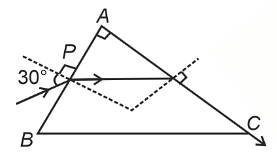
A light ray enters through a right angled prism at point P with the angle of incidence 30° as shown in figure. It travels through the prism parallel to its base BC and emerges along the face AC. The refractive index of the prism is :

- \(\frac{\sqrt5}{4}\)
- \(\frac{\sqrt5}{2}\)
- \(\frac{\sqrt3}{4}\)
- \(\frac{\sqrt3}{2}\)
The Correct Option is B
Solution and Explanation

Step 1: Relation in Prism
From the prism relation:
$$ r_1 + c = A $$
Rearranging for \( r_1 \):
$$ r_1 = 90^\circ - c \quad \text{...(1)} $$
Step 2: Expression for \( \cos c \)
We know:
$$ \sin c = \frac{1}{\mu} $$
Using trigonometric identity:
$$ \cos c = \frac{\sqrt{\mu^2 - 1}}{\mu} $$
Step 3: Apply Snell's Law on Incidence Surface
Using Snell’s law at the first surface:
$$ \sin 30^\circ = \mu \sin (r_1) $$
Substituting \( r_1 = 90^\circ - c \):
$$ \frac{1}{2} = \mu \sin (90^\circ - c) $$
Since \( \sin (90^\circ - c) = \cos c \), we get:
$$ \frac{1}{2} = \mu \times \frac{\sqrt{\mu^2 - 1}}{\mu} $$
Simplifying:
$$ \frac{1}{2} = \frac{\sqrt{\mu^2 - 1}}{1} $$
Step 4: Solve for \( \mu \)
Squaring both sides:
$$ \frac{1}{4} = \mu^2 - 1 $$
Rearranging:
$$ \mu^2 = \frac{5}{4} $$
Taking square root:
$$ \mu = \frac{\sqrt{5}}{2} $$
Conclusion
The refractive index \( \mu \) of the prism is \(\frac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\).
Top Questions on Refraction Through A Prism
- Figure shows the graph of angle of deviation \( \delta \) versus angle of incidence \( i \) for a light ray striking a prism. The prism angle is

- WBJEE - 2025
- Physics
- Refraction Through A Prism
- A right-angled prism ABC (refractive index \( \sqrt{2} \)) is kept on a plane mirror as shown in the figure. A ray of light is incident normally on the face AC. Trace the path of the ray as it passes through the prism.
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Physics
- Refraction Through A Prism
- Find the angle of deviation produced by the prism.
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Physics
- Refraction Through A Prism
- A ray of light is incident on face AB of a prism ABC with angle of prism \( A \) and emerges out from face AC. The prism is set in the position of minimum deviation with angle of deviation \( \delta \). Find: \begin{enumerate} \item the angle of incidence and \item the angle of refraction on face AB. \end{enumerate}
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Physics
- Refraction Through A Prism
- A laser beam of wavelength 500 nm and power 5 mW strikes normally on a perfectly reflecting surface of area 1 mm\(^2\) of a body. It rebounds back from the surface. Find the force exerted by the laser beam on the body.
- CBSE CLASS XII - 2025
- Physics
- Refraction Through A Prism
Questions Asked in NEET exam
- Two cities X and Y are connected by a regular bus service with a bus leaving in either direction every T min. A girl is driving scooty with a speed of 60 km/h in the direction X to Y. She notices that a bus goes past her every 30 minutes in the direction of her motion, and every 10 minutes in the opposite direction. Choose the correct option for the period T of the bus service and the speed (assumed constant) of the buses.
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Relative Velocity
- A physical quantity P is related to four observations a, b, c, and d as follows: P = a3 b2 (c / √d) The percentage errors of measurement in a, b, c, and d are 1%, 3%, 2%, and 4% respectively. The percentage error in the quantity P is:
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Dimensional analysis and its applications
What is Microalbuminuria ?
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Human physiology
The output (Y) of the given logic implementation is similar to the output of an/a …………. gate.

- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Logic gates
- An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litre has 18.20 moles of oxygen. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, its gauge pressure drops to 11 atmospheric pressure at temperature \(27^\circ\)C. The mass of the oxygen withdrawn from the cylinder is nearly equal to: [Given, \(R = \frac{100}{12} \text{ J mol}^{-1} \text{K}^{-1}\), and molecular mass of \(O_2 = 32 \text{ g/mol}\), 1 atm pressure = \(1.01 \times 10^5 \text{ N/m}^2\)]
- NEET (UG) - 2025
- Ideal-gas equation and absolute temperature