A convex lens $'A'$ of focal length $20\, cm$ and a concave lens $'B'$ of focal length $5\, cm$ are kept along the same axis with a distance $'d'$ between them. If a parallel beam of light falling on $'A'$ leaves $'B'$ as a parallel beam, then the distance $'d'$ in cm will be :
- 25
- 15
- 50
- 30
The Correct Option is B
Approach Solution - 1
We know that :
d = f1 - f2
Now, By using the formula
\(\frac{1}{f_1}+\frac{1}{f_1}-\frac{d}{f_1f_2}=\frac{1}{F}\)
So, for the emergent beam to parallel :
F = a, P = 0 is given
Hence,
\(⇒\frac{1}{20}-\frac{1}{5}+\frac{d}{100}=0\)
\(⇒d=15\)
So, the correct option is (B) : 15.
Approach Solution -2
Point \(F\) is the second focal length of \(A\) and first focal length of \(B\).
\(\therefore d=(20-5) \,cm =15\, cm\)
So, the correct option is (B) : 15.
Top Questions on Spherical Mirrors
- A concave mirror produces an image of an object such that the distance between the object and image is 20 cm. If the magnification of the image is \( -3 \), then the magnitude of the radius of curvature of the mirror is:
- JEE Main - 2025
- Physics
- Spherical Mirrors
- (ii) An object at a distance of 16 cm from a spherical mirror forms a virtual image at a distance of 12 cm behind the mirror. Determine the magnification of the image and type of the mirror.
- UP Board X - 2025
- Science
- Spherical Mirrors
- Image of an object formed by a concave mirror is real and of the size of the object. The object is placed -
- UP Board X - 2025
- Science
- Spherical Mirrors
- With the help of a suitable ray diagram, derive the formula \( \frac{1}{v} + \frac{1}{u} = \frac{1}{f} \) for a concave mirror.
- UP Board XII - 2025
- Physics
- Spherical Mirrors
- The length of the image formed by a concave mirror:
- UP Board XII - 2025
- Physics
- Spherical Mirrors
Questions Asked in JIPMER exam
- Binomial nomenclature was first introduced by
- JIPMER - 2015
- KCET - 2022
- Diversity In The Living World
- $2,4-DNP $ test can be used to identify :
- JIPMER - 2021
- Chemical Reactions
- A bacterial flagellum is composed of
- JIPMER - 2021
- Prokaryotic Cells
- How many moles of acidified $K_2Cr_2O_7$ is required to liberate $6$ moles of $I_2$ from an aqueous solution of $I^-$ ?
- JIPMER - 2020
- Mole concept and Molar Masses
- Find amount of charge flown from Y to X when switch S is closed.
- JIPMER - 2019
- Combination of capacitors
Concepts Used:
Spherical Mirrors
A spherical mirror is a mirror which has been cut out of a spherical surface.
There are two kinds of spherical mirrors:
- Convex Mirror
- Concave Mirror
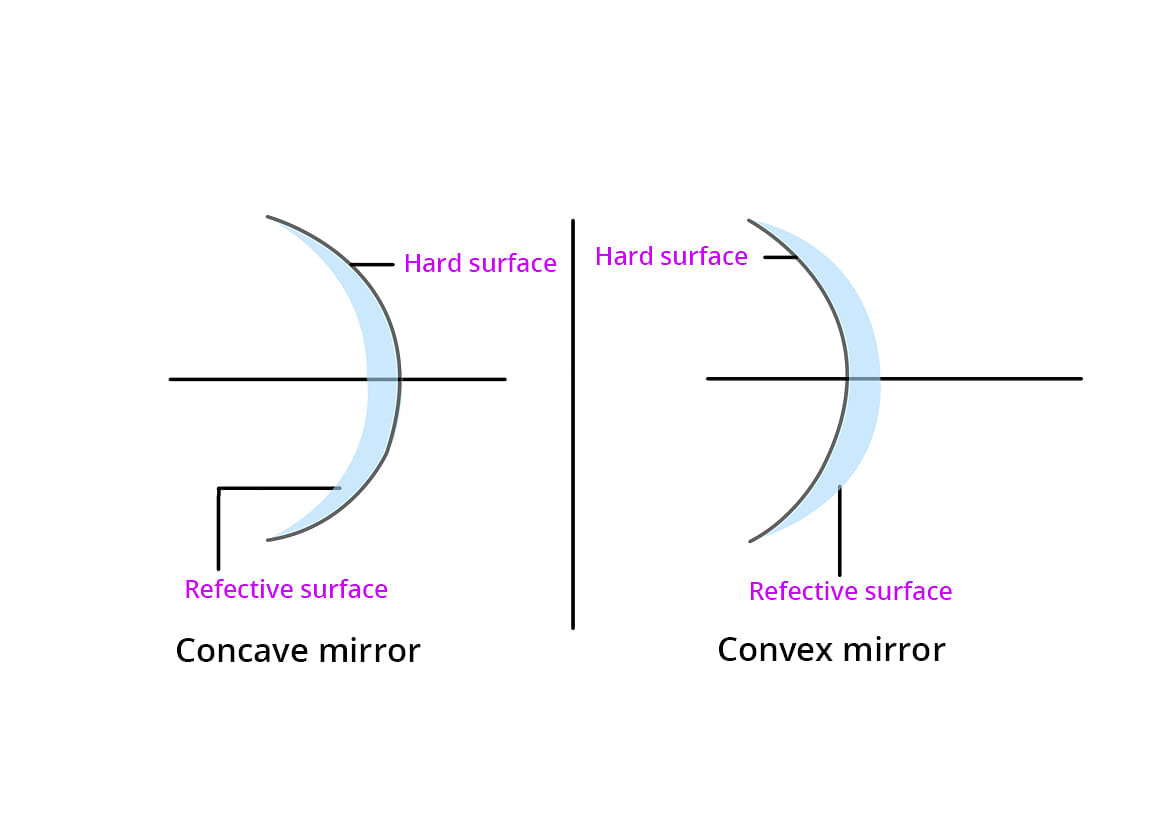
Concave Mirror
Concave mirrors are also called converging mirrors, because in these types of mirrors, light rays converge at a point after impact and reflect back from the reflective surface of the mirror.
Convex Mirror
The convex mirror has a reflective surface that is curved outward. Regardless of the distance between the subject and the mirrors, these mirrors are "always" virtual, upright and reduced.