Movement and accumulation of ions across a membrane against their concentration gradient can be explained by
Movement and accumulation of ions across a membrane against their concentration gradient can be explained by
Facilitated Diffusion
Passive Transport
Active Transport
Osmosis
The Correct Option is C
Approach Solution - 1
The movement and accumulation of ions across a membrane against their concentration gradient is described by a process known as active transport. Unlike passive transport mechanisms such as facilitated diffusion and osmosis, which rely on the natural kinetic energy of molecules moving down their concentration gradient, active transport requires energy input. This energy is typically provided by ATP (adenosine triphosphate). The process allows cells to maintain concentration differences across membranes, essential for various physiological functions. In summary, active transport is crucial for the uptake of ions and molecules regardless of external concentrations.
Approach Solution -2
Active transport is a cellular process that requires energy (usually in the form of ATP) to move ions or molecules against their concentration gradient, from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration. This process allows cells to maintain specific ion concentrations inside and outside the cell, which is essential for various cellular functions.
Therefore, The correct option is (C): Active Transport
Top Questions on Cell: the unit of life
- Which organelle in a eukaryotic cell is primarily responsible for synthesizing proteins destined for secretion?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- Cell: the unit of life
- Which organelle is primarily responsible for producing ATP in a cell?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- Cell: the unit of life
- Which of the following organisms or organelles contain 70S ribosomes?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- Cell: the unit of life
- What is the movement of cytoplasm within a cell called?
- MHT CET - 2024
- Biology
- Cell: the unit of life
- Given below are two statements: Statement I: Cell wall is freely permeable.
Statement II: Plasma membrane is selectively permeable.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below with reference to the structure of root hair:- MHT CET - 2024
- Biology
- Cell: the unit of life
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- Two cities X and Y are connected by a regular bus service with a bus leaving in either direction every T min. A girl is driving scooty with a speed of 60 km/h in the direction X to Y. She notices that a bus goes past her every 30 minutes in the direction of her motion, and every 10 minutes in the opposite direction. Choose the correct option for the period T of the bus service and the speed (assumed constant) of the buses.
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Relative Velocity
- A physical quantity P is related to four observations a, b, c, and d as follows: P = a3 b2 (c / √d) The percentage errors of measurement in a, b, c, and d are 1%, 3%, 2%, and 4% respectively. The percentage error in the quantity P is:
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Dimensional analysis and its applications
What is Microalbuminuria ?
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Human physiology
The output (Y) of the given logic implementation is similar to the output of an/a …………. gate.

- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Logic gates
- An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litre has 18.20 moles of oxygen. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, its gauge pressure drops to 11 atmospheric pressure at temperature \(27^\circ\)C. The mass of the oxygen withdrawn from the cylinder is nearly equal to: [Given, \(R = \frac{100}{12} \text{ J mol}^{-1} \text{K}^{-1}\), and molecular mass of \(O_2 = 32 \text{ g/mol}\), 1 atm pressure = \(1.01 \times 10^5 \text{ N/m}^2\)]
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Ideal-gas equation and absolute temperature
Concepts Used:
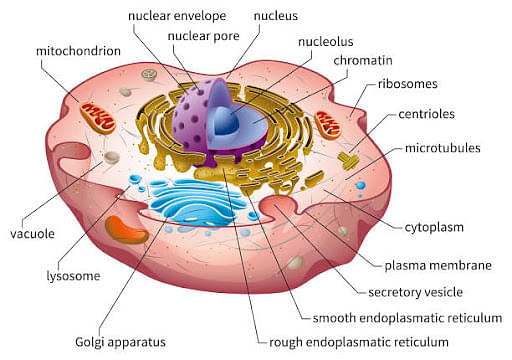
Cell: The Unit of Life
- A cell is derived as the functional and structural unit of life. Every cell is surrounded by a cell membrane that dissects the external and internal environments of the cell. The interior environment of a cell is called the cytoplasm.
- It carries cellular machinery and structural elements. The nucleus is present in the center of the cell, which includes all the hereditary information of an organism. Some of the molecules present in the cell are protein, carbohydrates, starch, and sugar.
Read More: Fundamental Unit of Life: Cell
Parts of Cell:
The different parts of a cell and their functions are as follows:
- Cell Membrane
- Cell Wall
- Nucleus
- Cytoplasm