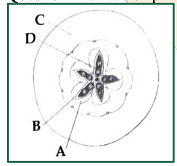
Which part of the fruit, labelled in the given figure makes it a false fruit?

Which part of the fruit, labelled in the given figure makes it a false fruit?
- A - Mesocarp
- B - Endocarp
- C - Thalamus
- D - Seed
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
In botany, a fruit is defined as the mature ovary of a flowering plant, usually containing seeds. However, a "false fruit" or "pseudocarp" includes other floral parts in addition to the ovary. In this context, the part of the fruit which contributes to making it a false fruit is the thalamus.
Explanation:
- The mesocarp is the middle layer of the pericarp, typically fleshy, and forms part of the true fruit structure.
- The endocarp is the innermost layer surrounding the seeds and is also a part of the true fruit structure.
- The thalamus is not part of the ovary itself but rather a part of the flower's receptacle and contributes to forming the fruit structure, thus creating a false fruit.
- The seed is the result of fertilized ovules and is contained within the fruit.
Thus, in the provided figure, the part labeled as the thalamus (option C) is responsible for making it a false fruit.
Top Questions on Morphology of flowering plants
- Match the LIST-I with LIST-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:LIST-I
(Characteristic, feature)LIST-II
(Family)A. Monoadelphous stamen I. Malvaceae B. Cremocarp III. Apiaceae C. Gynobasic style II. Lamiaceae D. Capitulum IV. Asteraceae - CUET (PG) - 2025
- Botany
- Morphology of flowering plants
- A flower is hypogynous with axile placentation and swollen placenta. Which family does this flower belong to?
- CUET (PG) - 2025
- Botany
- Morphology of flowering plants
- Choose the option that correctly describes the gynoecium of \textit{Michelia:
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Biology
- Morphology of flowering plants
Identify the types of aestivation in corolla labelled as 'a', 'b', 'c' and 'd'

- KCET - 2025
- Biology
- Morphology of flowering plants
- Diameter of the pollen grain is
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Biology
- Morphology of flowering plants
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- Two cities X and Y are connected by a regular bus service with a bus leaving in either direction every T min. A girl is driving scooty with a speed of 60 km/h in the direction X to Y. She notices that a bus goes past her every 30 minutes in the direction of her motion, and every 10 minutes in the opposite direction. Choose the correct option for the period T of the bus service and the speed (assumed constant) of the buses.
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Relative Velocity
- A physical quantity P is related to four observations a, b, c, and d as follows: P = a3 b2 (c / √d) The percentage errors of measurement in a, b, c, and d are 1%, 3%, 2%, and 4% respectively. The percentage error in the quantity P is:
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Dimensional analysis and its applications
What is Microalbuminuria ?
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Human physiology
The output (Y) of the given logic implementation is similar to the output of an/a …………. gate.

- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Logic gates
- An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litre has 18.20 moles of oxygen. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, its gauge pressure drops to 11 atmospheric pressure at temperature \(27^\circ\)C. The mass of the oxygen withdrawn from the cylinder is nearly equal to: [Given, \(R = \frac{100}{12} \text{ J mol}^{-1} \text{K}^{-1}\), and molecular mass of \(O_2 = 32 \text{ g/mol}\), 1 atm pressure = \(1.01 \times 10^5 \text{ N/m}^2\)]
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Ideal-gas equation and absolute temperature
Concepts Used:
Morphology of Flowering Plants
Morphology in flowering plants tells us that every plant has two systems such as a root system and a shoot system. The root system digs deep into the ground and structures a system of its own. On the other hand, the shoot system is the one that is above ground level and includes various plant parts.
Root System
The descending part of the plant grows under the soil roots. During the germination process, the radicle from the seed grows earthward and branches out. The branches along with the primary root are called the root system. Roots lack chlorophyll and therefore they are not green in color. Roots are positively geotropic and hydrotropic, that is, they grow downwards ground and water, and negatively phototropic, which is growing away from light.
There are three types of root systems found in plants are as follows:
- TapRoot System
- Fibrous Root System
- Adventitious Root System
Shoot System
The stem is also an essential element of the plant. It is the ascending portion of the plant axis that bears branches, flowers, leaves, and fruits, as well as aiding in water and mineral conduction. It is the plant's aerial portion, brought about from an embryo's plumule or germinating seeds. Young stems are ordinarily green, but they finally turn woody and brown.