Consider a thick biconvex lens (thickness t=4cm and refractive index n=1.5) whose magnitudes of the radii of curvature R1 and R2, of the first and second surfaces are 30cm and 20cm, respectively. Surface 2 is silvered to act as a mirror. A point object is placed at point A on the axis (OA= 60cm) as shown in the figure. If its image is formed at point Q, the distance d between O and Q is_____ cm. (Rounded off to two decimal places)
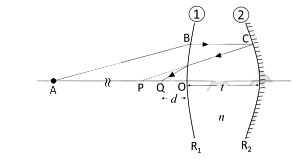

Correct Answer: 3.55
Solution and Explanation
Calculation of the Focal Length of a Thick Lens
The focal length \( f_L \) of the thick lens can be calculated using the lensmaker’s formula for a thick lens:
\[ \frac{1}{f_L} = (n-1) \left( \frac{1}{R_1} - \frac{1}{R_2} \right) + \frac{(n-1) t}{n R_1 R_2} \]
where:
- \( n = 1.5 \) (refractive index)
- \( t = 4 \) cm (thickness of the lens)
- \( R_1 = 30 \) cm (radius of curvature of the first surface)
- \( R_2 = -20 \) cm (radius of curvature of the second surface)
Step 1: Substituting the Given Values
\[ \frac{1}{f_L} = (1.5 - 1) \left( \frac{1}{30} - \frac{1}{-20} \right) + \frac{(1.5 - 1) \cdot 4}{1.5 \cdot 30 \cdot (-20)} \]
Step 2: Simplifying the Terms
\[ \frac{1}{f_L} = 0.5 \left( \frac{1}{30} + \frac{1}{20} \right) + \frac{0.5 \times 4}{1.5 \times 30 \times (-20)} \]
Calculating the individual terms:
- \( \frac{1}{30} = 0.0333 \)
- \( \frac{1}{20} = 0.05 \)
- \( \frac{0.5 \times 4}{1.5 \times 30 \times (-20)} = \frac{2}{-900} = -0.0022 \)
Step 3: Summing the Terms
\[ \frac{1}{f_L} = 0.5 (0.0333 + 0.05 - 0.0022) = 0.5 \times 0.0811 = 0.04055 \]
Thus, the focal length of the lens is:
\[ f_L = \frac{1}{0.04055} \approx 24.67 \text{ cm} \]
Calculation of the Equivalent Focal Length of the Lens-Mirror System
The equivalent focal length \( F \) of the lens-mirror system is given by:
\[ \frac{1}{F} = \frac{1}{f_L} + \frac{2}{f_m} \]
where the focal length of the mirror is:
\[ f_m = \frac{R_2}{2} = \frac{-20}{2} = -10 \text{ cm} \]
Step 4: Substituting the Values
\[ \frac{1}{F} = \frac{1}{24.67} + \frac{2}{-10} \]
\[ \frac{1}{F} = 0.04055 - 0.2 = -0.15945 \]
Thus, the equivalent focal length is:
\[ F = \frac{1}{-0.15945} \approx -6.27 \text{ cm} \]
Calculation of Image Distance
The object distance from the lens-mirror system is:
\[ u = -60 \text{ cm} \]
Using the lens formula for the system:
\[ \frac{1}{F} = \frac{1}{v} - \frac{1}{u} \]
Step 5: Substituting the Values
\[ \frac{1}{-6.27} = \frac{1}{v} - \frac{1}{-60} \]
Step 6: Solving for \( v \)
Rearranging the equation:
\[ -0.15945 = \frac{1}{v} + 0.01667 \]
\[ \frac{1}{v} = -0.15945 - 0.01667 = -0.17612 \]
Thus, the image distance is:
\[ v = \frac{1}{-0.17612} \approx -5.68 \text{ cm} \]
Calculation of Distance \( d \) Between O and Q
The distance \( d \) between \( O \) and \( Q \) is given by:
\[ d = |v| - t \]
Substituting the values:
\[ d = 5.68 - 4.00 = 3.50 \text{ cm} \]
Final Answer
The distance \( d \) between \( O \) and \( Q \) is 3.50 cm.
Top Questions on Wave optics
- Which of the following are true for a single slit diffraction? A. Width of central maxima increases with increase in wavelength keeping slit width constant.
B. Width of central maxima increases with decrease in wavelength keeping slit width constant.
C. Width of central maxima increases with decrease in slit width at constant wavelength.
D. Width of central maxima increases with increase in slit width at constant wavelength.
E. Brightness of central maxima increases for decrease in wavelength at constant slit width.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Wave optics
- The wavelength of light while it is passing through water is \(540\,\text{nm}\). The refractive index of water is \( \frac{4}{3} \). The wavelength of the same light when it is passing through a transparent medium having refractive index of \( \frac{3}{2} \) is _________ nm.
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Wave optics
- When an unpolarized light falls at a particular angle on a glass plate (placed in air), it is observed that the reflected beam is linearly polarized. The angle of refracted beam with respect to the normal is ___. ($\tan^{-1}(1.52) = 57.7^\circ$, refractive indices of air and glass are 1.00 and 1.52, respectively.)
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Wave optics
- The kinetic energy of a simple harmonic oscillator is oscillating with angular frequency of 176 rad/s. The frequency of this simple harmonic oscillator is _________ Hz. [Take $\pi = \frac{22}{7}$]}
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Wave optics
- A particle having electric charge $3 \times 10^{-19}$ C and mass $6 \times 10^{-27}$ kg is accelerated by applying an electric potential of 1.21 V. Wavelength of the matter wave associated with the particle is $\alpha \times 10^{-12}$ m. The value of $\alpha$ is _________. (Take Planck's constant $= 6.6 \times 10^{-34}$ J.s)
- JEE Main - 2026
- Physics
- Wave optics
Questions Asked in IIT JAM exam
- Consider a volume V enclosed by a closed surface S having unit surface normal \(\hat{n}\). For \(\mathbf{r} = x\hat{i} + y\hat{j} + z\hat{k}\), the value of the surface integral \(\frac{1}{9} \oint_{S} \mathbf{r} \cdot \hat{n} \,dS\) is
- IIT JAM PH - 2025
- Vector Calculus
- For a Zener diode as shown in the circuit diagram below, the Zener voltage \(V_Z\) is 3.7 V. For a load resistance (\(R_L\)) of 1 k\(\Omega\), a current \(I_1\) flows through the load. If \(R_L\) is decreased to 500 \(\Omega\), the current changes to \(I_2\). The ratio \(\frac{I_2}{I_1}\) is \rule{1cm{0.15mm}. (up to two decimal places)}

- IIT JAM PH - 2025
- Analog Electronics
- The shortest distance between an object and its real image formed by a thin convex lens of focal length 20 cm is _____ cm. (in integer)
- If \(\left(\frac{1-i}{1+i}\right)^{n/2} = -1\), where \(i = \sqrt{-1}\), one possible value of n is
- IIT JAM PH - 2025
- Complex numbers
- In a two-level atomic system, the excited state is 0.2 eV above the ground state. Considering the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution, the temperature at which 2% of the atoms will be in the excited state is _____ K. (up to two decimal places)
(Boltzmann constant \(k_B = 8.62 \times 10^{-5}\) eV/K)
- IIT JAM PH - 2025
- Mechanics