Question:
In fluid mosaic model of plasma membrane
In fluid mosaic model of plasma membrane
Updated On: Jul 12, 2022
- Upper layer is non-polar and hydrophilic
- Polar layer is hydrophobic
- Phospholipids form a bimolecular layer in middle part
- Proteins form a middle layer
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is C
Solution and Explanation
Chemically a biomembrane consists of lipids (20-70%), proteins (20-70%), carbohydrates (1-5%) and water (20%). The important lipids of the membrane are phospholipids (some hundred types), sterols, (e.g. cholesterol), glycolipids, sphingolipid (e.g., sphingomyelin, cerebrosides). Protein can be fibrous or globular structural carrier, receptor or enzymatic. The lipid molecules are amphiatic or amphipathic, that is, they possess both polar hydrophilic (water loving) and non-polar hydrophobic (water repelling) ends. The hydrophilic region is in the form of head while hydrophobic part contains two tails of fatty acids. It results in formation of a lipid bilayer. Most common lipid of the bilayer is phospholipids. Protein molecules also possess both polar and non-polar side chains. Usually their poly hydrophilic linkages are towards the outer side. The non-polar or hydrophobic linkage are either kept folded inside or used to establish connections with hydrophobic parts of the lipids.
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on Cell: the unit of life
- Which organelle in a eukaryotic cell is primarily responsible for synthesizing proteins destined for secretion?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- Cell: the unit of life
- Which organelle is primarily responsible for producing ATP in a cell?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- Cell: the unit of life
- Which of the following organisms or organelles contain 70S ribosomes?
- MHT CET - 2025
- Biology
- Cell: the unit of life
- What is the movement of cytoplasm within a cell called?
- MHT CET - 2024
- Biology
- Cell: the unit of life
- Given below are two statements: Statement I: Cell wall is freely permeable.
Statement II: Plasma membrane is selectively permeable.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below with reference to the structure of root hair:- MHT CET - 2024
- Biology
- Cell: the unit of life
View More Questions
Questions Asked in AIPMT exam
- The terga, sterna and pleura of cockroach body are joined by
- AIPMT - 2015
- Cockroach
- Three identical spherical shells, each of mass m and radius r are placed as shown in figure. Consider an axis X X' which is touching to two shells and passing through diameter of third shell. Moment of inertia of the system consisting of these three spherical shells about XX' axis is
- AIPMT - 2015
- Moment Of Inertia
- The species $ {Ar, K^+}$ and $ {Ca^{2+}}$ contain the same number of electrons. In which order do their radii increase?
- AIPMT - 2015
- properties of d block elements
- The hilum is a scar on the
- AIPMT - 2015
- Post-Fertilisation : Structures And Events
- The heat of combustion of carbon to $ {CO_2}$ is $ {- 393.5 \, kJ/mol}$. The heat released upon formation of 35.2 g of $ {CO_2}$ from carbon and oxygen gas is:
- AIPMT - 2015
- Enthalpy change
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
Cell: The Unit of Life
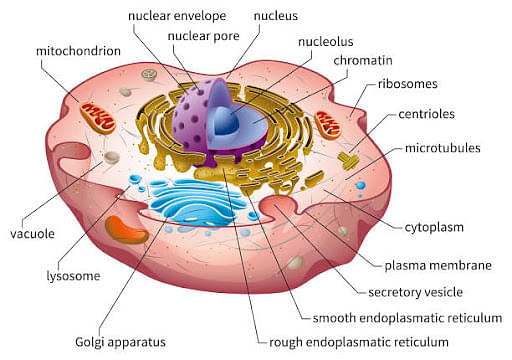
- A cell is derived as the functional and structural unit of life. Every cell is surrounded by a cell membrane that dissects the external and internal environments of the cell. The interior environment of a cell is called the cytoplasm.
- It carries cellular machinery and structural elements. The nucleus is present in the center of the cell, which includes all the hereditary information of an organism. Some of the molecules present in the cell are protein, carbohydrates, starch, and sugar.
Read More: Fundamental Unit of Life: Cell
Parts of Cell:
The different parts of a cell and their functions are as follows:
- Cell Membrane
- Cell Wall
- Nucleus
- Cytoplasm