A 25-year-old male patient complained of palpitations, sweating, and restlessness. He has a complaint of sweaty palms. Clinical findings are depicted in the image given below.
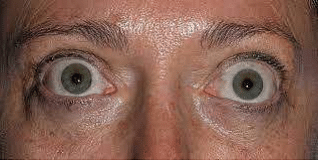
What is the diagnostic test done on this patient?

What is the diagnostic test done on this patient?
Anti-thyroglobulin antibody
Anti-thyroid peroxidase antibody
Thyroid receptor antibody
Elevated ultrasensitive thyrotropin levels
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
The clinical presentation of the patient, which includes palpitations, sweating, restlessness, and sweaty palms, suggests a hyperthyroid state, commonly seen in conditions like Graves' disease. In order to confirm the suspicion of Graves' disease, the diagnostic test that should be done is the measurement of Thyroid Receptor Antibody levels.
Graves' disease is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the presence of autoantibodies against the thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor (TSHR), known as Thyroid Receptor Antibodies. These antibodies can mimic the action of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), causing overproduction of thyroid hormones, which results in symptoms typical of hyperthyroidism.
Therefore, the appropriate diagnostic test for confirming the condition in this patient is the detection of Thyroid Receptor Antibody levels.
Top Questions on Human Endocrine System
Match the hormone with its site of production:

- KCET - 2025
- Biology
- Human Endocrine System
- Identify the statement/s given below that does not correspond to the functions of cortisol i) Maintains cardiovascular system and kidney functions
ii) Produces anti-inflammatory reactions
iii) Maintains electrolyte balance, osmosis and blood pressure
iv) Suppresses immune response
v) Stimulates RBC production- KCET - 2025
- Biology
- Human Endocrine System
- Which of the following hormones is secreted by the anterior pituitary gland and stimulates the thyroid gland to release thyroxine?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- Human Endocrine System
- What is required for the synthesis of thyroxine hormone ?
- UP Board X - 2025
- Science
- Human Endocrine System
- Match the following:
Hormones Chemical Nature A) Insulin IV) Protein B) Estrogen I) Steroid C) Oxytocin II) Peptide D) Thyroxine III) Amine
Identify the correct match:- AP EAPCET - 2025
- Zoology
- Human Endocrine System
Questions Asked in NEET PG exam
Which of the following cranial nerves is responsible for the motor innervation of the muscles of mastication?
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The normal pH of arterial blood is:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
Which enzyme is deficient in Gaucher’s disease?
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The anticoagulant effect of heparin is monitored using:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science
The causative agent of malaria is:
- NEET (PG) - 2025
- General Science