Question:
A ray parallel to principal axis is incident at \(30^{\circ}\) from normal on concave mirror having radius of curvature \(R\). The point on principal axis where rays are focussed is \(Q\) such that \(PQ\) is

A ray parallel to principal axis is incident at \(30^{\circ}\) from normal on concave mirror having radius of curvature \(R\). The point on principal axis where rays are focussed is \(Q\) such that \(PQ\) is

Updated On: Sep 11, 2025
- $\frac {R}{2}$
- $\frac{R}{\sqrt{3}}$
- $\frac{2\sqrt{R}-R}{\sqrt{2}}$
- $R\left(1-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)$
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is D
Solution and Explanation
From similar triangles,
$\frac{Q C}{\sin 30^{\circ}}=\frac{R}{\sin 120^{\circ}}$
or $Q C=R \times \frac{\sin 30^{\circ}}{\sin 120^{\circ}}=\frac{R}{\sqrt{3}}$
Thus $P Q=P C-Q C=R-\frac{R}{\sqrt{3}}$
$=R\left(1-\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\right)$
$\frac{Q C}{\sin 30^{\circ}}=\frac{R}{\sin 120^{\circ}}$
or $Q C=R \times \frac{\sin 30^{\circ}}{\sin 120^{\circ}}=\frac{R}{\sqrt{3}}$
Thus $P Q=P C-Q C=R-\frac{R}{\sqrt{3}}$
$=R\left(1-\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\right)$

Was this answer helpful?
2
1
Top Questions on Spherical Mirrors
- A concave mirror produces an image of an object such that the distance between the object and image is 20 cm. If the magnification of the image is \( -3 \), then the magnitude of the radius of curvature of the mirror is:
- JEE Main - 2025
- Physics
- Spherical Mirrors
- (ii) An object at a distance of 16 cm from a spherical mirror forms a virtual image at a distance of 12 cm behind the mirror. Determine the magnification of the image and type of the mirror.
- UP Board X - 2025
- Science
- Spherical Mirrors
- Image of an object formed by a concave mirror is real and of the size of the object. The object is placed -
- UP Board X - 2025
- Science
- Spherical Mirrors
- With the help of a suitable ray diagram, derive the formula \( \frac{1}{v} + \frac{1}{u} = \frac{1}{f} \) for a concave mirror.
- UP Board XII - 2025
- Physics
- Spherical Mirrors
- The length of the image formed by a concave mirror:
- UP Board XII - 2025
- Physics
- Spherical Mirrors
View More Questions
Questions Asked in BITSAT exam
- What is the dot product of the vectors \( \mathbf{a} = (2, 3, 1) \) and \( \mathbf{b} = (1, -1, 4) \)?
- BITSAT - 2025
- Vector Algebra
- Find the determinant of the matrix \( A = \begin{bmatrix} 2 & 3 \\ 4 & 5 \end{bmatrix} \).
- BITSAT - 2025
- Matrices
- A convex lens has focal length 20 cm. An object is placed at a distance of 40 cm from the lens. What is the position of the image formed?
- BITSAT - 2025
- Ray optics and optical instruments
- What is the value of \( \sin 30^\circ \)?
- BITSAT - 2025
- Trigonometry
- The area enclosed between the curve \(y = \log_e(x + e)\) and the coordinate axes is:
- BITSAT - 2025
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
Spherical Mirrors
A spherical mirror is a mirror which has been cut out of a spherical surface.
There are two kinds of spherical mirrors:
- Convex Mirror
- Concave Mirror
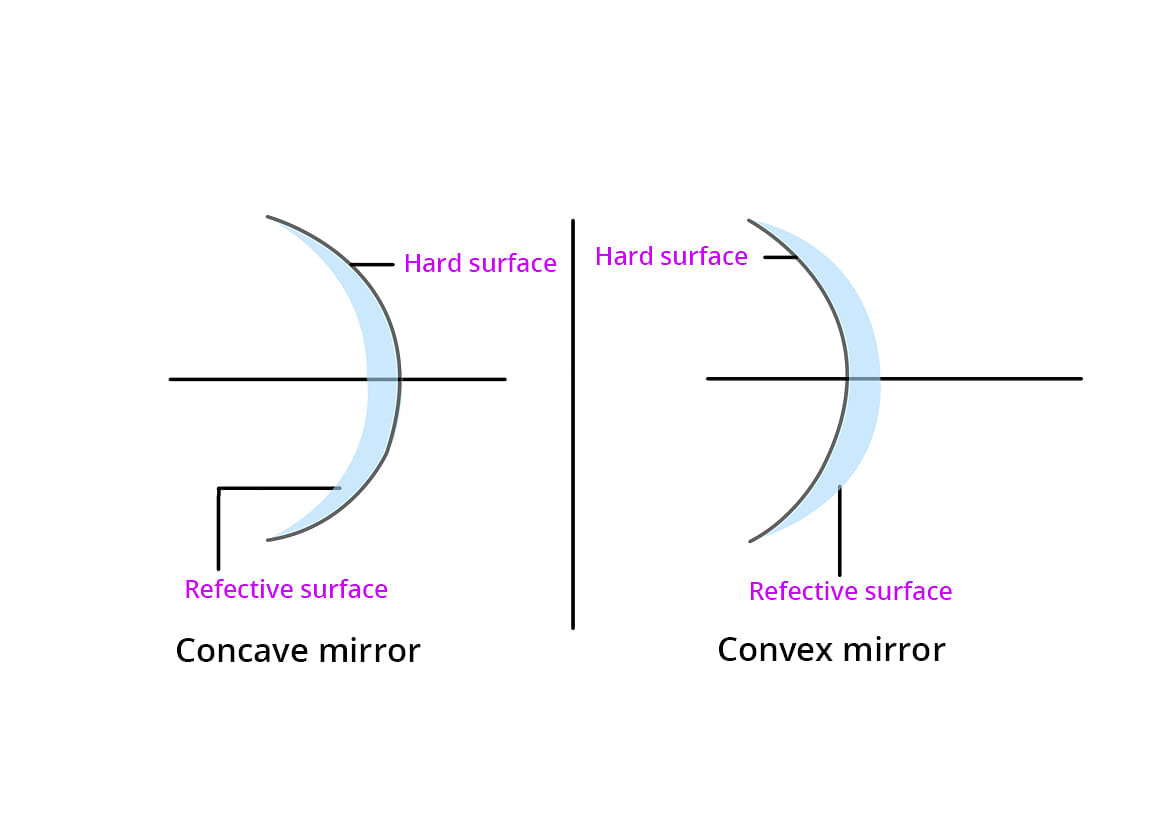
Concave Mirror
Concave mirrors are also called converging mirrors, because in these types of mirrors, light rays converge at a point after impact and reflect back from the reflective surface of the mirror.
Convex Mirror
The convex mirror has a reflective surface that is curved outward. Regardless of the distance between the subject and the mirrors, these mirrors are "always" virtual, upright and reduced.