Describe the various types of placentations found in flowering plants.
Solution and Explanation
Placentation refers to the arrangement of ovules inside the ovary. It is of five basic types.
(A) Marginal placentation - The ovary in which the placenta forms a ridge along the ventral suture of the ovary and the ovules develop on two separate rows is known to have marginal placentation. This type of placentation is found in peas.

(B) Parietal placentation - When the ovules develop on the inner walls of the ovary, the ovary is said to have parietal placentation.

(C) Axile placentation - In axile placentation, the placenta is axial and ovules are attached to it. Examples include China rose, lemon, and tomato.

(D) Basal placentation - The ovary in which the placenta develops from its base and a single ovule is found attached to the base is said to have basal placentation. It is found in marigold and sunflower.

(E) Free central placentation - In free central placentation, the ovules develop on the central axis while the septa are absent. This type of placentation is found in Dianthus and primrose.

Top Questions on The Flower
- Identify the type of flowers based on the position of calyx, corolla and androecium with respect to the ovary from the given figures (a) and (b).
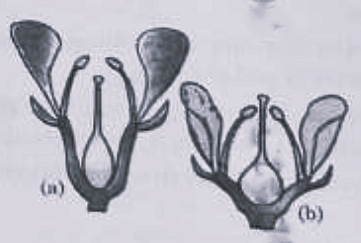
- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Biology
- The Flower
- Match List I with List II
List I (Types of Stamens) List II (Example) A Monoadelphous I Citrus B Diadelphous II Pea C Polyadelphous III Lily D Epiphyllous IV China-rose
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Biology
- The Flower
- Identify the correct description about the given figure.

- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Biology
- The Flower
- Identify the set of correct statement:
A. The flowers of Vallisneria are colourful and produce nectar.
B. The flowers of waterlily are not pollinated by water.
C. In most of water-pollinated species, the pollen grains are protected from wetting.
D. Pollen grains of some hydrophytes are long and ribbon like.
E. In some hydrophytes, the pollen grains are carried passively inside water.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Biology
- The Flower
- Which of the following is an example of actinomorphic flower?
- NEET (UG) - 2024
- Biology
- The Flower
Questions Asked in CBSE Class XI exam
- Balance the following redox reactions by ion-electron method:
(a)MnO4- (aq) + I - (aq) → MnO2(s) + I2(s) (in basic medium)
(b) MnO4- (aq) + SO2(g) → Mn2+(aq) +HSO4- (aq) (in acidic solution)
(c) H2O2(aq)+Fe2+(aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + H2O (l) (in acidic solution)
(d) Cr2O72-+ SO2(g) → Cr3+ (aq) +SO42- (aq) (in acidic solution)- CBSE Class XI
- Oxidation Number
- Write the resonance structures for SO3 , NO2 and NO3-
- CBSE Class XI
- Kossel-Lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding
- At 700 K, equilibrium constant for the reaction:
\(H_2 (g) + I_2 (g) ⇋ 2HI (g)\)
is 54.8. If 0.5 mol L–1 of HI(g) is present at equilibrium at 700 K, what are the concentration of H2(g) and I2(g) assuming that we initially started with HI(g) and allowed it to reach equilibrium at 700 K?- CBSE Class XI
- Law Of Chemical Equilibrium And Equilibrium Constant
- Find the mean deviation about the mean for the data 4, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 17.
- CBSE Class XI
- Statistics
Find the mean deviation about the mean for the data 38, 70, 48, 40, 42, 55, 63, 46, 54, 44.
- CBSE Class XI
- Statistics