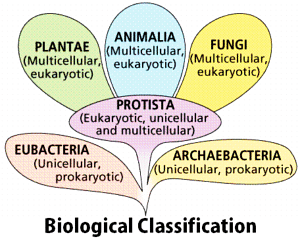
Biological Classification
The process of grouping living organisms into categories is called biological classification. The most modern 5-kingdom classification was put ahead by an eminent scientist R.H.Whittaker. The five-kingdom classification is based on the criteria like cell structure, mode of nutrition, body form, and reproduction. One of the most important characteristics of this system is that it follows the evolutionary sequence of living organisms. The organisms are classified into distinct taxa or levels like Kingdom, Phylum, Division, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species. The 5 kingdoms are as follows: