Question:
Heating of ore in the absence of air below its melting point is called
Heating of ore in the absence of air below its melting point is called
Updated On: May 1, 2024
- Leaching
- Roasting
- Smelting
- Calcination
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
The Correct Option is D
Solution and Explanation
Calcination is the process in which concentrated ore is heated to a high temp (just below its fusion temp) in the absence of air.
Hydrated ores convert into oxides-
$Al _{2} O _{3} \cdot 2 H _{2} O {->[\Delta]} Al _{2} O _{3}+2 H _{2} O$
$F e _{2} O _{3} \cdot 3 H _{2} O {->[\Delta]}F e _{2} O _{3}+3 H _{2} O$
Roasting is the process in which air is passed while heating the concentrated ore below its melting point.
Smelting is a metallurgical process in which less electropositive metal ore such as $PbO$, $Cr _{2} O _{3}$ are reduced to free metal using the powerful reducing agent like $Al , C , CO$ etc.
Metals like $Cu$ and Tin are separated from their respective oxides by poling process using green bamboo stick.
Was this answer helpful?
1
0
Top Questions on General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- What is used for the Thermite Reaction?
- BCECE - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- In the extraction of iron using blast furnace to remove the impurity (X), chemical (Y) is added to the ore. X and Y are respectively
- TS EAMCET - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Which of the following compounds is used to cover the surface of a metallic object to prevent corrosion?
- KEAM - 2025
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- The incorrect statement about the Hall-Heroult process is:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Select the correct statement:
- KCET - 2024
- Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
View More Questions
Concepts Used:
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
What are Ores and Minerals?
Minerals are the naturally occurring, homogeneous inorganic solid substances. They are having a definite chemical composition and crystalline structure, hardness and color. For example, copper pyrite, calamine, etc.
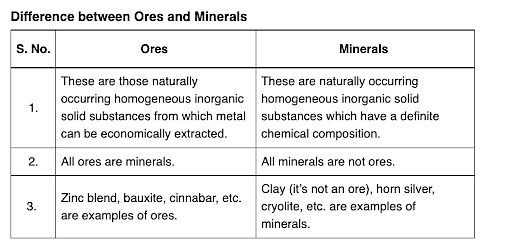
Impurities in an ore are called gauge. The removal of a gauge from the ore is called concentration ore.
Several steps are involved in the extraction of pure metal from ores. Major steps are as follows –
- Concentration of the ore
- Isolation of the metal from its concentrated ore
- Purification of the metal