The reaction that does NOT take place in a blast furnace between 900 K to 1500 K temperature range during extraction of iron is?
The reaction that does NOT take place in a blast furnace between 900 K to 1500 K temperature range during extraction of iron is?
FeO + CO \(\to\) Fe + CO2
C + CO2 \(\to\) 2CO
CaO + SiO2 \(\to\) CaSiO3
Fe2O3 + CO \(\to\) 2FeO + CO2
The Correct Option is D
Approach Solution - 1
The reaction FeO + CO → Fe + CO2 is a reduction reaction essential for extracting iron. Hence, this reaction does occur.
C + CO2 → 2CO represents the formation of CO, which is a reducing agent vital for further reactions. This takedns place.
CaO + SiO2 → CaSiO3 is a slag formation reaction to remove impurities and occurs within the furnace's temperature range.
The reaction Fe2O3 + CO → 2FeO + CO2 is not a typical occurrence at the given temperature range in the blast furnace process, as Fe2O3 is reduced in stages to obtain metallic iron, not reverted to FeO.
Fe2O3 + CO → 2FeO + CO2
Approach Solution -2
Fe2O3 + CO → 2FeO + CO2
This reaction does not take place at between 900 K to 1500 K temperature range during extraction of iron.
It takes place at between 500 K to 800 K temperature range.
So, the correct option is (D): Fe2O3 + CO \(\to\) 2FeO + CO2
Top Questions on General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- What is used for the Thermite Reaction?
- BCECE - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- In the extraction of iron using blast furnace to remove the impurity (X), chemical (Y) is added to the ore. X and Y are respectively
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Which of the following compounds is used to cover the surface of a metallic object to prevent corrosion?
- KEAM - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- The incorrect statement about the Hall-Heroult process is:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Select the correct statement:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- Two cities X and Y are connected by a regular bus service with a bus leaving in either direction every T min. A girl is driving scooty with a speed of 60 km/h in the direction X to Y. She notices that a bus goes past her every 30 minutes in the direction of her motion, and every 10 minutes in the opposite direction. Choose the correct option for the period T of the bus service and the speed (assumed constant) of the buses.
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Relative Velocity
- A physical quantity P is related to four observations a, b, c, and d as follows: P = a3 b2 (c / √d) The percentage errors of measurement in a, b, c, and d are 1%, 3%, 2%, and 4% respectively. The percentage error in the quantity P is:
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Dimensional analysis and its applications
What is Microalbuminuria ?
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Human physiology
The output (Y) of the given logic implementation is similar to the output of an/a …………. gate.

- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Logic gates
- An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litre has 18.20 moles of oxygen. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, its gauge pressure drops to 11 atmospheric pressure at temperature \(27^\circ\)C. The mass of the oxygen withdrawn from the cylinder is nearly equal to: [Given, \(R = \frac{100}{12} \text{ J mol}^{-1} \text{K}^{-1}\), and molecular mass of \(O_2 = 32 \text{ g/mol}\), 1 atm pressure = \(1.01 \times 10^5 \text{ N/m}^2\)]
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Ideal-gas equation and absolute temperature
Concepts Used:
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
What are Ores and Minerals?
Minerals are the naturally occurring, homogeneous inorganic solid substances. They are having a definite chemical composition and crystalline structure, hardness and color. For example, copper pyrite, calamine, etc.
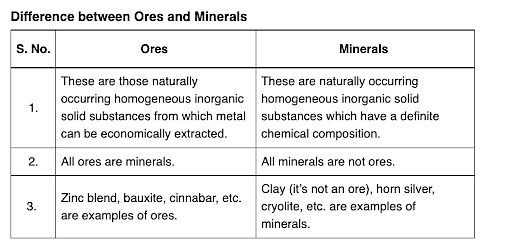
Impurities in an ore are called gauge. The removal of a gauge from the ore is called concentration ore.
Several steps are involved in the extraction of pure metal from ores. Major steps are as follows –
- Concentration of the ore
- Isolation of the metal from its concentrated ore
- Purification of the metal