Question:
A male patient presented to the emergency room with seizures. He has a history of fever, headache, and confusion. An MRI brain was done, and it showed inflammation involving the bitemporal lobe. What is the most likely aetiology for this presentation?
A male patient presented to the emergency room with seizures. He has a history of fever, headache, and confusion. An MRI brain was done, and it showed inflammation involving the bitemporal lobe. What is the most likely aetiology for this presentation?
Updated On: Jun 18, 2025
- Cytomegalovirus
Toxoplasma gondii
Herpes simplex virus
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
The clinical presentation described in the question involves a male patient with seizures, fever, headache, confusion, and MRI indications of bitemporal lobe inflammation. To determine the most likely aetiology, we need to consider common causes of encephalitis with these specific symptoms:
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV): The most common cause of encephalitis presenting with acute onset of fever, seizures, altered mental status, and focal neurological deficits. The classic MRI finding is inflammation in the temporal lobes, specifically the bitemporal region. HSV encephalitis is often the first consideration in such a presentation.
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV): Generally occurs in immunocompromised individuals, leading to a more diffuse encephalitis not typically limited to the temporal lobes.
- Toxoplasma gondii: Typically causes multiple ring-enhancing lesions in the brain, more common in immunocompromised patients, such as those with AIDS.
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB): Can cause chronic meningitis or tuberculomas, identifiable with different MRI patterns, usually not limited to bitemporal regions.
Based on the described symptoms and MRI findings, Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) is the most consistent cause. HSV targets the temporal lobes and is known for causing focal neurological symptoms alongside systemic features.
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on Neuroanatomy
- The trigeminal nerve is the largest nerve with following branches:
A. Olfactory
B. Ophthalmic
C. Maxillary
D. Mandibular
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:- CUET (PG) - 2025
- Zoology
- Neuroanatomy
- There was a question related to Shrugging off the Shoulder in Neck Surgery. What is it related to?
- NEET MDS - 2024
- Surgery
- Neuroanatomy
- A patient came to the medical OPD with complaints of polyuria. He has a history of undergoing total hypophysectomy. His Na+ levels are found to be 155 mEq/ L, urine osmolarity was 200 mOsm/L. What is the definitive management in this patient?
- NEET (PG) - 2023
- Medicine
- Neuroanatomy
- A 78-year-old woman presents with a progressive decline in daily activity. She gives a history of convulsions and visual hallucinations. She does not talk to anyone and keeps looking at the sky. Pathological examination shows the presence of Lewy bodies within the neurons. What is the most probable diagnosis?
- NEET (PG) - 2023
- Medicine
- Neuroanatomy
- A patient who is a known case of hypertension on multiple anti-hypertensive medications came to OPD. His ECG finding is given below. Which of the following drugs is responsible for the ECG finding?
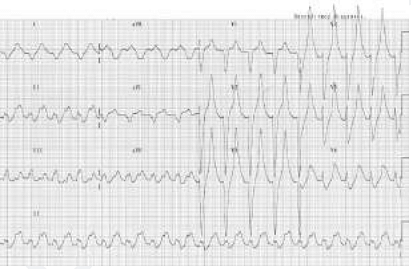
- NEET (PG) - 2023
- Medicine
- Neuroanatomy
View More Questions
Questions Asked in NEET PG exam
Which of the following cranial nerves is responsible for the motor innervation of the muscles of mastication?
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The normal pH of arterial blood is:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
Which enzyme is deficient in Gaucher’s disease?
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The anticoagulant effect of heparin is monitored using:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The causative agent of malaria is:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
View More Questions