What is the equation for the equilibrium constant $ ({{K}_{c}}) $ for the following reaction? $ \frac{1}{2}A(g)+\frac{1}{3}B(g)\frac{2}{3}C(g) $
- $ {{K}_{c}}=\frac{{{[A]}^{1/2}}{{[B]}^{1/3}}}{{{[C]}^{3/2}}} $
- $ {{K}_{c}}=\frac{{{[C]}^{3/2}}}{{{[A]}^{2}}{{[B]}^{3}}} $
- $ {{K}_{c}}=\frac{{{[C]}^{2/3}}}{{{[A]}^{1/2}}{{[B]}^{1/3}}} $
- $ {{K}_{c}}=\frac{{{[C]}^{2/3}}}{{{[A]}^{1/2}}+{{[B]}^{1/3}}} $
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
Top Questions on Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
- Consider the following gaseous equilibrium in a closed container of volume $V$ at temperature $T$:
P$_2$(g) + Q$_2$(g) $\rightleftharpoons$ 2PQ(g)
Initially, 2 moles each of P$_2$(g), Q$_2$(g) and PQ(g) are present at equilibrium. One mole each of P$_2$ and Q$_2$ are added. The number of moles of P$_2$, Q$_2$ and PQ at the new equilibrium respectively are
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
- $X_2(g) + Y_2(g) \rightleftharpoons 2Z(g)$. Equilibrium moles of $X_2, Y_2, Z$ are 3, 3, 9 mol (in 1 L). 10 mol of Z(g) is added. New equilibrium moles of Z(g) is ___. (Nearest integer)
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
- Observe the following equilibrium in a 1 L flask:
A(g) <=> B(g)
At temperature T (in K), the equilibrium concentrations of A and B are 0.5 M and 0.375 M respectively.
Then 0.1 moles of A is added into the flask and the system is heated to temperature T again to re-establish equilibrium.
The new equilibrium concentrations (in M) of A and B respectively are:- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
- The plot of \(\log_{10}K\) vs \(\frac{1}{T}\) gives a straight line. The intercept and slope respectively are (where \(K\) is equilibrium constant).
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
- For the reaction \( \mathrm{A \rightleftharpoons B} \), the number of moles of A and B at equilibrium in a \(1\,\text{L}\) vessel are \(0.50\) and \(0.375\), respectively. If \(0.10\) mol of A is added further, determine the number of moles of A and B at the new equilibrium.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
Questions Asked in Rajasthan PMT exam
- 300 cal of heat is supplied to raise the temperature of 50 g of air from $ 20{}^\circ C $ to $ 30{}^\circ C $ without any change in its volume. Change in internal energy per gram of air is
- Rajasthan PMT - 2011
- internal energy
- The velocity of water flowing in a non-uniform tube is 20 cm/s at a point where the tube radius is 0.2 cm. The velocity at another point, where the radius is 0.1 cm, is
- Rajasthan PMT - 2011
- mechanical properties of fluid
- Block A of mass 4 kg and block B of mass 6 kg are resting on a horizontal surface as shown in the figure. There is no friction between the block B and the horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between the blocks is 0.2. If the value of $ g=10\,m/{{s}^{2}}, $ the maximum horizontal force F that can be applied on block B without any relative motion between A and B is
- The excess pressure inside a soap bubble A is twice that in another soap bubble B. The ratio of volumes of A and B is
- Rajasthan PMT - 2011
- Surface Tension
- The unit of surface tension is
- Rajasthan PMT - 2011
- Surface Tension
Concepts Used:
Law of Chemical Equilibrium
Law of Chemical Equilibrium states that at a constant temperature, the rate of a chemical reaction is directly proportional to the product of the molar concentrations of the reactants each raised to a power equal to the corresponding stoichiometric coefficients as represented by the balanced chemical equation.
Let us consider a general reversible reaction;
A+B ↔ C+D
After some time, there is a reduction in reactants A and B and an accumulation of the products C and D. As a result, the rate of the forward reaction decreases and that of backward reaction increases.
Eventually, the two reactions occur at the same rate and a state of equilibrium is attained.
By applying the Law of Mass Action;
The rate of forward reaction;
Rf = Kf [A]a [B]b
The rate of backward reaction;
Rb = Kb [C]c [D]d
Where,
[A], [B], [C] and [D] are the concentrations of A, B, C and D at equilibrium respectively.
a, b, c, and d are the stoichiometric coefficients of A, B, C and D respectively.
Kf and Kb are the rate constants of forward and backward reactions.
However, at equilibrium,
Rate of forward reaction = Rate of backward reaction.
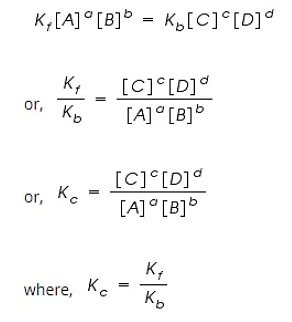
Kc is called the equilibrium constant expressed in terms of molar concentrations.
The above equation is known as the equation of Law of Chemical Equilibrium.