What is Kc for the following equilibrium when the equilibrium concentration of each substance is: [SO2]= 0.60 M, [O2] = 0.82 M and [SO3] = 1.90 M ?
\(2SO_2(g) + O_2(g) ⇋ 2SO_3(g)\)
\(2SO_2(g) + O_2(g) ⇋ 2SO_3(g)\)
Solution and Explanation
The equilibrium constant (Kc) for the give reaction is:
\(K_c =\frac {[SO_3]^2}{[SO_2]^2[O_2]}\)
\(K_c= \frac {(1.90)^2 M^2}{(0.60)^2(0.821) M^3 }\)
\(K_c = 12.239 \ M^{-1}\) (approximately)
Hence, Kc for the equilibrium is 12.239 M-1.
Top Questions on Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
- Consider the following gaseous equilibrium in a closed container of volume $V$ at temperature $T$:
P$_2$(g) + Q$_2$(g) $\rightleftharpoons$ 2PQ(g)
Initially, 2 moles each of P$_2$(g), Q$_2$(g) and PQ(g) are present at equilibrium. One mole each of P$_2$ and Q$_2$ are added. The number of moles of P$_2$, Q$_2$ and PQ at the new equilibrium respectively are
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
- $X_2(g) + Y_2(g) \rightleftharpoons 2Z(g)$. Equilibrium moles of $X_2, Y_2, Z$ are 3, 3, 9 mol (in 1 L). 10 mol of Z(g) is added. New equilibrium moles of Z(g) is ___. (Nearest integer)
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
- Observe the following equilibrium in a 1 L flask:
A(g) <=> B(g)
At temperature T (in K), the equilibrium concentrations of A and B are 0.5 M and 0.375 M respectively.
Then 0.1 moles of A is added into the flask and the system is heated to temperature T again to re-establish equilibrium.
The new equilibrium concentrations (in M) of A and B respectively are:- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
- The plot of \(\log_{10}K\) vs \(\frac{1}{T}\) gives a straight line. The intercept and slope respectively are (where \(K\) is equilibrium constant).
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
- For the reaction \( \mathrm{A \rightleftharpoons B} \), the number of moles of A and B at equilibrium in a \(1\,\text{L}\) vessel are \(0.50\) and \(0.375\), respectively. If \(0.10\) mol of A is added further, determine the number of moles of A and B at the new equilibrium.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Chemistry
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
Questions Asked in CBSE Class XI exam
- Balance the following redox reactions by ion-electron method:
(a)MnO4- (aq) + I - (aq) → MnO2(s) + I2(s) (in basic medium)
(b) MnO4- (aq) + SO2(g) → Mn2+(aq) +HSO4- (aq) (in acidic solution)
(c) H2O2(aq)+Fe2+(aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + H2O (l) (in acidic solution)
(d) Cr2O72-+ SO2(g) → Cr3+ (aq) +SO42- (aq) (in acidic solution)- CBSE Class XI
- Oxidation Number
- Write the resonance structures for SO3 , NO2 and NO3-
- CBSE Class XI
- Kossel-Lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding
- Find the mean deviation about the mean for the data 4, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 17.
- CBSE Class XI
- Statistics
Find the mean deviation about the mean for the data 38, 70, 48, 40, 42, 55, 63, 46, 54, 44.
- CBSE Class XI
- Statistics
- Find the mean deviation about the median for the data.13, 17, 16, 14, 11, 13, 10, 16, 11, 18, 12, 17.
- CBSE Class XI
- Statistics
Concepts Used:
Law of Chemical Equilibrium
Law of Chemical Equilibrium states that at a constant temperature, the rate of a chemical reaction is directly proportional to the product of the molar concentrations of the reactants each raised to a power equal to the corresponding stoichiometric coefficients as represented by the balanced chemical equation.
Let us consider a general reversible reaction;
A+B ↔ C+D
After some time, there is a reduction in reactants A and B and an accumulation of the products C and D. As a result, the rate of the forward reaction decreases and that of backward reaction increases.
Eventually, the two reactions occur at the same rate and a state of equilibrium is attained.
By applying the Law of Mass Action;
The rate of forward reaction;
Rf = Kf [A]a [B]b
The rate of backward reaction;
Rb = Kb [C]c [D]d
Where,
[A], [B], [C] and [D] are the concentrations of A, B, C and D at equilibrium respectively.
a, b, c, and d are the stoichiometric coefficients of A, B, C and D respectively.
Kf and Kb are the rate constants of forward and backward reactions.
However, at equilibrium,
Rate of forward reaction = Rate of backward reaction.
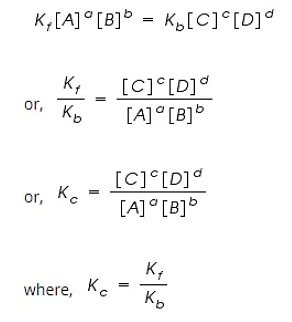
Kc is called the equilibrium constant expressed in terms of molar concentrations.
The above equation is known as the equation of Law of Chemical Equilibrium.