Organise a discussion in your class on the topic – Are viruses living or non-living?
Solution and Explanation
Viruses are microscopic organisms that have characteristics of both living and non-living. A virus consists of a strand of DNA or RNA covered by a protein coat. This presence of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) suggests that viruses are alive. In addition, they can also respond to their environment (inside the host cell) in a limited manner.
However, some other characters, such as their inability to reproduce without using the host cell machinery and their acellular nature, indicate that viruses are non-living. Therefore, classifying viruses has remained a mystery for modern systematics.
Top Questions on Viruses, Viroids, Prions And Lichens
- Fungal part of lichen is called
- Tripura JEE - 2024
- Biology
- Viruses, Viroids, Prions And Lichens
- The genetic material of influenza is
- Tripura JEE - 2024
- Biology
- Viruses, Viroids, Prions And Lichens
- Which of the following is the genetic material in Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)?
- CUET (PG) - 2023
- Biology
- Viruses, Viroids, Prions And Lichens
- Match List I with List II
LIST I
(Microbe)LIST II
(Natural habitat)A. Streptomyces I. Aquatic habitat B. Influenza virus II. Terrestrial Environment C. Spirulina III. Sewage treatment D. Giardia IV. Airborne pathogen Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- CUET (PG) - 2023
- Biology
- Viruses, Viroids, Prions And Lichens
- Arrange the events of virus replication in a host cell:
A. Attachment
B. Packing of viral genome with structural proteins
C. Release of genomic material in the host cytoplasm
D. Synthesis of viral genes and proteins
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- CUET (PG) - 2023
- Zoology
- Viruses, Viroids, Prions And Lichens
Questions Asked in CBSE Class XI exam
- Balance the following redox reactions by ion-electron method:
(a)MnO4- (aq) + I - (aq) → MnO2(s) + I2(s) (in basic medium)
(b) MnO4- (aq) + SO2(g) → Mn2+(aq) +HSO4- (aq) (in acidic solution)
(c) H2O2(aq)+Fe2+(aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + H2O (l) (in acidic solution)
(d) Cr2O72-+ SO2(g) → Cr3+ (aq) +SO42- (aq) (in acidic solution)- CBSE Class XI
- Oxidation Number
- Write the resonance structures for SO3 , NO2 and NO3-
- CBSE Class XI
- Kossel-Lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding
- At 700 K, equilibrium constant for the reaction:
\(H_2 (g) + I_2 (g) ⇋ 2HI (g)\)
is 54.8. If 0.5 mol L–1 of HI(g) is present at equilibrium at 700 K, what are the concentration of H2(g) and I2(g) assuming that we initially started with HI(g) and allowed it to reach equilibrium at 700 K?- CBSE Class XI
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
- Find the mean deviation about the mean for the data 4, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 17.
- CBSE Class XI
- Statistics
Find the mean deviation about the mean for the data 38, 70, 48, 40, 42, 55, 63, 46, 54, 44.
- CBSE Class XI
- Statistics
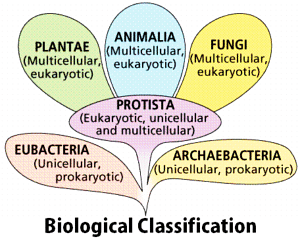
Concepts Used:
Biological Classification
The process of grouping living organisms into categories is called biological classification. The most modern 5-kingdom classification was put ahead by an eminent scientist R.H.Whittaker. The five-kingdom classification is based on the criteria like cell structure, mode of nutrition, body form, and reproduction. One of the most important characteristics of this system is that it follows the evolutionary sequence of living organisms. The organisms are classified into distinct taxa or levels like Kingdom, Phylum, Division, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species. The 5 kingdoms are as follows: