Question:
A patient comes to the casualty with a severe headache. His BP was found to be 160/100mmHg. CT scan revealed a subarachnoid hemorrhage. What is the next best step in the management of this patient?
A patient comes to the casualty with a severe headache. His BP was found to be 160/100mmHg. CT scan revealed a subarachnoid hemorrhage. What is the next best step in the management of this patient?
Updated On: Jun 18, 2025
- Nimodipine
- Angiography
- Surgery
- Fibrinolytic therapy
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
A patient presenting with a severe headache and a blood pressure of 160/100mmHg, coupled with a CT scan indicating a subarachnoid hemorrhage, requires a specific approach for effective management. Given these circumstances:
- Identify the immediate cause: Subarachnoid hemorrhage is often caused by the rupture of an aneurysm or an arteriovenous malformation.
- Priority management: The initial step in managing such a condition once confirmed via CT scan is to secure the source of bleeding to prevent rebleeding, which is a significant risk.
- Next best step: In this scenario, the focus should be on identifying and addressing the source of the hemorrhage. Hence, cerebral angiography is the appropriate next step. It not only provides a detailed view of any vascular abnormalities but also guides further interventions.
- Role of other options:
- Nimodipine: Primarily used to prevent cerebral vasospasm post-subarachnoid hemorrhage, but not the immediate next step.
- Surgery: May be required following angiography findings.
- Fibrinolytic therapy: Not indicated in cases of subarachnoid hemorrhage due to the risk of exacerbating bleeding.
Thus, the correct next step in managing this patient's condition is cerebral angiography.
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on Neuroanatomy
- The trigeminal nerve is the largest nerve with following branches:
A. Olfactory
B. Ophthalmic
C. Maxillary
D. Mandibular
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:- CUET (PG) - 2025
- Zoology
- Neuroanatomy
- There was a question related to Shrugging off the Shoulder in Neck Surgery. What is it related to?
- NEET MDS - 2024
- Surgery
- Neuroanatomy
- A patient came to the medical OPD with complaints of polyuria. He has a history of undergoing total hypophysectomy. His Na+ levels are found to be 155 mEq/ L, urine osmolarity was 200 mOsm/L. What is the definitive management in this patient?
- NEET (PG) - 2023
- Medicine
- Neuroanatomy
- A 78-year-old woman presents with a progressive decline in daily activity. She gives a history of convulsions and visual hallucinations. She does not talk to anyone and keeps looking at the sky. Pathological examination shows the presence of Lewy bodies within the neurons. What is the most probable diagnosis?
- NEET (PG) - 2023
- Medicine
- Neuroanatomy
- A patient who is a known case of hypertension on multiple anti-hypertensive medications came to OPD. His ECG finding is given below. Which of the following drugs is responsible for the ECG finding?
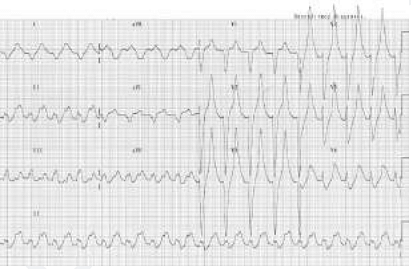
- NEET (PG) - 2023
- Medicine
- Neuroanatomy
View More Questions
Questions Asked in NEET PG exam
Which of the following cranial nerves is responsible for the motor innervation of the muscles of mastication?
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The normal pH of arterial blood is:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
Which enzyme is deficient in Gaucher’s disease?
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The anticoagulant effect of heparin is monitored using:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The causative agent of malaria is:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
View More Questions