Match the content of List I with List II:
List-I List-II 1 Polyembryony p Black pepper 2 Perisperm q Banana 3 False fruit r Lemon 4 Parthenocarpy s Apple
Choose the correct option from the following :
| List-I | List-II | ||
| 1 | Polyembryony | p | Black pepper |
| 2 | Perisperm | q | Banana |
| 3 | False fruit | r | Lemon |
| 4 | Parthenocarpy | s | Apple |
Show Hint
Understanding plant structures aids in identifying their biological functions and economic importance.
- 1-r, 2-p, 3-s, 4-q
- 1-p, 2-r, 3-s, 4-q
- 1-q, 2-p, 3-s, 4-r
- 1-r, 2-s, 3-p, 4-q
The Correct Option is A
Approach Solution - 1
Matching plant reproductive features with examples:
1. Polyembryony - r. Lemon: Citrus fruits like lemon often show multiple embryos (nucellar embryony).
2. Perisperm - p. Black pepper: The nutritive tissue in pepper seeds is derived from the nucellus (perisperm).
3. False fruit - s. Apple: Apples develop from the thalamus (accessory tissue) rather than just the ovary.
4. Parthenocarpy - q. Banana: Commercial bananas develop fruits without fertilization.
The correct matching is: (A) 1-r, 2-p, 3-s, 4-q
Other options are incorrect because: - (B) Incorrectly links polyembryony with black pepper - (C) Mismatches parthenocarpy with lemon - (D) Wrongly assigns perisperm to apple
Approach Solution -2
Polyembryony is a biological phenomenon in which a single fertilized egg (zygote) gives rise to multiple embryos, leading to the development of two or more genetically identical offspring. This occurs in various plants and animals, including some insects, mammals, and flowering plants.
Perisperm is a diploid nutritive tissue found in the seeds of some plants, derived from the nucellus (a part of the ovule). It serves as a food reserve for the developing embryo, similar to the endosperm, but unlike endosperm (which is triploid in most angiosperms), perisperm retains the maternal (2n) ploidy level.
A false fruit (also called pseudocarp or accessory fruit) is a fruit in which non-ovarian tissues (such as the receptacle, calyx, or thalamus) contribute significantly to its structure, unlike true fruits that develop solely from the ovary.
Parthenocarpy is the natural or artificial development of seedless fruits without fertilization. Unlike normal fruits that form after pollination and fertilization, parthenocarpic fruits develop without seeds because the ovary is stimulated to grow even in the absence of fertilization.
1. Polyembryony - r. Lemon: Citrus fruits like lemon often show multiple embryos (nucellar embryony).
2. Perisperm - p. Black pepper: The nutritive tissue in pepper seeds is derived from the nucellus (perisperm).
3. False fruit - s. Apple: Apples develop from the thalamus (accessory tissue) rather than just the ovary.
4. Parthenocarpy - q. Banana: Commercial bananas develop fruits without fertilization.
The correct matching is: (A) 1-r, 2-p, 3-s, 4-q
Top Questions on The Seed
- In the seeds of cereals, the outer covering of endosperm separates the embryo by a protein-rich layer called:
Identify the part of the seed from the given figure which is destined to form root when the seed germinates.
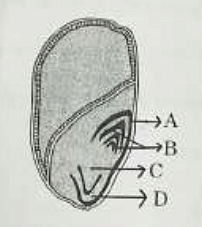
- What is the ideal seed rate for okra for rainy season crop?
- Which of the following is true for essentiality of germination? (A) Viability of seed
(B) Proper environment
(C) Seed free from dormancy
(D) Thin seed coat - Which of the following annuals require the isolation distance of 50-100 meters for seed production?
(A) Antirrhinum
(B) Marigold
(C) Larkspur
(D) Nasturtium
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Questions Asked in KCET exam
Match the following:
In the following, \( [x] \) denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to \( x \).
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- If \[ y = \frac{\cos x}{1 + \sin x} \] then:
- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- A function \( f(x) \) is given by:
\[ f(x) = \begin{cases} \frac{1}{e^x - 1}, & \text{if } x \neq 0 \\ \frac{1}{e^x + 1}, & \text{if } x = 0 \end{cases} \] Then, which of the following is true?- KCET - 2025
- Limits
- The function f(x) is given by:
For x < 0:
f(x) = ex + axFor x ≥ 0:
f(x) = b(x - 1)2
The function is differentiable at x = 0. Then,- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- The function \( f(x) = \tan x - x \)
- KCET - 2025
- Derivatives