An object 5.0 cm in length is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. Find the position of the image, its nature and size.
Solution and Explanation
Object distance, \(u = −20\ cm \)
Object height, \(h = 5\ cm\)
Radius of curvature, \(R = 30\ cm \)
Radius of curvature \(= 2 × \text {Focal length}\)
\(R = 2f \)
\(f = 15\ cm \)
According to the mirror formula,
\(\frac 1v+\frac 1u=\frac 1f\)
\(\frac 1v=\frac 1f-\frac 1u\)
\(\frac 1v=\frac {1}{15}+\frac {1}{20}\)
\(\frac 1v=\frac {4+3}{60}\)
\(\frac 1v=\frac {7}{60}\)
\(v= 8.57\)
The positive value of v indicates that the image is formed behind the mirror.
Magnfication, \(m=-\frac {\text {Image\ distance}}{\text{Object\ distance}}\)
\(m =-\frac {8.57}{-20}\)
\(m=0.428\)
The positive value of magnification indicates that the image is formed is virtual.
Magnfication, \(m=-\frac {\text {Height \ of the \ Image}}{\text{Height \ of the \ Object}}\)
\(m = \frac {h'}{h}\)
\(h'=m \times h\)
\(h' =0.428 \times 5\)
\(h'=2.14\ cm\)
The positive value of image height indicates that the image formed is erect.
Therefore, the image formed is virtual, erect, and smaller in size.
Top Questions on Spherical Mirrors
- A concave mirror produces an image of an object such that the distance between the object and image is 20 cm. If the magnification of the image is \( -3 \), then the magnitude of the radius of curvature of the mirror is:
- JEE Main - 2025
- Physics
- Spherical Mirrors
- (ii) An object at a distance of 16 cm from a spherical mirror forms a virtual image at a distance of 12 cm behind the mirror. Determine the magnification of the image and type of the mirror.
- UP Board X - 2025
- Science
- Spherical Mirrors
- Image of an object formed by a concave mirror is real and of the size of the object. The object is placed -
- UP Board X - 2025
- Science
- Spherical Mirrors
- With the help of a suitable ray diagram, derive the formula \( \frac{1}{v} + \frac{1}{u} = \frac{1}{f} \) for a concave mirror.
- UP Board XII - 2025
- Physics
- Spherical Mirrors
- The length of the image formed by a concave mirror:
- UP Board XII - 2025
- Physics
- Spherical Mirrors
Questions Asked in CBSE X exam
- Find 'mean' and 'mode' of the following data : Frequency Distribution Table
Class 0 – 15 15 – 30 30 – 45 45 – 60 60 – 75 75 – 90 Frequency 11 8 15 7 10 9 - CBSE Class X - 2025
- Statistics
Leaves of the sensitive plant move very quickly in response to ‘touch’. How is this stimulus of touch communicated and explain how the movement takes place?
- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Plant Biology
- Two statements are given below. They are Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read both the statements carefully and choose the correct option. Assertion (A): Rupees is accepted as medium of exchange in India.
Reason (R): The World Bank legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment in India.- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Money and Credit
- Two statements are given below. They are Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read both the statements carefully and choose the correct option:
Assertion (A): Rupees is accepted as medium of exchange in India.
Reason (R): The World Bank legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment in India.- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Money and Credit
Read the following sources of loan carefully and choose the correct option related to formal sources of credit:
(i) Commercial Bank
(ii) Landlords
(iii) Government
(iv) Money Lende- CBSE Class X - 2025
- Money and Credit
Concepts Used:
Spherical Mirrors
A spherical mirror is a mirror which has been cut out of a spherical surface.
There are two kinds of spherical mirrors:
- Convex Mirror
- Concave Mirror
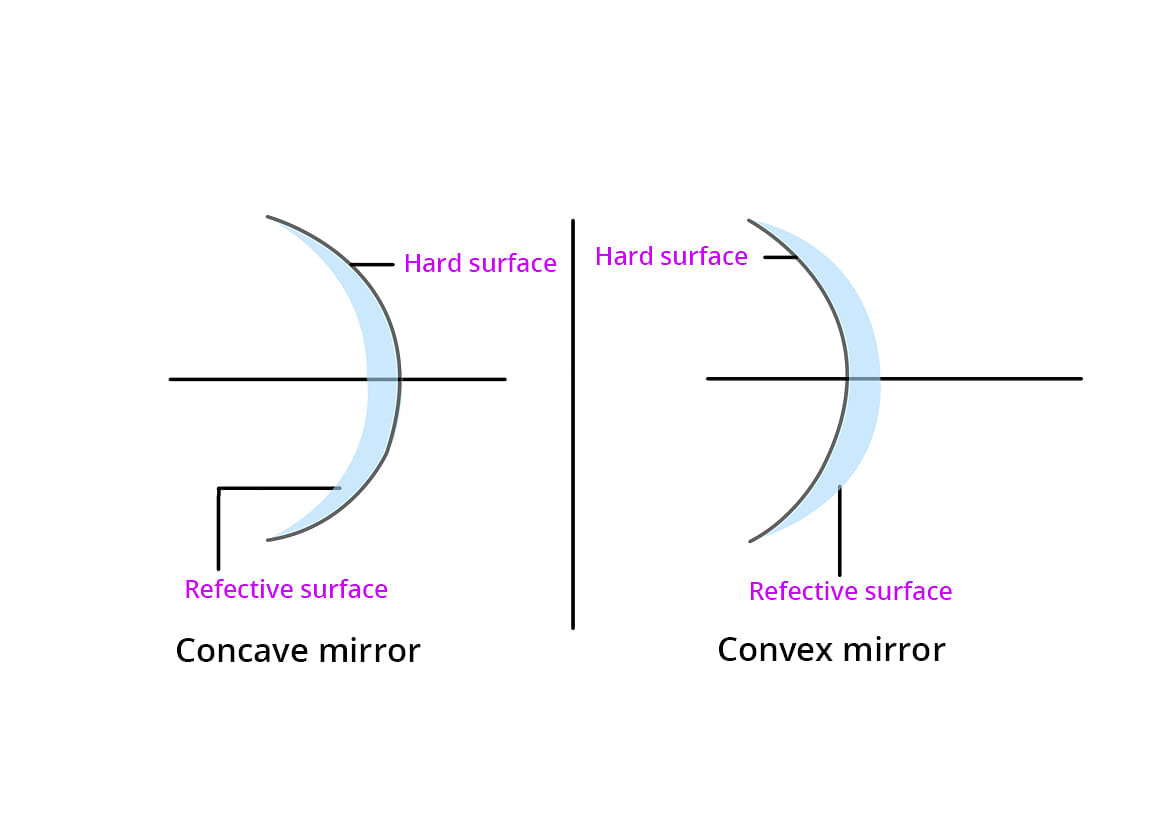
Concave Mirror
Concave mirrors are also called converging mirrors, because in these types of mirrors, light rays converge at a point after impact and reflect back from the reflective surface of the mirror.
Convex Mirror
The convex mirror has a reflective surface that is curved outward. Regardless of the distance between the subject and the mirrors, these mirrors are "always" virtual, upright and reduced.