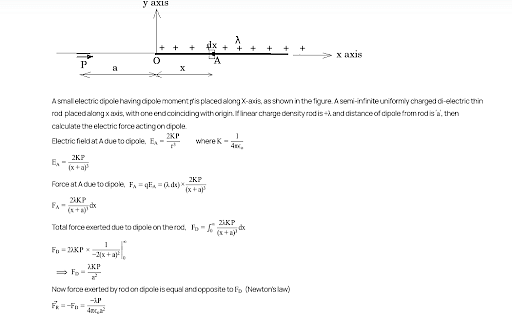
A dipole is placed in an electric field as shown. In which direction will it move


towards the right as its potential energy will increase.
towards the left as its potential energy will increase
towards the right as its potential energy will decrease
towards the left as its potential energy will decrease
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
To determine the direction in which the dipole will move, we need to understand the interaction between a dipole and an electric field.
A dipole consists of two equal and opposite charges separated by a distance. When placed in a uniform electric field \(\vec{E}\), the dipole experiences a torque but not a net force. However, in a non-uniform electric field, the dipole experiences a net force that moves it from higher potential energy to lower potential energy.
The potential energy \(U\) of a dipole in an electric field is given by:
\(U = -\vec{p} \cdot \vec{E}\)
where \(\vec{p}\) is the dipole moment vector. The dipole will move in a direction that decreases its potential energy.
Given the options and the correct answer, the dipole moves:
- Towards the right as its potential energy will decrease.
Thus, in a non-uniform electric field as depicted, the dipole moves towards the region of the strongest field (right), decreasing its potential energy.
In summary, in a non-uniform field, a dipole experiences a force in the direction of increasing electric field gradient. Therefore, it will move towards the right where its potential energy decreases.
Top Questions on Electric Field
- The electric field (\( \vec{E} \)) and electric potential (\( V \)) at a point inside a charged hollow metallic sphere are respectively:
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Field
- Consider a circular loop that is uniformly charged and has a radius $ \sqrt{2} $. Find the position along the positive $ z $-axis of the cartesian coordinate system where the electric field is maximum if the ring was assumed to be placed in the $ xy $-plane at the origin:
- JEE Main - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Field
Two large plane parallel conducting plates are kept 10 cm apart as shown in figure. The potential difference between them is $ V $. The potential difference between the points A and B (shown in the figure) is:

- JEE Main - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Field
Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Net dipole moment of a polar linear isotropic dielectric substance is not zero even in the absence of an external electric field. Reason
(R): In absence of an external electric field, the different permanent dipoles of a polar dielectric substance are oriented in random directions.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:- JEE Main - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Field
A metallic ring is uniformly charged as shown in the figure. AC and BD are two mutually perpendicular diameters. Electric field due to arc AB to O is ‘E’ magnitude. What would be the magnitude of electric field at ‘O’ due to arc ABC?

- JEE Main - 2025
- Physics
- Electric Field
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- Two cities X and Y are connected by a regular bus service with a bus leaving in either direction every T min. A girl is driving scooty with a speed of 60 km/h in the direction X to Y. She notices that a bus goes past her every 30 minutes in the direction of her motion, and every 10 minutes in the opposite direction. Choose the correct option for the period T of the bus service and the speed (assumed constant) of the buses.
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Relative Velocity
- A physical quantity P is related to four observations a, b, c, and d as follows: P = a3 b2 (c / √d) The percentage errors of measurement in a, b, c, and d are 1%, 3%, 2%, and 4% respectively. The percentage error in the quantity P is:
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Dimensional analysis and its applications
What is Microalbuminuria ?
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Human physiology
The output (Y) of the given logic implementation is similar to the output of an/a …………. gate.

- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Logic gates
- An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litre has 18.20 moles of oxygen. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, its gauge pressure drops to 11 atmospheric pressure at temperature \(27^\circ\)C. The mass of the oxygen withdrawn from the cylinder is nearly equal to: [Given, \(R = \frac{100}{12} \text{ J mol}^{-1} \text{K}^{-1}\), and molecular mass of \(O_2 = 32 \text{ g/mol}\), 1 atm pressure = \(1.01 \times 10^5 \text{ N/m}^2\)]
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Ideal-gas equation and absolute temperature
Concepts Used:
Electric Dipole
An electric dipole is a pair of equal and opposite point charges -q and q, separated by a distance of 2a. The direction from q to -q is said to be the direction in space.
p=q×2a
where,
p denotes the electric dipole moment, pointing from the negative charge to the positive charge.
Force Applied on Electric Dipole