A person spent Rs 50000 to purchase a desktop computer and a laptop computer. He sold the desktop at 20% profit and the laptop at 10% loss. If overall he made a 2% profit then the purchase price, in rupees, of the desktop is
Approach Solution - 1
Using Alligation Rule, the ratio of cost prices of desktop and laptop will be
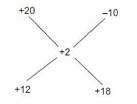
Let the total cost be ₹50,000.
We are told that the cost of the desktop is \(\frac{2}{5}\) of the total cost.
So, the cost of the desktop is: \[ \text{Cost of desktop} = \frac{2}{5} \times 50000 \] Now calculate the product: \[ = \frac{2 \times 50000}{5} = \frac{100000}{5} = 20000 \] ∴ The cost of the desktop is ₹20,000.
Approach Solution -2
Let D be the cost of the desktop and L be the cost of the laptop.
Step 1: Given equations
- From the statement: "0.2 times D minus 0.1 times L is equal to 2% of ₹50,000": \[ 0.2D - 0.1L = 0.02 \times 50000 = 1000 \tag{1} \]
- Multiplying equation (1) by 10 to eliminate decimals: \[ 2D - L = 10000 \tag{2} \]
- We are also given that the total cost of the desktop and laptop is ₹50,000: \[ D + L = 50000 \tag{3} \]
Step 2: Solving the system
Add equations (2) and (3):
\[ 2D - L + D + L = 10000 + 50000 \] \[ 3D = 60000 \] \[ D = \frac{60000}{3} = \boxed{20000} \]
Final Answer: \( \boxed{D = 20000} \)
Top Questions on Percentage
- A salesman gets a commission of 12% on the sales of products. He sold products worth 67000 last month. This month, the company changed the payment structure. A salesman would get a fixed pay of 5000 and 8% commission on the sales exceeding 32000. If he makes a sale of 67000, his earning from the previous month will reduce by
- If \(x + \frac{1}{x} = 3\), then the value of \(x^3 + \frac{1}{x^3}\) is:
- XAT - 2026
- General Aptitude
- Percentage
- A man spends $ \frac{2}{5} $ of his salary on rent, $ \frac{1}{4} $ on food, and $ \frac{1}{10} $ on transportation. What fraction of his salary is left?
- A number is increased by 25% and then decreased by 20%. What is the net % change?
- In an exam, the ratio of boys to girls is 3:2. If 20% of the boys and 30% of the girls fail, what is the overall percentage of students who fail?
Questions Asked in CAT exam
- The passage given below is followed by four summaries. Choose the option that best captures the essence of the passage.
In the dynamic realm of creativity, artists often find themselves at the crossroads between drawing inspiration from diverse cultures and inadvertently crossing into the territory of cultural appropriation. Inspiration is the lifeblood of creativity, driving artists to create works that resonate across borders. In a globalized era of the modern world, artists draw from a vast array of cultural influences. When approached respectfully, inspiration becomes a bridge, fostering understanding and appreciation of cultural diversity. However, the line between inspiration and cultural appropriation can be thin and easily blurred.
Cultural appropriation occurs when elements from a particular culture are borrowed without proper understanding, respect, or acknowledgment. This leads to the commodification of sacred symbols, the reinforcement of stereotypes, and the erasure of the cultural context from which these elements originated. It is essential to recognize that the impact of cultural appropriation extends beyond the realm of artistic expression, influencing societal perceptions and perpetuating power imbalances.- CAT - 2025
- Para Summary
- The number of distinct integers $n$ for which $\log_{\left(\frac14\right)}(n^2 - 7n + 11)>0$ is:
- CAT - 2025
- Linear Inequalities
- In the set of consecutive odd numbers $\{1, 3, 5, \ldots, 57\}$, there is a number $k$ such that the sum of all the elements less than $k$ is equal to the sum of all the elements greater than $k$. Then, $k$ equals?
- CAT - 2025
- Number Systems
- The number of distinct pairs of integers $(x, y)$ satisfying the inequalities $x>y \ge 3$ and $x + y<14$ is:
- CAT - 2025
- Number Systems
For any natural number $k$, let $a_k = 3^k$. The smallest natural number $m$ for which \[ (a_1)^1 \times (a_2)^2 \times \dots \times (a_{20})^{20} \;<\; a_{21} \times a_{22} \times \dots \times a_{20+m} \] is:
- CAT - 2025
- Linear Inequalities