In blast furnace iron oxide is reduced by
- Hot blast of air
- Carbon monoxide
- Carbon
- Silica
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation
An oxidation-reduction reaction occurring in a blast furnace is required to create iron from its ore.
As carbon is a more reactive element than iron, it is utilized to reduce iron using carbon monoxide (CO).
When carbon combines with oxygen, it creates carbon monoxide, which subsequently reacts with iron oxide to create elemental iron.
2C + O2 → 2CO
Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2
Magnetite and hematite are sources of iron. The two most typical iron ores are these two.
By adding ore, limestone, and coke to the blast furnace, iron may be produced from hematite. Metal silicates that are iron-bearing are the major contaminant in hematite.
The reduction of ferrous oxides in the molten ore in the blast furnace is the first step in the extraction process. In the blast furnace, carbon-based coke combines with oxygen to produce carbon monoxide and iron oxides that have been reduced by carbon monoxide.
Top Questions on General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- What is used for the Thermite Reaction?
- BCECE - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- In the extraction of iron using blast furnace to remove the impurity (X), chemical (Y) is added to the ore. X and Y are respectively
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Which of the following compounds is used to cover the surface of a metallic object to prevent corrosion?
- KEAM - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- The incorrect statement about the Hall-Heroult process is:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Select the correct statement:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Questions Asked in KCET exam
Match the following:
In the following, \( [x] \) denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to \( x \).
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- If \[ y = \frac{\cos x}{1 + \sin x} \] then:
- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- A function \( f(x) \) is given by:
\[ f(x) = \begin{cases} \frac{1}{e^x - 1}, & \text{if } x \neq 0 \\ \frac{1}{e^x + 1}, & \text{if } x = 0 \end{cases} \] Then, which of the following is true?- KCET - 2025
- Limits
- The function f(x) is given by:
For x < 0:
f(x) = ex + axFor x ≥ 0:
f(x) = b(x - 1)2
The function is differentiable at x = 0. Then,- KCET - 2025
- Differentiability
- The function \( f(x) = \tan x - x \)
- KCET - 2025
- Derivatives
Concepts Used:
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
What are Ores and Minerals?
Minerals are the naturally occurring, homogeneous inorganic solid substances. They are having a definite chemical composition and crystalline structure, hardness and color. For example, copper pyrite, calamine, etc.
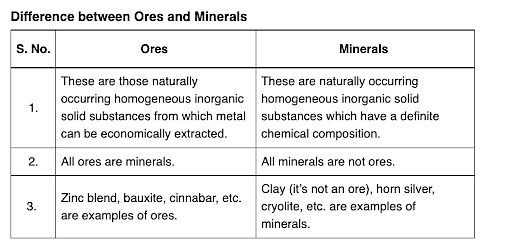
Impurities in an ore are called gauge. The removal of a gauge from the ore is called concentration ore.
Several steps are involved in the extraction of pure metal from ores. Major steps are as follows –
- Concentration of the ore
- Isolation of the metal from its concentrated ore
- Purification of the metal