Question:
Given the following Bayesian Network consisting of four Bernoulli random variables and the associated conditional probability tables :
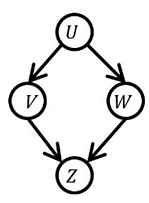
P(.) U = 0 0.5 U = 1 0.5
P(V = 0| .) P(V = 1| .) U = 0 0.5 0.5 U = 1 0.5 0.5 P(W = 0| .) P(W = 1| .) U = 0 1 0 U = 1 0 1
P(Z = 0| .) P(Z = 1| .) V = 0 W = 0 0.5 0.5 V = 0 W = 1 1 0 V = 1 W = 0 1 0 V = 1 W = 1 0.5 0.5
The value of P(U = 1, V = 1, W = 1,Z= 1) = ______. (rounded off to three decimal places)
Given the following Bayesian Network consisting of four Bernoulli random variables and the associated conditional probability tables :

The value of P(U = 1, V = 1, W = 1,Z= 1) = ______. (rounded off to three decimal places)

| P(.) | |
| U = 0 | 0.5 |
| U = 1 | 0.5 |
| P(V = 0| .) | P(V = 1| .) | |
| U = 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| U = 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| P(W = 0| .) | P(W = 1| .) | |
| U = 0 | 1 | 0 |
| U = 1 | 0 | 1 |
| P(Z = 0| .) | P(Z = 1| .) | ||
| V = 0 | W = 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| V = 0 | W = 1 | 1 | 0 |
| V = 1 | W = 0 | 1 | 0 |
| V = 1 | W = 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
Updated On: Jan 30, 2026
Hide Solution
Verified By Collegedunia
Correct Answer: 0.125
Solution and Explanation
The correct answer is 0.125
Was this answer helpful?
0
0
Top Questions on Random variables
If the probability function for a random variable \( x \) is given as \( f(x) = \frac{x+3}{15} \) when \( x = 1, 2, 3 \), find the sum of the values of the probability distribution for \( x \).
- CUET (PG) - 2025
- Economics
- Random variables
- Suppose that the random variable \( X \) takes on the values: -1, 0, and 2 with probabilities \( \frac{1}{8} \), \( \frac{1}{2} \), and \( \frac{3}{8} \) respectively. Find the expected value of \( X \).
- CUET (PG) - 2025
- Economics
- Random variables
- If \(f(X) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}} e^{-\frac{x^2}{2}}; -\infty<x<\infty\) and \(Y = |X|\), then E(Y) is
- CUET (PG) - 2025
- Statistics
- Random variables
- If, \(f(x; \alpha, \beta) = \begin{cases} \alpha \beta x^{\beta-1} e^{-\alpha x^\beta} & ; x>0 \text{ and } \alpha, \beta>0 \\ 0 & ; \text{otherwise} \end{cases}\), then the probability density function of \(Y=x^\beta\) is
- CUET (PG) - 2025
- Statistics
- Random variables
- If, \(f(X) = \frac{C\theta^x}{x}\); \(x = 1,2, \dots\); \(0<\theta<1\), then E(X) is equal to
- CUET (PG) - 2025
- Statistics
- Random variables
View More Questions
Questions Asked in GATE DA exam
- Which of the following statements is/are correct?
- GATE DA - 2025
- Linear Algebra
- Choose the most appropriate word to complete the analogy:
Courage : Bravery :: Yearning :- GATE DA - 2025
- Analogies
- When does the worst case of binary search occur?
- GATE DA - 2025
- Algorithm
- Suppose that insertion sort is applied to the array \([1,2,3,5,7,9,11,x,15,13]\) and it takes exactly 2 swaps to sort the array. Select all possible values of \( x \).
- GATE DA - 2025
- Algorithm
- Given the lists: \[ A = [1,2,3], \quad B = [4,5,6] \] Which of the following statements will result in \[ A = [1,2,3,4,5,6]? \]
- GATE DA - 2025
- Programming in Python
View More Questions