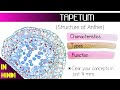
The tapetum
- is a nutritive layer which generally degenerates at maturity
- helps in dispersal of pollen grains
- helps in the dehiscence of anther
- None of the above
The Correct Option is A
Approach Solution - 1
Approach Solution -2
Ans. The anther's innermost cell layer, known as the tapetum, surrounds growing microspores and/or pollen mother cells (PMCs) and provides them with the nutrients and enzymes they need to develop into mature pollen.
- In plants, sexual reproduction occurs between two distinct sexes.
- The reproductive cells of a flowering plant are called gametes.
- Due to the presence of both male and female gametes, the flower may reproduce sexually.
- In the anther and pollen sac where pollen grains are produced, the male gamete pollen grains grow.
- Each pollen sac is surrounded by four layers: the tapetum, endothecium, middle layer, and epidermis.
- The outermost layer is the epidermis, while the tapetum is the deepest layer.
- A consistent layer of tapetum surrounds the sporogenous tissue.
- The intermediate layer's nourishment is transferred to sporogenous tissues through the tapetum.
- These sporogenous tissues receive their nutrients from the tapetum and produce pollen grains.
- Various enzymes, hormones, amino acids, and nutritional components are given to microsporocytes via the tapetum during the formation of pollen grains.
- In the initial stages of microsporogenesis, the tapetal cells of the tapetum store the food.
- It feeds the spore mother cells by transferring nutrients from the middle layer.
- In order to thicken the exine, it generates ubisch bodies covered in sporopollenin.
- A pollen-kitt of ripe pollen grains is produced by the oily substance that it secretes.
- It increases the exine's protein content in order to improve stigma compatibility.
- The secretion of the callose enzyme, which separates the callose chemicals utilized to create four pollen types, is a notable operation that tapetum engages in.
Learn with videos:
Top Questions on Pre-Fertilisation: Structures And Events
- Which of the following statements about pollen grains is incorrect?
- MHT CET - 2024
- Biology
- Pre-Fertilisation: Structures And Events
- which layer of microsporangium nourishes the developing pollen grains ?
- CUET (UG) - 2023
- Biology
- Pre-Fertilisation: Structures And Events
- In Vallisneria, the pollination is carried by :
- CUET (UG) - 2023
- Biology
- Pre-Fertilisation: Structures And Events
- Consider the following statements $\&$ choose the correct answer from the given options. Statement 1: Innermost layer of microsporangium is tapetum. Statement 2: Cells of tapetum possess dense cytoplasm more than one nucleus and nourishes developing pollen grains.
- KCET - 2021
- Biology
- Pre-Fertilisation: Structures And Events
- How many microsporangia are located at the corners of a typical bilobed anther of angiosperm?
- KCET - 2021
- Biology
- Pre-Fertilisation: Structures And Events
Concepts Used:
Pre-fertilization events - Monoecious Plant
Fertilization in plants may be a process during which they undergo amphimixis in consequence of pollination and germination. During a physicochemical process, the male gametes (known as pollen) infusion with the feminine gametes (known as ovum) forms diploid zygote after carpal pollinates. The whole process happens in a zygote which later germinates into a seed. During the method, what happens is male gametes are transferred into female reproductive organs through pollinators (butterflies, birds, honey bees, bats, and flower beetles). This leads to an embryo being formed during a seed. Flowers are the reproductive organs of angiosperms and reproduce in a completely different method.
Read More: Flower Structure
The two important pre-fertilization procedures are gametogenesis and gamete transfer. The female and male reproductive forms in flowers are the androecium and the gynoecium which distinguishes and goes through development.
"Mono" means single so a monoecious plant is one that bears both male and female sex organs on same plant. The monoecious plant can produce bisexual flowers or unisexual flowers. A dioecious plant is one that bears both male and female sex organs on different plants.
Read Further: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants