Question:
Seeds of which plants is commonly called "black pearl"
Seeds of which plants is commonly called "black pearl"
Updated On: Jul 28, 2022
- Piper nigrum
- Argemone maxicana
- Elettaria cardamomum
- Coffea arabica
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is A
Solution and Explanation
Answer (a) Piper nigrum
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on The Seed
- In the seeds of cereals, the outer covering of endosperm separates the embryo by a protein-rich layer called:
- Match the content of List I with List II:Choose the correct option from the following :
List-I List-II 1 Polyembryony p Black pepper 2 Perisperm q Banana 3 False fruit r Lemon 4 Parthenocarpy s Apple - KCET - 2024
- Biology
- The Seed
Identify the part of the seed from the given figure which is destined to form root when the seed germinates.
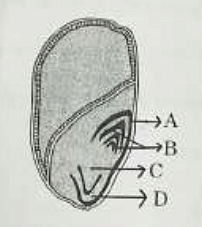
- What is the ideal seed rate for okra for rainy season crop?
- Which of the following is true for essentiality of germination? (A) Viability of seed
(B) Proper environment
(C) Seed free from dormancy
(D) Thin seed coat
View More Questions
Questions Asked in Manipur exam
- Which of the following is not a reflex action?
- Manipur - 2009
- neural control and coordination
- Which one of the following is not an insectivorous plant?
- Manipur - 2009
- Nutrition
- Inflammation of joints due to accumulation of uric acid crystals is called as
- Manipur - 2009
- locomotion and movement
- Iodine is obtained from alga
- Manipur - 2007
- Plant Kingdom
- The artificial system of classification is based on
- Manipur - 2007
- Morphology of flowering plants
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
Seed
The matured and fertilized ovule, which comprises an active embryo reserve food and protective coating, is referred to as a seed. Seeds are ripened ovules that contain an embryonic plant with sufficient reserve food for embryo development. Ovules evolve into seeds after fertilization.
Types of Seed:
- Monocotyledonous seeds: Seeds having only one cotyledon, called monocotyledonous seeds.
- Dicotyledonous seeds: Seeds with two cotyledons, called dicotyledonous seeds.
- Albuminous seeds: Seeds having an endosperm. These seeds have thin membrane cotyledons and endosperm that hold on and feed the seedling during its early growth.
- Exalbuminous seeds: Food gathers in the endosperm tissue of exalbuminous seeds early in development, but it is utilized by the growing embryo and mature seeds without endosperm.