Question:
Tapetum is found in
Tapetum is found in
Updated On: Jun 26, 2023
- anther
- androecium
- ovary
- ovule
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is A
Approach Solution - 1
Tapetum is the innermost layer of a developing anther. The tapetal nudei may divide once or more and sometimes these divisions are accompanied by nudear fusions resulting in large polyploid nudei which may divide again. The tapetal layer is of great physiological significance since all the food material entering into the sporogenous tissue diffuse through this layer. At maturity these cells degenerate and provide nourishment to developing microspores or pollens inside.
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
Approach Solution -2
The specialized nutritive tissue known as tapetum may be discovered in another blooming plant. As it gives the pollen grains' growing pollen grains sustenance, it is a crucial component of the pollen grain.
Tapetum comes in two primary varieties: secretory tapetum and plasmodial tapetum.
Secretory tapetum: first - A glandular tapetum is another name for a secretory tapetum. The tapetum's cells disintegrate after developing walls, yet its cells have cytoplasm. Pro-orbicular secretion is the primary function of the secretory tapetum. The sporopollenin is applied to the preorbitals. This contributes to the development of the pollen's exine, or outer coating. Acorales, a monocot, contains it.
Platyhelminthic tapetum: Amoeboid tapetum is another name for them. The tapetum cell wall diffuses and dissolves in some varieties, making it impossible to concentrate them in later stages of growth. A multinucleate plasmodium is when the protoplast in the plasmodial tapetum faces. The most typical kind of tapetum is this one. The twisted Dade is where it is mostly found. Angiosperms have the plasmodial form of the tapetum. The tapetal peri-plasmodium is created when the tapetal cells assemble. The medical division in the locule then produces additional protoplast from fused tapetal cells. The primary hosts of Plasmodium tapetum include Typhe, Alisme, Butomus, etc.
Tapetum comes in two primary varieties: secretory tapetum and plasmodial tapetum.
Secretory tapetum: first - A glandular tapetum is another name for a secretory tapetum. The tapetum's cells disintegrate after developing walls, yet its cells have cytoplasm. Pro-orbicular secretion is the primary function of the secretory tapetum. The sporopollenin is applied to the preorbitals. This contributes to the development of the pollen's exine, or outer coating. Acorales, a monocot, contains it.
Platyhelminthic tapetum: Amoeboid tapetum is another name for them. The tapetum cell wall diffuses and dissolves in some varieties, making it impossible to concentrate them in later stages of growth. A multinucleate plasmodium is when the protoplast in the plasmodial tapetum faces. The most typical kind of tapetum is this one. The twisted Dade is where it is mostly found. Angiosperms have the plasmodial form of the tapetum. The tapetal peri-plasmodium is created when the tapetal cells assemble. The medical division in the locule then produces additional protoplast from fused tapetal cells. The primary hosts of Plasmodium tapetum include Typhe, Alisme, Butomus, etc.
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on The Flower
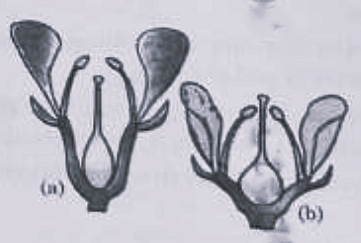
- Identify the type of flowers based on the position of calyx, corolla and androecium with respect to the ovary from the given figures (a) and (b).
- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Biology
- The Flower
- Match List I with List II
List I (Types of Stamens) List II (Example) A Monoadelphous I Citrus B Diadelphous II Pea C Polyadelphous III Lily D Epiphyllous IV China-rose
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Biology
- The Flower
- Identify the correct description about the given figure.

- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Biology
- The Flower
- Identify the set of correct statement:
A. The flowers of Vallisneria are colourful and produce nectar.
B. The flowers of waterlily are not pollinated by water.
C. In most of water-pollinated species, the pollen grains are protected from wetting.
D. Pollen grains of some hydrophytes are long and ribbon like.
E. In some hydrophytes, the pollen grains are carried passively inside water.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Biology
- The Flower
- Which of the following is an example of actinomorphic flower?
- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Biology
- The Flower
View More Questions
Questions Asked in UP CPMT exam
- The concepts of 'struggle for existence' and 'survival of the fittest' are essential parts of the evolutionary theory given by
- UP CPMT - 2015
- What Are The Evidences For Evolution?
- Which of the following is a gymnosperm in which vessels are found?
- UP CPMT - 2015
- Plant Kingdom
- If earth suddenly shrinks by one-third of its present radius, the acceleration due to gravity will be
- UP CPMT - 2015
- Gravitation
- If a wire is stretched to make it $0.1\%$ longer, its resistance will
- UP CPMT - 2015
- Current electricity
- Boiling point of chloroform was raised by $0.323 \,K$, when $0.5143\, g$ of anthracene was dissolved in its $35 \,g$. Molecular mass of anthracene is $(K_b$ for $CHCl_3 = 3.9 \,K \,kg\,, mol^{-1})$
- UP CPMT - 2015
- Solutions
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
Structure of a Flower
The flower structure comprises four major parts or whorls—known as the calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium.
Diversity of Flowers:
Flowers come in a range of sizes and shapes, but their anatomy, in general, is the same: sepals, petals, stamen, and carpel. A whorl, or circular positioning, is created by arranging these parts in a circular pattern.
Flowers come in various forms:
- Complete flower - The sepals, petals, stamens, and pistil all constitute a complete flower.
- Incomplete flower - An incomplete flower is one that lacks one or more of these structures.
Parts of a flower:
- Vegetative Part: A flower's vegetative component comprises the following:
- Petals
- Sepals
- Reproductive Part: Flowers consist of the reproductive organs of the plant. A flower's reproductive parts involves the following:
- Pistil
- Stamen
- Leaf
- Stem
- Receptacle